IS-IS for SR-MPLS
Name |
Function |
Carried In |
|---|---|---|
Prefix-SID Sub-TLV |
Advertises SR-MPLS prefix SIDs. |
|
Adj-SID Sub-TLV |
Advertises SR-MPLS adjacency SIDs on a P2P network. |
|
LAN-Adj-SID Sub-TLV |
Advertises SR-MPLS adjacency SIDs on a LAN. |
|
SID/Label Sub-TLV |
Advertises SR-MPLS SIDs or MPLS labels. |
SR-Capabilities Sub-TLV and SR Local Block Sub-TLV |
SID/Label Binding TLV |
Advertises the mapping between prefixes and SIDs. |
IS-IS LSP |
SR-Capabilities Sub-TLV |
Advertises SR-MPLS capabilities. |
IS-IS Router Capability TLV-242 |
SR-Algorithm Sub-TLV |
Advertises the algorithm that is used. For details, see SR-MPLS Flex-Algo. |
IS-IS Router Capability TLV-242 |
IS-IS FAD sub-TLV |
Advertises the Flex-Algo definition (FAD) of IS-IS. For details, see SR-MPLS Flex-Algo. |
IS-IS Router Capability TLV-242 |
SR Local Block Sub-TLV |
Advertises the range of labels reserved for local SIDs. |
IS-IS Router Capability TLV-242 |
IS-IS TLV Extensions for SIDs
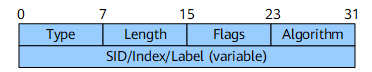
Prefix-SID Sub-TLV
Field |
Length |
Description |
|---|---|---|
Type |
8 bits |
Unassigned. The recommended value is 3. |
Length |
8 bits |
Packet length. |
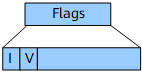
Flags |
8 bits |
Flags field. Figure 2 shows the format of this field.
In this field:
When computing the outgoing label for a packet destined for a prefix, a node must consider the P and E flags in the prefix SID advertised by the next hop, regardless of whether the optimal path to the prefix SID passes through the next hop. When propagating (from either Level-1 to Level-2 or Level-2 to Level-1) a reachability advertisement originated by another IS-IS speaker, the local node must set the P flag and clear the E flag in relevant prefix SIDs. The following behavior is associated with the settings of P and E flags:
|
Algorithm |
8 bits |
Algorithm that is used.
|
SID/Index/Label (variable) |
Variable |
This field contains either of the following information based on the V and L flags:
|
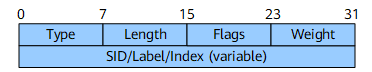
Adj-SID Sub-TLV
Field |
Length |
Description |
|---|---|---|
Type |
8 bits |
Unassigned. The recommended value is 31. |
Length |
8 bits |
Packet length. |
Flags |
8 bits |
Flags field. Figure 4 shows the format of this field.
In this field:
|
Weight |
8 bits |
Weight of the Adj-SID for the purpose of load balancing. |
SID/Index/Label (variable) |
Variable |
This field contains either of the following information based on the V and L flags:
|
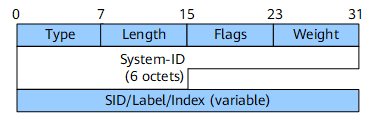
A designated intermediate system (DIS) is elected as a medium during IS-IS communications on a LAN. On the LAN, a node only needs to advertise one adjacency to the DIS and obtain all adjacency information from the DIS, without the need to exchange adjacency information with other nodes.
When SR is used, each node needs to advertise the Adj-SID of each of its neighbors. On the LAN, each node advertises only an IS-IS Extended IS reachability TLV-22 to the DIS and encapsulates the set of Adj-SIDs (for each of its neighbors) inside a newly defined sub-TLV: LAN-Adj-SID sub-TLV. This sub-TLV contains the set of Adj-SIDs assigned by a node to each of its LAN neighbors.
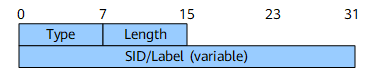
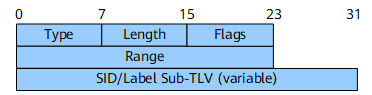
The SID/Label sub-TLV contains a SID or an MPLS label. It is a part of the SR-Capabilities sub-TLV.
