SR-MPLS TTL
The TTL field in MPLS packets transmitted over public SR-MPLS TE and SR-MPLS BE tunnels are processed in either of the following modes:
Uniform mode
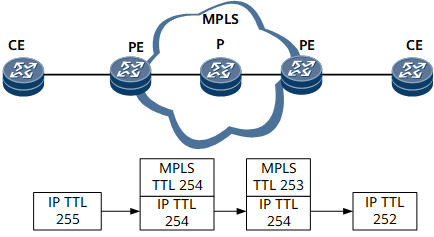
When an IP packet passes through an SR-MPLS network, the IP TTL decreases by 1 and is mapped to the MPLS TTL field on the ingress PE1. Then, the MPLS TTL decreases by 1 each time the packet passes through a node on the SR-MPLS network. After the packet arrives at the egress PE2, the MPLS TTL decreases by 1 and is compared with the IP TTL value. Then, the smaller value is mapped to the IP TTL field. Figure 1 shows how the TTL is processed in uniform mode.
Pipe mode
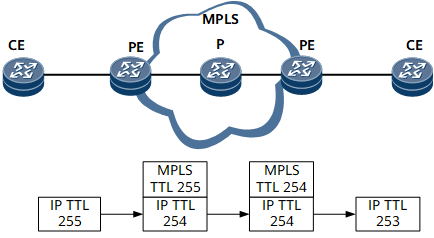
When an IP packet passes through an SR-MPLS network, the IP TTL decreases by 1 and the MPLS TTL is a fixed value on the ingress PE1. Then, the MPLS TTL decreases by 1 each time the packet passes through a node on the SR-MPLS network. After the packet arrives at the egress PE2, the IP TTL decreases by 1. To summarize, in pipe mode, the IP TTL in a packet decreases by 1 only on the ingress PE1 and egress PE2 no matter how many hops exist between the ingress and egress on an SR-MPLS network. Figure 2 shows how the TTL is processed in pipe mode.