Example for Configuring L3VPN Routes to Be Recursed to Manually Configured SR-MPLS TE Policies (DSCP-Based)
This section provides an example for configuring L3VPN routes to be recursed to manually configured SR-MPLS TE Policies based on the DSCP value to ensure secure communication between users of the same VPN.
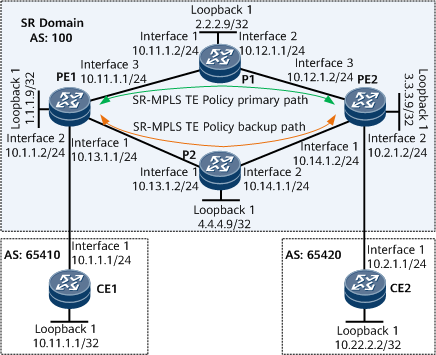
Networking Requirements
CE1 and CE2 belong to a VPN instance named vpna.
The VPN target used by vpna is 111:1.
Configure L3VPN routes to be recursed to SR-MPLS TE Policies to ensure secure communication between users of the same VPN. Because multiple links exist between PEs on the public network, other links must be able to provide protection for the primary link.
Precautions
If an interface connecting a PE to a CE is bound to a VPN instance, Layer 3 configurations, such as the IP address and routing protocol configuration, on the interface will be deleted. Reconfigure them if needed.
Configuration Roadmap
The configuration roadmap is as follows:
Configure IS-IS on the backbone network for the PEs to communicate.
Enable MPLS and SR for each device on the backbone network, and configure static adjacency SIDs.
Configure an SR-MPLS TE Policy with primary and backup paths on each PE.
Configure SBFD and HSB on each PE to enhance SR-MPLS TE Policy reliability.
Establish an MP-IBGP peer relationship between PEs for them to exchange routing information.
Create a VPN instance and enable the IPv4 address family on each PE. Then, bind each PE's interface connecting the PE to a CE to the corresponding VPN instance.
Configure an SR-MPLS TE Policy group on each PE and define mappings between the color and DSCP values.
Configure a tunnel selection policy on each PE for the specified SR-MPLS TE Policy group to be preferentially selected.
Establish an EBGP peer relationship between each CE-PE pair for the CE and PE to exchange routing information.
Data Preparation
To complete the configuration, you need the following data:
MPLS LSR IDs of PEs and Ps
VPN target and RD of vpna
Procedure
- Configure interface IP addresses for each device on the backbone network.
# Configure PE1.
<HUAWEI> system-view [~HUAWEI] sysname PE1 [*HUAWEI] commit [~PE1] interface loopback 1 [*PE1-LoopBack1] ip address 1.1.1.9 32 [*PE1-LoopBack1] quit [*PE1] interface gigabitethernet0/1/0 [*PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] ip address 10.13.1.1 24 [*PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] quit [*PE1] interface gigabitethernet0/1/16 [*PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/16] ip address 10.11.1.1 24 [*PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/16] quit [*PE1] commit
# Configure P1.
<HUAWEI> system-view [~HUAWEI] sysname P1 [*HUAWEI] commit [~P1] interface loopback 1 [*P1-LoopBack1] ip address 2.2.2.9 32 [*P1-LoopBack1] quit [*P1] interface gigabitethernet0/1/0 [*P1-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] ip address 10.11.1.2 24 [*P1-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] quit [*P1] interface gigabitethernet0/1/8 [*P1-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] ip address 10.12.1.1 24 [*P1-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] quit [*P1] commit
# Configure PE2.
<HUAWEI> system-view [~HUAWEI] sysname PE2 [*HUAWEI] commit [~PE2] interface loopback 1 [*PE2-LoopBack1] ip address 3.3.3.9 32 [*PE2-LoopBack1] quit [*PE2] interface gigabitethernet0/1/0 [*PE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] ip address 10.14.1.2 24 [*PE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] quit [*PE2] interface gigabitethernet0/1/16 [*PE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/16] ip address 10.12.1.2 24 [*PE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/16] quit [*PE2] commit
# Configure P2.
<HUAWEI> system-view [~HUAWEI] sysname P2 [*HUAWEI] commit [~P2] interface loopback 1 [*P2-LoopBack1] ip address 4.4.4.9 32 [*P2-LoopBack1] quit [*P2] interface gigabitethernet0/1/0 [*P2-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] ip address 10.13.1.2 24 [*P2-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] quit [*P2] interface gigabitethernet0/1/8 [*P2-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] ip address 10.14.1.1 24 [*P2-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] quit [*P2] commit
- Configure an IGP for each device on the backbone network to implement interworking between PEs and Ps. In this example, the IGP is IS-IS.
