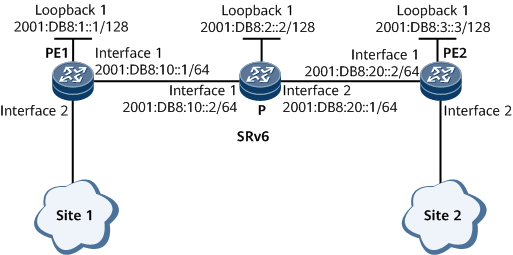
Example for Configuring EVPN VPWS over SRv6 BE
This section provides an example for configuring SRv6 BE to carry EVPN VPWSs.
Networking Requirements
On the network shown in Figure 1, PE1, the P, and PE2 are in the same AS and run IS-IS to implement IPv6 network connectivity. It is required that a bidirectional SRv6 BE path be deployed between PE1 and PE2 to carry EVPN VPWSs.
Configuration Roadmap
The configuration roadmap is as follows:
Enable IPv6 forwarding and configure an IPv6 address for each interface on PE1, the P, and PE2.
Enable IS-IS, configure an IS-IS level, and specify a network entity title (NET) on PE1, the P, and PE2.
Configure EVPN VPWS and EVPL instances on each PE and bind the EVPL instance to an access-side sub-interface.
Establish a BGP EVPN peer relationship between PEs.
Configure SRv6 BE on PEs.
Data Preparation
To complete the configuration, you need the following data:
EVPN instance name: evrf1
RD and RT of the EVPN instance
Procedure
- Enable IPv6 forwarding and configure an IPv6 address for each interface. The following example uses the configuration of PE1. The configurations of other devices are similar to the configuration of PE1. For configuration details, see Configuration Files in this section.
<HUAWEI> system-view [~HUAWEI] sysname PE1 [*HUAWEI] commit [~PE1] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/0 [~PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] ipv6 enable [*PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] ipv6 address 2001:DB8:10::1 64 [*PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] quit [*PE1] interface LoopBack 1 [*PE1-LoopBack1] ip address 1.1.1.1 32 [*PE1-LoopBack1] ipv6 enable [*PE1-LoopBack1] ipv6 address 2001:DB8:1::1 128 [*PE1-LoopBack1] quit [*PE1] commit
Configure an IPv4 address for the loopback interface because the EVPN source address needs to be an IPv4 address. This example uses the configuration of PE1. The configurations of other devices are similar to the configuration of PE1. For configuration details, see Configuration Files in this section.
- Configure IS-IS.
# Configure PE1.
[~PE1] isis 1 [*PE1-isis-1] is-level level-1 [*PE1-isis-1] cost-style wide [*PE1-isis-1] network-entity 10.0000.0000.0001.00 [*PE1-isis-1] ipv6 enable topology ipv6 [*PE1-isis-1] quit [*PE1] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/0 [*PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] isis ipv6 enable 1 [*PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] quit [*PE1] interface loopback1 [*PE1-LoopBack1] isis ipv6 enable 1 [*PE1-LoopBack1] commit [~PE1-LoopBack1] quit
# Configure the P.
[~P] isis 1 [*P-isis-1] is-level level-1 [*P-isis-1] cost-style wide [*P-isis-1] network-entity 10.0000.0000.0002.00 [*P-isis-1] ipv6 enable topology ipv6 [*P-isis-1] quit [*P] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/0 [*P-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] isis ipv6 enable 1 [*P-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] quit [*P] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/8 [*P-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] isis ipv6 enable 1 [*P-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] quit [*P] interface loopback1 [*P-LoopBack1] isis ipv6 enable 1 [*P-LoopBack1] commit [~P-LoopBack1] quit
# Configure PE2.
[~PE2] isis 1 [*PE2-isis-1] is-level level-1 [*PE2-isis-1] cost-style wide [*PE2-isis-1] network-entity 10.0000.0000.0003.00 [*PE2-isis-1] ipv6 enable topology ipv6 [*PE2-isis-1] quit [*PE2] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/0 [*PE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] isis ipv6 enable 1 [*PE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] quit [*PE2] interface loopback1 [*PE2-LoopBack1] isis ipv6 enable 1 [*PE2-LoopBack1] commit [~PE2-LoopBack1] quit
After the configuration is complete, perform the following operations to check whether IS-IS is successfully configured:
# Display IS-IS neighbor information. The following example uses the command output on PE1.
[~PE1] display isis peer Peer information for ISIS(1) System Id Interface Circuit Id State HoldTime Type PRI -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 0000.0000.0002* GE0/1/0 0000.0000.0002.01 Up 8s L1 64 Total Peer(s): 1
