BGP-LS Extension of SRv6 Flex-Algo
In scenarios where a controller dynamically orchestrates an SRv6 TE Policy based on Flex-Algo, forwarders need to report information such as node attributes, link attributes, and SRv6 SIDs to the controller through BGP-LS. BGP-LS information is encapsulated in Node NLRI/Link NLRI information and advertised to the controller.
BGP-LS is extended to implement the preceding functions, as described in Table 1.
Attribute |
TLV |
Sub-TLV |
|---|---|---|
Node attributes |
FAD |
Flex-Algo Exclude Any Affinity |
Flex-Algo Include Any Affinity |
||
Flex Algo Include All Affinity |
||
Flex-Algo Definition Flags |
||
SR-Algorithm TLV |
None |
|
Link attributes |
Application Specific Link Attributes TLV |
TE Metric |
Min/Max Unidirectional Link Delay |
||
Extended Administrative Group (color) |
||
Unidirectional Link Loss TLV |
||
SRv6 End.X SID TLV |
None |
|
SRv6 LAN End.X SID TLV |
None |
|
SRv6 SID attributes |
SRv6 Endpoint Function TLV |
None |
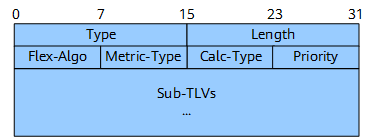
FAD TLV
The FAD TLV is carried in the Node NLRI. Figure 1 shows the format of the FAD TLV.
Figure 1 describes the fields in the FAD TLV.
Field |
Length |
Description |
|---|---|---|
Type |
16 bits |
Type of the TLV. |
Length |
16 bits |
Total length of the TLV (excluding the Type and Length fields). |
Flex-Algo |
8 bits |
Flex-Algo ID, which is an integer ranging from 128 to 255. |
Metric-Type |
8 bits |
Metric type used during calculation. This field can be set to an IGP metric, minimum unidirectional link delay, or TE metric value. |
Calc-Type |
8 bits |
Calculation type, which can currently only be SPF and does not need setting. |
Priority |
8 bits |
Priority of the TLV. |
Sub-TLVs |
Variable |
Optional sub-TLVs, which can define some constraints. |
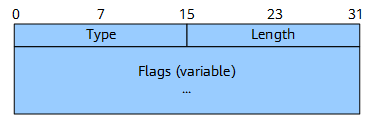
The sub-TLVs of the FAD TLV include Flex-Algo Exclude Any Affinity, Flex-Algo Include Any Affinity, Flex-Algo Include All Affinity, and Flex-Algo Definition Flags.
The Flex-Algo Exclude Any Affinity, Flex-Algo Include Any Affinity, and Flex-Algo Include All Affinity sub-TLVs have the same format, as shown in Figure 2.
Figure 3 shows the format of the Flex-Algo Definition Flags sub-TLV.
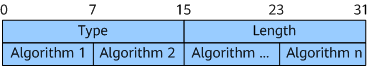
SR-Algorithm TLV
Table 3 describes the fields in the SR-Algorithm TLV.
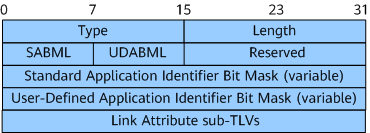
Application Specific Link Attributes TLV
Figure 5 shows the format of the Application Specific Link Attributes TLV.
Table 4 describes the fields in the Application Specific Link Attributes TLV.
Field |
Length |
Description |
|---|---|---|
Type |
16 bits |
Type of the TLV. |
Length |
16 bits |
Total length of the TLV (excluding the Type and Length fields). |
SABML |
8 bits |
Standard Application Identifier Bit Mask Length, in octets. The value must be 0, 4, or 8. If the Standard Application Identifier Bit Mask field does not exist, the SABML field must be set to 0. |
UDABML |
8 bits |
User-Defined Application Identifier Bit Mask Length, in octets. The value must be 0, 4, or 8. If the User-Defined Application Identifier Bit Mask field does not exist, the UDABML field must be set to 0. |
Standard Application Identifier Bit Mask |
Variable |
Standard Application Identifier Bit Mask, where each bit represents a standard application. |
User-Defined Application Identifier Bit Mask |
Variable |
User-Defined Application Identifier Bit Mask, where each bit represents a user-defined application. |
Link Attribute Sub-TLVs |
Variable |
Sub-TLVs contained in the TLV. |
The Application Specific Link Attributes TLV carries sub-TLVs, such as TE Metric, Min/Max Unidirectional Link Delay, Extended Administrative Group (color), and Unidirectional Link Loss.