# Configure PE1.
[~PE1] isis 1 [*PE1-isis-1] is-level level-1 [*PE1-isis-1] network-entity 10.0000.0000.0001.00 [*PE1-isis-1] quit [*PE1] interface loopback 1 [*PE1-LoopBack1] isis enable 1 [*PE1-LoopBack1] quit [*PE1] interface gigabitethernet0/1/0 [*PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] isis enable 1 [*PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] quit [*PE1] interface gigabitethernet0/1/16 [*PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/16] isis enable 1 [*PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/16] quit [*PE1] commit
# Configure P1.
[~P1] isis 1 [*P1-isis-1] is-level level-1 [*P1-isis-1] network-entity 10.0000.0000.0002.00 [*P1-isis-1] quit [*P1] interface loopback 1 [*P1-LoopBack1] isis enable 1 [*P1-LoopBack1] quit [*P1] interface gigabitethernet0/1/0 [*P1-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] isis enable 1 [*P1-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] quit [*P1] interface gigabitethernet0/1/8 [*P1-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] isis enable 1 [*P1-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] quit [*P1] commit
# Configure PE2.
[~PE2] isis 1 [*PE2-isis-1] is-level level-1 [*PE2-isis-1] network-entity 10.0000.0000.0003.00 [*PE2-isis-1] quit [*PE2] interface loopback 1 [*PE2-LoopBack1] isis enable 1 [*PE2-LoopBack1] quit [*PE2] interface gigabitethernet0/1/16 [*PE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/16] isis enable 1 [*PE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/16] quit [*PE2] interface gigabitethernet0/1/0 [*PE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] isis enable 1 [*PE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] quit [*PE2] commit
# Configure P2.
[~P2] isis 1 [*P2-isis-1] is-level level-1 [*P2-isis-1] network-entity 10.0000.0000.0004.00 [*P2-isis-1] quit [*P2] interface loopback 1 [*P2-LoopBack1] isis enable 1 [*P2-LoopBack1] quit [*P2] interface gigabitethernet0/1/0 [*P2-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] isis enable 1 [*P2-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] quit [*P2] interface gigabitethernet0/1/8 [*P2-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] isis enable 1 [*P2-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] quit [*P2] commit
- Configure basic MPLS functions for each device on the backbone network.
# Configure PE1.
[~PE1] mpls lsr-id 1.1.1.9 [*PE1] mpls [*PE1-mpls] commit [~PE1-mpls] quit
# Configure P1.
[~P1] mpls lsr-id 2.2.2.9 [*P1] mpls [*P1-mpls] commit [~P1-mpls] quit
# Configure PE2.
[~PE2] mpls lsr-id 3.3.3.9 [*PE2] mpls [*PE2-mpls] commit [~PE2-mpls] quit
# Configure P2.
[~P2] mpls lsr-id 4.4.4.9 [*P2] mpls [*P2-mpls] commit [~P2-mpls] quit
- Enable SR for each device on the backbone network.