# Display IS-IS routing table information. The following example uses the command output on PE1.
[~PE1] display isis route Route information for ISIS(1) ----------------------------- ISIS(1) Level-1 Forwarding Table -------------------------------- IPV6 Dest. ExitInterface NextHop Cost Flags -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 2001:DB8:1::1/128 GE0/1/0 Direct 10 D/-/L/- 2001:DB8:2::2/128 GE0/1/0 FE80::3A5D:67FF:FE31:307 10 A/-/-/- 2001:DB8:3::3/128 GE0/1/0 FE80::3A5D:67FF:FE31:307 20 A/-/-/- 2001:DB8:10::/64 GE0/1/0 Direct 20 A/-/-/- 2001:DB8:20::/64 GE0/1/0 FE80::3A5D:67FF:FE31:307 20 A/-/-/- Flags: D-Direct, A-Added to URT, L-Advertised in LSPs, S-IGP Shortcut, U-Up/Down Bit Set, LP-Local Prefix-Sid Protect Type: L-Link Protect, N-Node Protect
- Configure EVPN and EVPL instances on each PE and bind the EVPL instance to an access-side sub-interface.
# Configure PE1.
[~PE1] evpn source-address 1.1.1.1 [*PE1] evpn vpn-instance evrf1 vpws [*PE1-vpws-evpn-instance-evrf1] route-distinguisher 100:1 [*PE1-vpws-evpn-instance-evrf1] vpn-target 1:1 [*PE1-vpws-evpn-instance-evrf1] quit [*PE1] evpl instance 1 [*PE1-evpl1] evpn binding vpn-instance evrf1 [*PE1-evpl1] local-service-id 100 remote-service-id 200 [*PE1-evpl1] quit [*PE1] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/8.1 mode l2 [*PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/8.1] encapsulation dot1q vid 1 [*PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/8.1] evpl instance 1 [*PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/8.1] quit [*PE1] commit
# Configure PE2.
[~PE2] evpn source-address 3.3.3.3 [*PE2] evpn vpn-instance evrf1 vpws [*PE2-vpws-evpn-instance-evrf1] route-distinguisher 200:1 [*PE2-vpws-evpn-instance-evrf1] vpn-target 1:1 [*PE2-vpws-evpn-instance-evrf1] quit [*PE2] evpl instance 1 [*PE2-evpl1] evpn binding vpn-instance evrf1 [*PE2-evpl1] local-service-id 200 remote-service-id 100 [*PE2-evpl1] quit [*PE2] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/8.1 mode l2 [*PE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/8.1] encapsulation dot1q vid 1 [*PE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/8.1] evpl instance 1 [*PE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/8.1] quit [*PE2] commit
- Establish a BGP EVPN peer relationship between PEs.
# Configure PE1.
[~PE1] bgp 100 [*PE1-bgp] router-id 1.1.1.1 [*PE1-bgp] peer 2001:DB8:3::3 as-number 100 [*PE1-bgp] peer 2001:DB8:3::3 connect-interface loopback 1 [*PE1-bgp] l2vpn-family evpn [*PE1-bgp-af-evpn] peer 2001:DB8:3::3 enable [*PE1-bgp-af-evpn] quit [*PE1-bgp] quit [*PE1] commit
# Configure PE2.
[~PE2] bgp 100 [*PE2-bgp] router-id 3.3.3.3 [*PE2-bgp] peer 2001:DB8:1::1 as-number 100 [*PE2-bgp] peer 2001:DB8:1::1 connect-interface loopback 1 [*PE2-bgp] l2vpn-family evpn [*PE2-bgp-af-evpn] peer 2001:DB8:1::1 enable [*PE2-bgp-af-evpn] quit [*PE2-bgp] quit [*PE2] commit
After the configuration is complete, run the display bgp evpn peer command on the PEs and check whether BGP EVPN peer relationships have been established between the PEs. If the Established state is displayed in the command output, the BGP EVPN peer relationships have been established successfully.
- Deploy SRv6 BE between PEs.
# Configure PE1.
[~PE1] segment-routing ipv6 [*PE1-segment-routing-ipv6] encapsulation source-address 2001:DB8:1::1 [*PE1-segment-routing-ipv6] locator PE1 ipv6-prefix 2001:DB8:11:: 64 static 32 [*PE1-segment-routing-ipv6-locator] quit [*PE1-segment-routing-ipv6] quit [*PE1] isis 1 [*PE1-isis-1] segment-routing ipv6 locator PE1 [*PE1-isis-1] quit [*PE1] bgp 100 [*PE1-bgp] l2vpn-family evpn [*PE1-bgp-af-evpn] peer 2001:DB8:3::3 advertise encap-type srv6 [*PE1-bgp-af-evpn] quit [*PE1-bgp] quit [*PE1] evpl instance 1 [*PE1-evpl1] segment-routing ipv6 locator PE1 [*PE1-evpl1] quit [*PE1] evpn vpn-instance evrf1 vpws [*PE1-vpws-evpn-instance-evrf1] segment-routing ipv6 best-effort [*PE1-vpws-evpn-instance-evrf1] quit [*PE1] commit