Field |
Length |
Description |
|---|---|---|
Type |
8 bits |
Unassigned. The recommended value is 1. |
Length |
8 bits |
Packet length. |
SID/Label (variable) |
Variable |
If the Length field value is set to 3, the 20 rightmost bits indicate an MPLS label. |
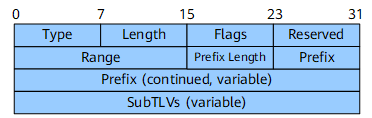
SID/Label Binding TLV
The SID/Label Binding TLV, which applies to SR and LDP interworking scenarios, can be used to advertise prefix-to-SID mappings.
Field |
Length |
Description |
|---|---|---|
Type |
8 bits |
Unassigned. The recommended value is 1. |
Length |
8 bits |
Packet length. |
Flags |
8 bits |
Flags field.
+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+ |F|M|S|D|A| | +-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+ |
Range |
16 bits |
Range of addresses and their associated prefix SIDs. |
Prefix Length |
8 bits |
Prefix length. |
Prefix |
Variable |
Prefix. |
SubTLVs |
Variable |
Sub-TLVs, for example, the SID/Label sub-TLV. |
IS-IS TLV Extensions for SR Capabilities
SR requires each node to advertise its SR capabilities and the range of global SIDs (or global indexes). To meet this requirement, the SR-Capabilities sub-TLV is defined and inserted into the IS-IS Router Capability TLV-242 for transmission. The SR-Capabilities sub-TLV can be propagated only within the same IS-IS level and must not be propagated across IS-IS levels.
Field |
Length |
Description |
|---|---|---|
Type |
8 bits |
Unassigned. The recommended value is 2. |
Length |
8 bits |
Packet length. |
Flags |
8 bits |
Flags field. Figure 9 shows the format of this field.
In this field:
|
Range |
24 bits |
SRGB range. For example, the originating node advertises SR-Capabilities of the following ranges: SR-Capability 1: range: 100; SID value: 100 SR-Capability 2: range: 100; SID value: 1000 SR-Capability 3: range: 100; SID value: 500 The receiving nodes concatenate the ranges in the received order and build the SRGB as follows: SRGB = [100, 199]
[1000, 1099]
[500, 599]
Different indexes may span multiple ranges. Index 0 indicates label 100. ... Index 99 indicates label 199. Index 100 indicates label 1000. Index 199 indicates label 1099. ... Index 200 indicates label 500. ... |
SID/Label Sub-TLV (variable) |
Variable |
For details, see SID/Label Sub-TLV. The SID/Label sub-TLV contains the first value of the involved SRGB. When multiple SRGBs are configured, ensure that the SRGB sequence is correct and the SRGBs do not overlap. |
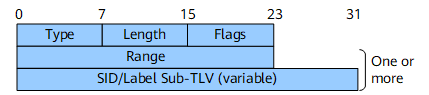
SR Local Block Sub-TLV
The SR Local Block sub-TLV contains the range of labels that a node has reserved for local SIDs. Local SIDs are used for adjacency SIDs, and may also be allocated by components other than the IS-IS protocol. For example, an application or a controller may instruct the node to allocate a specific local SID. Therefore, in order for such applications or controllers to know what local SIDs are available on the node, it is required that the node advertises its SR local block (SRLB).
Field |
Length |
Description |
|---|---|---|
Type |
8 bits |
Unassigned. The recommended value is 2. |
Length |
8 bits |
Packet length. |
Flags |
8 bits |
Flags field. This field is not defined currently. |
Range |
8 bits |
SRLB range. |
SID/Label Sub-TLV (variable) |
Variable |
For details, see SID/Label Sub-TLV. The SID/Label sub-TLV contains the first value of the involved SRLB. When multiple SRLBs are configured, ensure that the SRLB sequence is correct and the SRLBs do not overlap. |
A node advertising the SR Local Block sub-TLV may also have other label ranges, outside the SRLB, for its local allocation purposes that are not advertised in the SRLB. For example, it is possible that an adjacency SID is allocated using a local label, which is not part of the SRLB.