Configuring EVPN VPLS over SRv6 Flex-Algo
This section describes how to configure EVPN VPLS over SRv6 Flex-Algo.
Usage Scenario
EVPN VPLS uses the EVPN E-LAN model to carry MP2MP VPLS services.
EVPN VPLS over SRv6 Flex-Algo uses forwarding paths calculated based on Flex-Algos to carry EVPN E-LAN services on the public network.
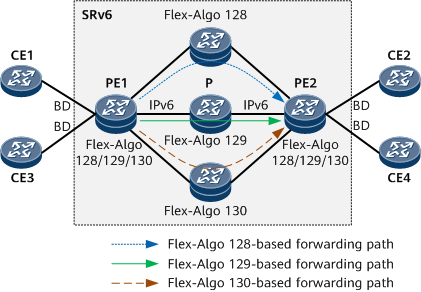
On the network shown in Figure 1, multiple links exist between PEs. You can configure the PEs to forward EVPN E-LAN services over a path calculated using a specified Flex-Algo.
Pre-configuration Tasks
Before performing the configuration, complete the following tasks:
Configure IS-IS to enable devices to communicate at the network layer.
- Enable the advertisement of IPv6 delay information if the Flex-Algo metric type is delay.
Procedure
- Configure Flex-Algo link attributes.
- Configure a FAD.
- Configure IPv6 IS-IS on each PE and P. For configuration details, see Configuring Basic IPv6 IS-IS Functions.
- Configure BD-EVPN functions on PEs.
- Establish a BGP EVPN peer relationship between PEs.
- Configure basic SRv6 functions.
- Enable IS-IS SRv6 on the PEs and Ps.
- Configure EVPN routes to carry SIDs and recurse to SRv6 BE paths based on the SIDs.
Verifying the Configuration
After configuring EVPN VPLS over SRv6 Flex-Algo, verify the configuration.
Run the display segment-routing ipv6 local-sid { end-dt2u | end-dt2ul | end-dt2m } [ sid ] [ bridge-domain bd-id ] forwarding command to check information about the SRv6 BE local SID table.
Run the display bgp evpn { all | route-distinguisher route-distinguisher | vpn-instance vpn-instance-name } routing-table [ { ad-route | es-route | inclusive-route | mac-route | prefix-route } prefix ] command to check BGP EVPN route information.
- Run the display isis process-id flex-algo [ flex-algo-id ] [ level-1 | level-2 ] command to check the preferred FAD in the LSDB.
- Run the display isis lsdb [ { level-1 | level-2 } | verbose | { local | lsp-id | is-name symbolic-name } ] * [ process-id | vpn-instance vpn-instance-name ] command to check IS-IS LSDB information.
- Run the display isis process-id route ipv6 flex-algo [ flex-algo-id ] [ verbose | [ level-1 | level-2 ] | ipv6-address [ prefix-length ] ] * or display isis route [ process-id ] ipv6 flex-algo [ flex-algo-id ] [ verbose | [ level-1 | level-2 ] | ipv6-address [ prefix-length ] ] * command to check Flex-Algo-related IS-IS route information.
- Run the display isis [ process-id ] spf-tree [ systemid systemid ] ipv6 flex-algo [ flex-algo-id ] [ [ level-1 | level-2 ] | verbose ] * command to check the SPF tree topology information of a specified Flex-Algo.