# Configure PE1.
[~PE1] segment-routing [*PE1-segment-routing] ipv4 adjacency local-ip-addr 10.11.1.1 remote-ip-addr 10.11.1.2 sid 330000 [*PE1-segment-routing] ipv4 adjacency local-ip-addr 10.13.1.1 remote-ip-addr 10.13.1.2 sid 330001 [*PE1-segment-routing] quit [*PE1] isis 1 [*PE1-isis-1] cost-style wide [*PE1-isis-1] segment-routing mpls [*PE1-isis-1] quit [*PE1] commit
# Configure P1.
[~P1] segment-routing [*P1-segment-routing] ipv4 adjacency local-ip-addr 10.11.1.2 remote-ip-addr 10.11.1.1 sid 330003 [*P1-segment-routing] ipv4 adjacency local-ip-addr 10.12.1.1 remote-ip-addr 10.12.1.2 sid 330002 [*P1-segment-routing] quit [*P1] isis 1 [*P1-isis-1] cost-style wide [*P1-isis-1] segment-routing mpls [*P1-isis-1] quit [*P1] commit
# Configure PE2.
[~PE2] segment-routing [*PE2-segment-routing] ipv4 adjacency local-ip-addr 10.12.1.2 remote-ip-addr 10.12.1.1 sid 330000 [*PE2-segment-routing] ipv4 adjacency local-ip-addr 10.14.1.2 remote-ip-addr 10.14.1.1 sid 330001 [*PE2-segment-routing] quit [*PE2] isis 1 [*PE2-isis-1] cost-style wide [*PE2-isis-1] segment-routing mpls [*PE2-isis-1] quit [*PE2] commit
# Configure P2.
[~P2] segment-routing [*P2-segment-routing] ipv4 adjacency local-ip-addr 10.13.1.2 remote-ip-addr 10.13.1.1 sid 330002 [*P2-segment-routing] ipv4 adjacency local-ip-addr 10.14.1.1 remote-ip-addr 10.14.1.2 sid 330003 [*P2-segment-routing] quit [*P2] isis 1 [*P2-isis-1] cost-style wide [*P2-isis-1] segment-routing mpls [*P2-isis-1] quit [*P2] commit
- Configure an SR-MPLS TE Policy on each PE.
# Configure PE1.
[~PE1] segment-routing [~PE1-segment-routing] segment-list pe1 [*PE1-segment-routing-segment-list-pe1] index 10 sid label 330000 [*PE1-segment-routing-segment-list-pe1] index 20 sid label 330002 [*PE1-segment-routing-segment-list-pe1] quit [*PE1-segment-routing] segment-list pe1backup [*PE1-segment-routing-segment-list-pe1backup] index 10 sid label 330001 [*PE1-segment-routing-segment-list-pe1backup] index 20 sid label 330003 [*PE1-segment-routing-segment-list-pe1backup] quit [*PE1-segment-routing] sr-te policy policy100 endpoint 3.3.3.9 color 100 [*PE1-segment-routing-te-policy-policy100] binding-sid 115 [*PE1-segment-routing-te-policy-policy100] mtu 1000 [*PE1-segment-routing-te-policy-policy100] diffserv-mode pipe af1 green [*PE1-segment-routing-te-policy-policy100] candidate-path preference 100 [*PE1-segment-routing-te-policy-policy100-path] segment-list pe1backup [*PE1-segment-routing-te-policy-policy100-path] quit [*PE1-segment-routing-te-policy-policy100] candidate-path preference 200 [*PE1-segment-routing-te-policy-policy100-path] segment-list pe1 [*PE1-segment-routing-te-policy-policy100-path] quit [*PE1-segment-routing-te-policy-policy100] quit [*PE1-segment-routing] quit [*PE1] commit
# Configure PE2.
[~PE2] segment-routing [~PE2-segment-routing] segment-list pe2 [*PE2-segment-routing-segment-list-pe2backup] index 10 sid label 330000 [*PE2-segment-routing-segment-list-pe2backup] index 20 sid label 330003 [*PE2-segment-routing-segment-list-pe2backup] quit [*PE2-segment-routing] segment-list pe2backup [*PE2-segment-routing-segment-list-pe2backup] index 10 sid label 330001 [*PE2-segment-routing-segment-list-pe2backup] index 20 sid label 330002 [*PE2-segment-routing-segment-list-pe2backup] quit [*PE2-segment-routing] sr-te policy policy200 endpoint 1.1.1.9 color 200 [*PE2-segment-routing-te-policy-policy200] binding-sid 115 [*PE2-segment-routing-te-policy-policy200] mtu 1000 [*PE2-segment-routing-te-policy-policy200] diffserv-mode pipe af1 green [*PE2-segment-routing-te-policy-policy200] candidate-path preference 100 [*PE2-segment-routing-te-policy-policy200-path] segment-list pe2backup [*PE2-segment-routing-te-policy-policy200-path] quit [*PE2-segment-routing-te-policy-policy200] candidate-path preference 200 [*PE2-segment-routing-te-policy-policy200-path] segment-list pe2 [*PE2-segment-routing-te-policy-policy200-path] quit [*PE2-segment-routing-te-policy-policy200] quit [*PE2-segment-routing] quit [*PE2] commit
After the configuration is complete, run the display sr-te policy command to check SR-MPLS TE Policy information. The following example uses the command output on PE1.