# Configure PE2.
[~PE2] segment-routing ipv6 [*PE2-segment-routing-ipv6] encapsulation source-address 2001:DB8:3::3 [*PE2-segment-routing-ipv6] locator PE2 ipv6-prefix 2001:DB8:30:: 64 static 32 [*PE2-segment-routing-ipv6-locator] quit [*PE2-segment-routing-ipv6] quit [*PE2] isis 1 [*PE2-isis-1] segment-routing ipv6 locator PE2 [*PE2-isis-1] quit [*PE2] bgp 100 [*PE2-bgp] l2vpn-family evpn [*PE2-bgp-af-evpn] peer 2001:DB8:1::1 advertise encap-type srv6 [*PE2-bgp-af-evpn] quit [*PE2-bgp] quit [*PE2] evpl instance 1 [*PE2-evpl1] segment-routing ipv6 locator PE2 [*PE2-evpl1] quit [*PE2] evpn vpn-instance evrf1 vpws [*PE2-vpws-evpn-instance-evrf1] segment-routing ipv6 best-effort [*PE2-vpws-evpn-instance-evrf1] quit [*PE2] commit
- Verify the configuration.
Run the display bgp evpn evpl command on each PE. The command output shows the EVPL status. The following example uses the command output on PE1.
[~PE1] display bgp evpn evpl Total EVPLs: 1 1 Up 0 Down EVPL ID : 1 State : up EVPL Type : none Interface : GigabitEthernet0/1/8.1 Ignore AcState : disable Local MTU : 1500 Local Control Word : false Local Redundancy Mode : all-active Local DF State : primary Local ESI : 0000.0000.0000.0000.0000 Remote Redundancy Mode : all-active Remote Primary DF Number : 1 Remote Backup DF Number : 0 Remote None DF Number : 0 Peer IP : 2001:DB8:3::3 Origin Nexthop IP : 2001:DB8:3::3 DF State : primary Remote MTU : 1500 Remote Control Word : false Remote ESI : 0000.0000.0000.0000.0000 Tunnel info : 1 tunnels NO.0 Tunnel Type : srv6-be, Tunnel ID : Last Interface UP Timestamp : 2020-02-12 7:37:20:398 Last Designated Primary Timestamp : -- Last Designated Backup Timestamp : --
Run the display bgp evpn all routing-table command on each PE. The command output shows the EVPN route sent from the peer end. The following example uses the command output on PE1.
[~PE1] display bgp evpn all routing-table Local AS number : 100 BGP Local router ID is 1.1.1.1 Status codes: * - valid, > - best, d - damped, x - best external, a - add path, h - history, i - internal, s - suppressed, S - Stale Origin : i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete EVPN address family: Number of A-D Routes: 2 Route Distinguisher: 100:1 Network(ESI/EthTagId) NextHop *> 0000.0000.0000.0000.0000:100 127.0.0.1 *>i 0000.0000.0000.0000.0000:200 2001:DB8:3::3 EVPN-Instance evrf1: Number of A-D Routes: 2 Network(ESI/EthTagId) NextHop *> 0000.0000.0000.0000.0000:100 127.0.0.1 *>i 0000.0000.0000.0000.0000:200 2001:DB8:3::3Run the display bgp evpn all routing-table ad-route command on PE1. The command output shows the A-D EVPN routes sent from the peer end.
