SRv6 TE Policy-based Data Forwarding
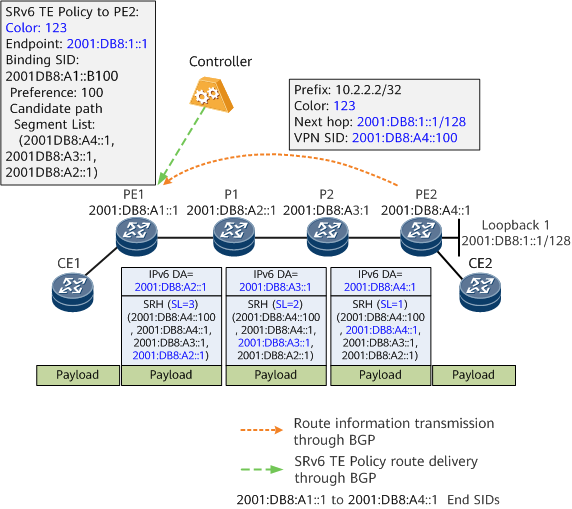
A controller delivers an SRv6 TE Policy to the headend PE1.
The endpoint PE2 advertises the BGP VPNv4 route 10.2.2.2/32 to PE1. The next-hop address in the BGP route is PE2's address 2001:DB8:1::1/128.
A tunnel policy is configured on PE1. After receiving the BGP route, PE1 recurses the route to the SRv6 TE Policy based on the color value and next hop of the route. The SID list encapsulated into the SRv6 TE Policy is <2001:DB8:A2::1, 2001:DB8:A3::1, 2001:DB8:A4::1>, which can also be expressed as (2001:DB8:A4::1, 2001:DB8:A3::1, 2001:DB8:A2::1) in data forwarding scenarios.
After receiving a common unicast packet from CE1, PE1 searches the routing table of the corresponding VPN instance and finds that the outbound interface of the route is an SRv6 TE Policy interface. PE1 then inserts an SRH carrying the SID list of the SRv6 TE Policy and encapsulates an IPv6 header into the packet. After completing these operations, PE1 forwards the packet to P1.
Transit nodes P1 and P2 forward the packet hop by hop based on the SRH information.
After receiving the packet, the endpoint PE2 searches the My Local SID Table and finds an End SID that matches the IPv6 destination address (DA) 2001:DB8:A4::1 in the packet. According to the instruction bound to the SID, PE2 decrements the SL value of the packet by 1 and changes the IPv6 DA to the VPN SID 2001:DB8:A4::100.
PE2 searches the My Local SID Table and finds an End.DT4 SID that matches the VPN SID 2001:DB8:A4::100. According to the instruction bound to the End.DT4 SID, PE2 decapsulates the packet by removing the SRH and outer IPv6 header, searches the routing table of the VPN instance corresponding to the VPN SID 2001:DB8:A4::100 based on the destination address in the inner packet, and forwards the packet to CE2.
SRv6 TE Policy Support for the Encap Mode
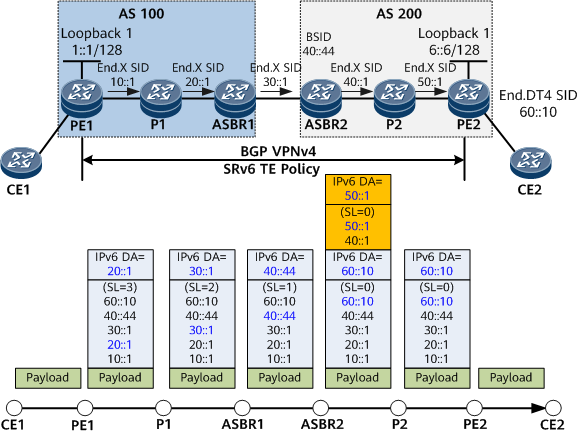
When delivering an SRv6 TE Policy, the SR-Policy module specifies an encapsulation mode: Encap, Insert, or Insert & Encap. Taking the network shown in Figure 2 as an example, assume that CE1 sends a data packet that needs to traverse two ASs to CE2.
If the Encap mode is enabled for the BSID of ASBR2 and the PSP flavor is not enabled for all the other SIDs, the main data forwarding process on the public network is as follows:
- The headend PE1 searches for the desired route according to the destination address, finds that the outbound interface points to an SRv6 TE Policy, and then encapsulates an IPv6 header and an SRH into the packet. P1 and ASBR1 in AS 100 forward this packet properly according to the SRH.
- When forwarding the packet, transit node ASBR2 searches the local SID table according to the DA information in the IPv6 header and finds a matching local BSID. In this case, ASBR2 needs to encapsulate the packet according to the encapsulation mode corresponding to the BSID. If the encapsulation mode is Encap, a new IPv6 header and an SRH need to be encapsulated, with the DA in the new IPv6 header set to the first SID of the SRv6 TE Policy in AS 200 (for example, End.X SID 40::1 of ASBR2). Because End.X SID 40::1 is a local SID, ASBR2 decrements the SL value by 1 and changes the DA to P2's End.X SID 50::1.
- After receiving the packet, P2 decapsulates it according to the USD flavor carried in the End.X SID 50::1, searches the forwarding table according to the DA 60::10 in the inner IPv6 header, and then forwards the packet to PE2.
- The endpoint PE2 searches the local SID table according to the DA 60::10 in the IPv6 header and finds a matching local End.DT4 SID. According to the instruction bound to the End.DT4 SID, PE2 decapsulates the packet, searches the routing table of the VPN instance corresponding to the End.DT4 SID according to the DA in the inner packet, and then forwards the packet to CE2.