[~PE1] display sr-te policy PolicyName : policy100 Endpoint : 3.3.3.9 Color : 100 TunnelId : 1 TunnelType : SR-TE Policy Binding SID : 115 MTU : 1000 Policy State : Up State Change Time : 2020-04-27 09:23:13 Admin State : Up Traffic Statistics : Disable BFD : Disable Backup Hot-Standby : Disable DiffServ-Mode : Pipe, AF1, Green Candidate-path Count : 2 Candidate-path Preference: 200 Path State : Active Path Type : Primary Protocol-Origin : Configuration(30) Originator : 0, 0.0.0.0 Discriminator : 200 Binding SID : - GroupId : 2 Policy Name : policy100 Template ID : - Segment-List Count : 1 Segment-List : pe1 Segment-List ID : 129 XcIndex : 68 List State : Up BFD State : - EXP : - TTL : - DeleteTimerRemain : - Weight : 1 Label : 330000, 330002 Candidate-path Preference: 100 Path State : Inactive (Valid) Path Type : - Protocol-Origin : Configuration(30) Originator : 0, 0.0.0.0 Discriminator : 100 Binding SID : - GroupId : 1 Policy Name : policy100 Template ID : - Segment-List Count : 1 Segment-List : pe1backup Segment-List ID : 194 XcIndex : - List State : Up BFD State : - EXP : - TTL : - DeleteTimerRemain : - Weight : 1 Label : 330001, 330003
- Configure SBFD and HSB on each PE.
# Configure PE1.
[~PE1] bfd [*PE1-bfd] quit [*PE1] sbfd [*PE1-sbfd] reflector discriminator 1.1.1.9 [*PE1-sbfd] quit [*PE1] segment-routing [*PE1-segment-routing] sr-te-policy seamless-bfd enable [*PE1-segment-routing] sr-te-policy backup hot-standby enable [*PE1-segment-routing] commit [~PE1-segment-routing] quit
# Configure PE2.
[~PE2] bfd [*PE2-bfd] quit [*PE2] sbfd [*PE2-sbfd] reflector discriminator 3.3.3.9 [*PE2-sbfd] quit [*PE2] segment-routing [*PE2-segment-routing] sr-te-policy seamless-bfd enable [*PE2-segment-routing] sr-te-policy backup hot-standby enable [*PE2-segment-routing] commit [~PE2-segment-routing] quit
- Establish an MP-IBGP peer relationship between PEs.
# Configure PE1.
[~PE1] bgp 100 [*PE1-bgp] peer 3.3.3.9 as-number 100 [*PE1-bgp] peer 3.3.3.9 connect-interface loopback 1 [*PE1-bgp] ipv4-family vpnv4 [*PE1-bgp-af-vpnv4] peer 3.3.3.9 enable [*PE1-bgp-af-vpnv4] commit [~PE1-bgp-af-vpnv4] quit [~PE1-bgp] quit
# Configure PE2.
[~PE2] bgp 100 [*PE2-bgp] peer 1.1.1.9 as-number 100 [*PE2-bgp] peer 1.1.1.9 connect-interface loopback 1 [*PE2-bgp] ipv4-family vpnv4 [*PE2-bgp-af-vpnv4] peer 1.1.1.9 enable [*PE2-bgp-af-vpnv4] commit [~PE2-bgp-af-vpnv4] quit [~PE2-bgp] quit
After completing the configuration, run the display bgp peer or display bgp vpnv4 all peer command on each PE. The following example uses the command output on PE1. The command output shows that a BGP peer relationship has been established between the PEs and is in the Established state.