[~PE1] display bgp evpn all routing-table ad-route 0000.0000.0000.0000.0000:200 BGP local router ID : 1.1.1.1 Local AS number : 100 Total routes of Route Distinguisher(200:1): 1 BGP routing table entry information of 0000.0000.0000.0000.0000:200: Label information (Received/Applied): 3/NULL From: 2001:DB8:3::3 (3.3.3.3) Route Duration: 0d00h03m43s Relay IP Nexthop: FE80::3AC2:67FF:FE31:307 Relay IP Out-Interface:GigabitEthernet0/1/0 Relay Tunnel Out-Interface: Original nexthop: 2001:DB8:3::3 Qos information : 0x0 Ext-Community: RT <1 : 1>, SoO <3.3.3.3 : 0>, EVPN L2 Attributes <MTU:1500 C:0 P:1 B:0> Prefix-sid: 2001:DB8:30::1:0:3C AS-path Nil, origin incomplete, localpref 100, pref-val 0, valid, internal, best, select, pre 255, IGP cost 20 Route Type: 1 (Ethernet Auto-Discovery (A-D) route) ESI: 0000.0000.0000.0000.0000, Ethernet Tag ID: 200 Not advertised to any peer yet EVPN-Instance evrf1: Number of A-D Routes: 1 BGP routing table entry information of 0000.0000.0000.0000.0000:200: Route Distinguisher: 200:1 Remote-Cross route Label information (Received/Applied): 3/NULL From: 2001:DB8:3::3 (3.3.3.3) Route Duration: 0d00h03m44s Relay IP Nexthop: FE80::3AC2:67FF:FE31:307 Relay IP Out-Interface:GigabitEthernet0/1/0 Relay Tunnel Out-Interface: Original nexthop: 2001:DB8:3::3 Qos information : 0x0 Ext-Community: RT <1 : 1>, SoO <3.3.3.3 : 0>, EVPN L2 Attributes <MTU:1500 C:0 P:1 B:0> Prefix-sid: 2001:DB8:30::1:0:3C AS-path Nil, origin incomplete, localpref 100, pref-val 0, valid, internal, best, select, pre 255, IGP cost 20 Route Type: 1 (Ethernet Auto-Discovery (A-D) route) ESI: 0000.0000.0000.0000.0000, Ethernet Tag ID: 200 Not advertised to any peer yet
Configuration Files
PE1 configuration file
# sysname PE1 # evpn vpn-instance evrf1 vpws route-distinguisher 100:1 segment-routing ipv6 best-effort vpn-target 1:1 export-extcommunity vpn-target 1:1 import-extcommunity # evpl instance 1 evpn binding vpn-instance evrf1 local-service-id 100 remote-service-id 200 segment-routing ipv6 locator PE1 # segment-routing ipv6 encapsulation source-address 2001:DB8:1::1 locator PE1 ipv6-prefix 2001:DB8:11:: 64 static 32 # isis 1 is-level level-1 cost-style wide network-entity 10.0000.0000.0001.00 # ipv6 enable topology ipv6 segment-routing ipv6 locator PE1 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ipv6 enable ipv6 address 2001:DB8:10::1/64 isis ipv6 enable 1 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/8.1 mode l2 encapsulation dot1q vid 1 evpl instance 1 # interface LoopBack1 ipv6 enable ip address 1.1.1.1 255.255.255.255 ipv6 address 2001:DB8:1::1/128 isis ipv6 enable 1 # bgp 100 router-id 1.1.1.1 peer 2001:DB8:3::3 as-number 100 peer 2001:DB8:3::3 connect-interface LoopBack1 # ipv4-family unicast undo synchronization # l2vpn-family evpn policy vpn-target peer 2001:DB8:3::3 enable peer 2001:DB8:3::3 advertise encap-type srv6 # evpn source-address 1.1.1.1 # return
P configuration file
# sysname P # isis 1 is-level level-1 cost-style wide network-entity 10.0000.0000.0002.00 # ipv6 enable topology ipv6 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ipv6 enable ipv6 address 2001:DB8:10::2/64 isis ipv6 enable 1 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/8 undo shutdown ipv6 enable ipv6 address 2001:DB8:20::1/64 isis ipv6 enable 1 # interface LoopBack1 ipv6 enable ipv6 address 2001:DB8:2::2/128 isis ipv6 enable 1 # return
PE2 configuration file
# sysname PE2 # evpn vpn-instance evrf1 vpws route-distinguisher 200:1 segment-routing ipv6 best-effort vpn-target 1:1 export-extcommunity vpn-target 1:1 import-extcommunity # evpl instance 1 evpn binding vpn-instance evrf1 local-service-id 200 remote-service-id 100 segment-routing ipv6 locator PE2 # segment-routing ipv6 encapsulation source-address 2001:DB8:3::3 locator PE2 ipv6-prefix 2001:DB8:30:: 64 static 32 # isis 1 is-level level-1 cost-style wide network-entity 10.0000.0000.0003.00 # ipv6 enable topology ipv6 segment-routing ipv6 locator PE2 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ipv6 enable ipv6 address 2001:DB8:20::2/64 isis ipv6 enable 1 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/8.1 mode l2 encapsulation dot1q vid 1 evpl instance 1 # interface LoopBack1 ipv6 enable ip address 3.3.3.3 255.255.255.255 ipv6 address 2001:DB8:3::3/128 isis ipv6 enable 1 # bgp 100 router-id 3.3.3.3 peer 2001:DB8:1::1 as-number 100 peer 2001:DB8:1::1 connect-interface LoopBack1 # ipv4-family unicast undo synchronization # l2vpn-family evpn policy vpn-target peer 2001:DB8:1::1 enable peer 2001:DB8:1::1 advertise encap-type srv6 # evpn source-address 3.3.3.3 # return