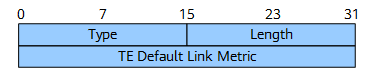
Figure 6 shows the format of the TE Metric sub-TLV.
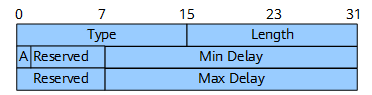
Figure 7 shows the format of the Min/Max Unidirectional Link Delay sub-TLV.
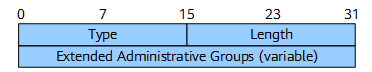
Figure 8 shows the format of the Extended Administrative Group (color) sub-TLV.
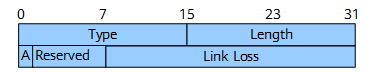
Figure 9 shows the format of the Unidirectional Link Loss sub-TLV.
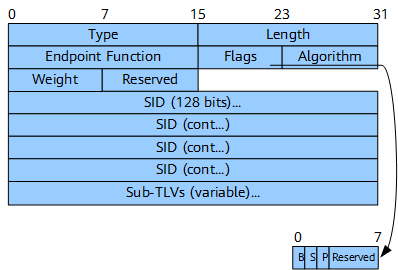
SRv6 End.X SID Sub-TLV
The SRv6 End.X SID sub-TLV is used to advertise SRv6 End.X SIDs associated with adjacencies. Figure 10 shows the format of the SRv6 End.X SID sub-TLV.
Table 5 describes the fields in the SRv6 End.X SID sub-TLV.
Field |
Length |
Description |
|---|---|---|
Type |
16 bits |
Type. |
Length |
16 bits |
Length. |
Endpoint Function |
16 bits |
Type of an SRv6 endpoint behavior. |
Flags |
8 bits |
Flags:
|
Algorithm |
8 bits |
Algorithm ID:
|
Weight |
8 bits |
Weight of the End.X SID used for load balancing. |
SID |
16 octets |
Advertised SRv6 SID. |
Sub-TLVs (variable) |
Variable |
Included sub-sub-TLVs. |
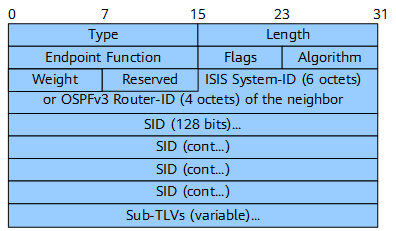
SRv6 LAN End.X SID Sub-TLV
The SRv6 LAN End.X SID sub-TLV is used to advertise SRv6 End.X SIDs associated with adjacencies on a LAN. Figure 11 shows the format of the SRv6 LAN End.X SID sub-TLV.
Compared with the SRv6 End.X SID sub-TLV, this sub-TLV has one more ISIS System-ID (6 octets) or OSPFv3 Router-ID (4 octets) of the neighbor field. Table 6 describes the fields in this sub-TLV.
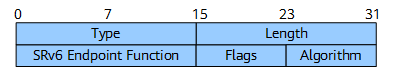
SRv6 Endpoint Function TLV
The SRv6 Endpoint Function TLV is an SRv6 SID NLRI attribute used to carry the instructions associated with each type of SID. Each SRv6 SID is associated with a network function instruction. Figure 12 shows the format of the SRv6 Endpoint Function TLV.
Table 7 describes the fields in the SRv6 Endpoint Function TLV.
Field |
Length |
Description |
|---|---|---|
Type |
16 bits |
Type of the TLV. |
Length |
16 bits |
Length of the Value field in the TLV, in bytes. |
SRv6 Endpoint Function |
16 bits |
Code value of the associated network function. |
Flags |
8 bits |
Flags, which are not in use currently. |
Algorithm |
8 bits |
Algorithm ID:
|