[~PE1] display bgp peer BGP local router ID : 1.1.1.9 Local AS number : 100 Total number of peers : 1 Peers in established state : 1 Peer V AS MsgRcvd MsgSent OutQ Up/Down State PrefRcv 3.3.3.9 4 100 2 6 0 00:00:12 Established 0 [~PE1] display bgp vpnv4 all peer BGP local router ID : 1.1.1.9 Local AS number : 100 Total number of peers : 1 Peers in established state : 1 Peer V AS MsgRcvd MsgSent OutQ Up/Down State PrefRcv 3.3.3.9 4 100 12 18 0 00:09:38 Established 0
- Create a VPN instance and enable the IPv4 address family on each PE. Then, bind each PE's interface connecting the PE to a CE to the corresponding VPN instance.
# Configure PE1.
[~PE1] ip vpn-instance vpna [*PE1-vpn-instance-vpna] ipv4-family [*PE1-vpn-instance-vpna-af-ipv4] route-distinguisher 100:1 [*PE1-vpn-instance-vpna-af-ipv4] vpn-target 111:1 both [*PE1-vpn-instance-vpna-af-ipv4] quit [*PE1-vpn-instance-vpna] quit [*PE1] interface gigabitethernet0/1/8 [*PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] ip binding vpn-instance vpna [*PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] ip address 10.1.1.2 24 [*PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] quit [*PE1] commit
# Configure PE2.
[~PE2] ip vpn-instance vpna [*PE2-vpn-instance-vpna] ipv4-family [*PE2-vpn-instance-vpna-af-ipv4] route-distinguisher 200:1 [*PE2-vpn-instance-vpna-af-ipv4] vpn-target 111:1 both [*PE2-vpn-instance-vpna-af-ipv4] quit [*PE2-vpn-instance-vpna] quit [*PE2] interface gigabitethernet0/1/8 [*PE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] ip binding vpn-instance vpna [*PE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] ip address 10.2.1.2 24 [*PE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] quit [*PE2] commit
- Configure a tunnel selection policy on each PE for the specified SR-MPLS TE Policy group to be preferentially selected.
# Configure PE1.
[~PE1] segment-routing [~PE1-segment-routing] sr-te-policy group 1 [*PE1-segment-routing-te-policy-group-1] endpoint 3.3.3.9 [*PE1-segment-routing-te-policy-group-1] color 100 match dscp ipv4 20 [*PE1-segment-routing-te-policy-group-1] quit [*PE1-segment-routing] quit [*PE1] tunnel-policy p1 [*PE1-tunnel-policy-p1] tunnel binding destination 3.3.3.9 sr-te-policy group 1 [*PE1-tunnel-policy-p1] quit [*PE1] ip vpn-instance vpna [*PE1-vpn-instance-vpna] ipv4-family [*PE1-vpn-instance-vpna-af-ipv4] tnl-policy p1 [*PE1-vpn-instance-vpna-af-ipv4] quit [*PE1-vpn-instance-vpna] quit [*PE1] commit
# Configure PE2.
[~PE2] segment-routing [~PE2-segment-routing] sr-te-policy group 1 [*PE2-segment-routing-te-policy-group-1] endpoint 1.1.1.9 [*PE2-segment-routing-te-policy-group-1] color 200 match dscp ipv4 20 [*PE2-segment-routing-te-policy-group-1] quit [*PE2-segment-routing] quit [*PE2] tunnel-policy p1 [*PE2-tunnel-policy-p1] tunnel binding destination 1.1.1.9 sr-te-policy group 1 [*PE2-tunnel-policy-p1] quit [*PE2] ip vpn-instance vpna [*PE2-vpn-instance-vpna] ipv4-family [*PE2-vpn-instance-vpna-af-ipv4] tnl-policy p1 [*PE2-vpn-instance-vpna-af-ipv4] quit [*PE2-vpn-instance-vpna] quit [*PE2] commit
After completing the configuration, run the display sr-te policy group 1 command on each PE. The command output shows the SR-MPLS TE Policy group status.
The following example uses the command output on PE1.
[~PE1] display sr-te policy group 1 SR-TE Policy Group Information ------------------------------------------------------------------------------- GroupID : 1 GroupState : UP GTunnelID : 67 GTunnelType : SR-TE Policy Group Endpoint : 3.3.3.9 UP/ALL Num : 1/1 ------------------------------------------------------------------------------- TunnelId AfType Color Dscp ------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 65 IPV4 100 20 ------------------------------------------------------------------------------- - Establish an EBGP peer relationship between each CE-PE pair.
# Configure CE1.
<HUAWEI> system-view [~HUAWEI] sysname CE1 [*HUAWEI] commit [~CE1] interface loopback 1 [*CE1-LoopBack1] ip address 10.11.1.1 32 [*CE1-LoopBack1] quit [*CE1] interface gigabitethernet0/1/0 [*CE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] ip address 10.1.1.1 24 [*CE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] quit [*CE1] bgp 65410 [*CE1-bgp] peer 10.1.1.2 as-number 100 [*CE1-bgp] network 10.11.1.1 32 [*CE1-bgp] quit [*CE1] commit

The configuration of CE2 is similar to the configuration of CE1. For configuration details, see "Configuration Files" in this section.
After the configuration is complete, run the display ip vpn-instance verbose command on the PEs to check VPN instance configurations. Check that each PE can successfully ping its connected CE.

If a PE has multiple interfaces bound to the same VPN instance, use the -a source-ip-address parameter to specify a source IP address when running the ping -vpn-instance vpn-instance-name -a source-ip-address dest-ip-address command to ping the CE that is connected to the remote PE. If the source IP address is not specified, the ping operation may fail.
# Configure PE1.
[~PE1] bgp 100 [~PE1-bgp] ipv4-family vpn-instance vpna [*PE1-bgp-vpna] peer 10.1.1.1 as-number 65410 [*PE1-bgp-vpna] commit [~PE1-bgp-vpna] quit [~PE1-bgp] quit

The configuration of PE2 is similar to the configuration of PE1. For configuration details, see "Configuration Files" in this section.
After the configuration is complete, run the display bgp vpnv4 vpn-instance peer command on the PEs to check whether BGP peer relationships have been established between the PEs and CEs. If the Established state is displayed in the command output, the BGP peer relationships have been established successfully.
The following example uses the command output on PE1 to show that a BGP peer relationship has been established between PE1 and CE1.
[~PE1] display bgp vpnv4 vpn-instance vpna peer BGP local router ID : 1.1.1.9 Local AS number : 100 VPN-Instance vpna, Router ID 1.1.1.9: Total number of peers : 1 Peers in established state : 1 Peer V AS MsgRcvd MsgSent OutQ Up/Down State PrefRcv 10.1.1.1 4 65410 91 90 0 01:15:39 Established 1 - Verify the configuration.
After completing the configuration, run the display ip routing-table vpn-instance vpn-instance-name command on each PE to check information about the loopback interface route toward a CE.
The following example uses the command output on PE1.
[~PE1] display ip routing-table vpn-instance vpna Route Flags: R - relay, D - download to fib, T - to vpn-instance, B - black hole route ------------------------------------------------------------------------------ Routing Table: vpna Destinations : 7 Routes : 7 Destination/Mask Proto Pre Cost Flags NextHop Interface 10.1.1.0/24 Direct 0 0 D 10.1.1.2 GigabitEthernet0/1/8 10.1.1.2/32 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 GigabitEthernet0/1/8 10.1.1.255/32 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 GigabitEthernet0/1/8 10.11.1.1/32 EBGP 255 0 RD 10.1.1.1 GigabitEthernet0/1/8 10.22.2.2/32 IBGP 255 0 RD 3.3.3.9 SR-TE Policy Group 127.0.0.0/8 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 InLoopBack0 255.255.255.255/32 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 InLoopBack0
Run the display ip routing-table vpn-instance vpna verbose command on each PE to check details about the loopback interface route toward a CE.
The following example uses the command output on PE1.
[~PE1] display ip routing-table vpn-instance vpna 10.22.2.2 verbose Route Flags: R - relay, D - download to fib, T - to vpn-instance, B - black hole route ------------------------------------------------------------------------------ Routing Table : vpna Summary Count : 1 Destination: 10.22.2.2/32 Protocol: IBGP Process ID: 0 Preference: 255 Cost: 0 NextHop: 3.3.3.9 Neighbour: 3.3.3.9 State: Active Adv Relied Age: 01h18m38s Tag: 0 Priority: low Label: 48180 QoSInfo: 0x0 IndirectID: 0x10000B9 Instance: RelayNextHop: 0.0.0.0 Interface: SR-TE Policy Group TunnelID: 0x000000003300000041 Flags: RD
The command output shows that the VPN route has been successfully recursed to the specified SR-MPLS TE Policy.
CEs in the same VPN can ping each other. For example, CE1 can ping CE2 at 10.22.2.2.
[~CE1] ping -a 10.11.1.1 10.22.2.2 PING 10.22.2.2: 56 data bytes, press CTRL_C to break Reply from 10.22.2.2: bytes=56 Sequence=1 ttl=251 time=72 ms Reply from 10.22.2.2: bytes=56 Sequence=2 ttl=251 time=34 ms Reply from 10.22.2.2: bytes=56 Sequence=3 ttl=251 time=50 ms Reply from 10.22.2.2: bytes=56 Sequence=4 ttl=251 time=50 ms Reply from 10.22.2.2: bytes=56 Sequence=5 ttl=251 time=34 ms --- 10.22.2.2 ping statistics --- 5 packet(s) transmitted 5 packet(s) received 0.00% packet loss round-trip min/avg/max = 34/48/72 ms
Configuration Files
PE1 configuration file
# sysname PE1 # ip vpn-instance vpna ipv4-family route-distinguisher 100:1 tnl-policy p1 vpn-target 111:1 export-extcommunity vpn-target 111:1 import-extcommunity # bfd # sbfd reflector discriminator 1.1.1.9 # mpls lsr-id 1.1.1.9 # mpls # segment-routing ipv4 adjacency local-ip-addr 10.11.1.1 remote-ip-addr 10.11.1.2 sid 330000 ipv4 adjacency local-ip-addr 10.13.1.1 remote-ip-addr 10.13.1.2 sid 330001 sr-te-policy backup hot-standby enable sr-te-policy seamless-bfd enable segment-list pe1 index 10 sid label 330000 index 20 sid label 330002 segment-list pe1backup index 10 sid label 330001 index 20 sid label 330003 sr-te-policy group 1 endpoint 3.3.3.9 color 100 match dscp ipv4 20 sr-te policy policy100 endpoint 3.3.3.9 color 100 diffserv-mode pipe af1 green binding-sid 115 mtu 1000 candidate-path preference 200 segment-list pe1 candidate-path preference 100 segment-list pe1backup # isis 1 is-level level-1 cost-style wide network-entity 10.0000.0000.0001.00 segment-routing mpls # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ip address 10.13.1.1 255.255.255.0 isis enable 1 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/8 undo shutdown ip binding vpn-instance vpna ip address 10.1.1.2 255.255.255.0 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/16 undo shutdown ip address 10.11.1.1 255.255.255.0 isis enable 1 # interface LoopBack1 ip address 1.1.1.9 255.255.255.255 isis enable 1 # bgp 100 peer 3.3.3.9 as-number 100 peer 3.3.3.9 connect-interface LoopBack1 # ipv4-family unicast undo synchronization peer 3.3.3.9 enable # ipv4-family vpnv4 policy vpn-target peer 3.3.3.9 enable # ipv4-family vpn-instance vpna peer 10.1.1.1 as-number 65410 # tunnel-policy p1 tunnel binding destination 3.3.3.9 sr-te-policy group 1 # return
P1 configuration file
# sysname P1 # mpls lsr-id 2.2.2.9 # mpls # segment-routing ipv4 adjacency local-ip-addr 10.12.1.1 remote-ip-addr 10.12.1.2 sid 330002 ipv4 adjacency local-ip-addr 10.11.1.2 remote-ip-addr 10.11.1.1 sid 330003 # isis 1 is-level level-1 cost-style wide network-entity 10.0000.0000.0002.00 segment-routing mpls # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ip address 10.11.1.2 255.255.255.0 isis enable 1 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/8 undo shutdown ip address 10.12.1.1 255.255.255.0 isis enable 1 # interface LoopBack1 ip address 2.2.2.9 255.255.255.255 isis enable 1 # return
PE2 configuration file
# sysname PE2 # ip vpn-instance vpna ipv4-family route-distinguisher 200:1 tnl-policy p1 vpn-target 111:1 export-extcommunity vpn-target 111:1 import-extcommunity # bfd # sbfd reflector discriminator 3.3.3.9 # mpls lsr-id 3.3.3.9 # mpls # segment-routing ipv4 adjacency local-ip-addr 10.12.1.2 remote-ip-addr 10.12.1.1 sid 330000 ipv4 adjacency local-ip-addr 10.14.1.2 remote-ip-addr 10.14.1.1 sid 330001 sr-te-policy backup hot-standby enable sr-te-policy seamless-bfd enable segment-list pe2 index 10 sid label 330000 index 20 sid label 330003 segment-list pe2backup index 10 sid label 330001 index 20 sid label 330002 sr-te-policy group 1 endpoint 1.1.1.9 color 200 match dscp ipv4 20 sr-te policy policy200 endpoint 1.1.1.9 color 200 diffserv-mode pipe af1 green binding-sid 115 mtu 1000 candidate-path preference 200 segment-list pe2 candidate-path preference 100 segment-list pe2backup # isis 1 is-level level-1 cost-style wide network-entity 10.0000.0000.0003.00 segment-routing mpls # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ip address 10.14.1.2 255.255.255.0 isis enable 1 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/8 undo shutdown ip binding vpn-instance vpna ip address 10.2.1.2 255.255.255.0 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/16 undo shutdown ip address 10.12.1.2 255.255.255.0 isis enable 1 # interface LoopBack1 ip address 3.3.3.9 255.255.255.255 isis enable 1 # bgp 100 peer 1.1.1.9 as-number 100 peer 1.1.1.9 connect-interface LoopBack1 # ipv4-family unicast undo synchronization peer 1.1.1.9 enable # ipv4-family vpnv4 policy vpn-target peer 1.1.1.9 enable # ipv4-family vpn-instance vpna peer 10.2.1.1 as-number 65420 # tunnel-policy p1 tunnel binding destination 1.1.1.9 sr-te-policy group 1 # return
P2 configuration file
# sysname P2 # mpls lsr-id 4.4.4.9 # mpls # segment-routing ipv4 adjacency local-ip-addr 10.13.1.2 remote-ip-addr 10.13.1.1 sid 330002 ipv4 adjacency local-ip-addr 10.14.1.1 remote-ip-addr 10.14.1.2 sid 330003 # isis 1 is-level level-1 cost-style wide network-entity 10.0000.0000.0004.00 segment-routing mpls # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ip address 10.13.1.2 255.255.255.0 isis enable 1 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/8 undo shutdown ip address 10.14.1.1 255.255.255.0 isis enable 1 # interface LoopBack1 ip address 4.4.4.9 255.255.255.255 isis enable 1 # return
CE1 configuration file
# sysname CE1 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ip address 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.0 # interface LoopBack1 ip address 10.11.1.1 255.255.255.255 # bgp 65410 peer 10.1.1.2 as-number 100 # ipv4-family unicast network 10.11.1.1 255.255.255.255 peer 10.1.1.2 enable # returnCE2 configuration file
# sysname CE2 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ip address 10.2.1.1 255.255.255.0 # interface LoopBack1 ip address 10.22.2.2 255.255.255.255 # bgp 65420 peer 10.2.1.2 as-number 100 # ipv4-family unicast network 10.22.2.2 255.255.255.255 peer 10.2.1.2 enable # return