Example for Configuring VPN FRR for EVPN L3VPNv6 over SRv6 BE
This section provides an example for configuring VPN FRR for EVPN L3VPNv6 over SRv6 BE.
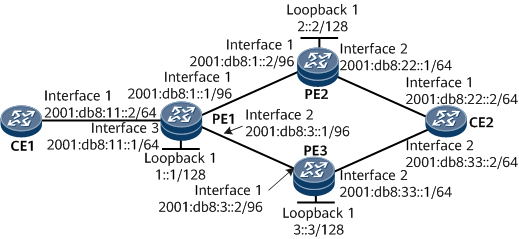
Networking Requirements
PE1, PE2, and PE3 are in the same AS and run IS-IS to implement IPv6 network connectivity.
The PEs are Level-2 devices that belong to IS-IS process 1.
It is required that a bidirectional SRv6 BE path be deployed between PE1 and PE2 as well as between PE1 and PE3 to carry EVPN L3VPNv6 services. In addition, VPN FRR needs to be configured on PE1 to improve network reliability.

Interfaces 1 through 3 in this example represent GE 0/1/0, GE 0/1/8, and GE 0/1/16, respectively.
Precautions
When configuring VPN FRR for EVPN L3VPNv6 over SRv6 BE, note the following:
In a VPN FRR scenario, after the primary path recovers, traffic switches back to this path. Because the order in which nodes undergo IGP convergence differs, packet loss may occur during the switchback. To resolve this problem, run the route-select delay delay-value command to configure a route selection delay so that traffic is switched back only after forwarding entries on the devices along the primary path are updated. The delay specified using delay-value depends on various factors, such as the number of routes on the devices. Set a proper delay as needed.
Configuration Roadmap
The configuration roadmap is as follows:
Enable IPv6 forwarding and configure an IPv6 address for each PE interface.
Enable IS-IS, configure an IS-IS level, and specify a network entity title (NET) on each PE.
Configure an IPv6 VPN instance on each PE, and connect each PE to a CE.
Establish an EBGP peer relationship between each PE and its connected CE.
Establish a BGP EVPN peer relationship between PEs.
Configure SRv6 on each PE, and enable IS-IS SRv6.
- Enable VPN FRR on PE1 and configure BFD to detect peer locator reachability to speed up VPN FRR switching.
Data Preparation
To complete the configuration, you need the following data:
IPv6 address of each PE interface
IS-IS process ID of each PE
IS-IS level of each PE
VPN instance name, RD, and RT on each PE
Procedure
- Enable IPv6 forwarding and configure an IPv6 address for each interface. The following example uses the configuration of PE1. The configurations of other devices are similar to the configuration of PE1. For configuration details, see Configuration Files in this section.
<HUAWEI> system-view [~HUAWEI] sysname PE1 [*HUAWEI] commit [~PE1] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/0 [~PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] ipv6 enable [*PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] ipv6 address 2001:db8:1::1 96 [*PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] quit [*PE1] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/8 [*PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] ipv6 enable [*PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] ipv6 address 2001:db8:3::1 96 [*PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] quit [*PE1] interface LoopBack 1 [*PE1-LoopBack1] ipv6 enable [*PE1-LoopBack1] ipv6 address 1::1 128 [*PE1-LoopBack1] quit [*PE1] commit
- Configure IS-IS.
# Configure PE1.
[~PE1] isis 1 [*PE1-isis-1] is-level level-2 [*PE1-isis-1] cost-style wide [*PE1-isis-1] network-entity 10.0000.0000.0001.00 [*PE1-isis-1] ipv6 enable topology ipv6 [*PE1-isis-1] quit [*PE1] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/0 [*PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] isis ipv6 enable 1 [*PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] quit [*PE1] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/8 [*PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] isis ipv6 enable 1 [*PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] quit [*PE1] interface loopback1 [*PE1-LoopBack1] isis ipv6 enable 1 [*PE1-LoopBack1] commit [~PE1-LoopBack1] quit
# Configure PE2.
[~PE2] isis 1 [*PE2-isis-1] is-level level-2 [*PE2-isis-1] cost-style wide [*PE2-isis-1] network-entity 10.0000.0000.0002.00 [*PE2-isis-1] ipv6 enable topology ipv6 [*PE2-isis-1] quit [*PE2] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/0 [*PE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] isis ipv6 enable 1 [*PE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] quit [*PE2] interface loopback1 [*PE2-LoopBack1] isis ipv6 enable 1 [*PE2-LoopBack1] commit [~PE2-LoopBack1] quit
# Configure PE3.
[~PE3] isis 1 [*PE3-isis-1] is-level level-2 [*PE3-isis-1] cost-style wide [*PE3-isis-1] network-entity 10.0000.0000.0004.00 [*PE3-isis-1] ipv6 enable topology ipv6 [*PE3-isis-1] quit [*PE3] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/0 [*PE3-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] isis ipv6 enable 1 [*PE3-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] quit [*PE3] interface loopback1 [*PE3-LoopBack1] isis ipv6 enable 1 [*PE3-LoopBack1] commit [~PE3-LoopBack1] quit
After the configuration is complete, perform the following operations to check whether IS-IS is successfully configured:
# Display IS-IS neighbor information. The following example uses the command output on PE1.
[~PE1] display isis peer Peer information for ISIS(1) System Id Interface Circuit Id State HoldTime Type PRI -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 0000.0000.0004* GE0/1/8 0000.0000.0004.02 Up 7s L2 64 0000.0000.0002* GE0/1/0 0000.0000.0002.02 Up 9s L2 64 Total Peer(s): 2
# Display IS-IS routing table information. The following example uses the command output on PE1.
[~PE1] display isis route Route information for ISIS(1) ----------------------------- ISIS(1) Level-2 Forwarding Table -------------------------------- IPV6 Dest. ExitInterface NextHop Cost Flags -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 1::/128 Loop1 Direct 0 D/-/L/- 2::/128 GE0/1/0 FE80::3A92:6CFF:FE31:307 10 A/-/-/- 3::/128 GE0/1/8 FE80::3A92:6CFF:FE41:305 10 A/-/-/- 2001:DB8:1::/96 GE0/1/0 Direct 10 D/-/L/- 2001:DB8:3::/96 GE0/1/8 Direct 10 D/-/L/- Flags: D-Direct, A-Added to URT, L-Advertised in LSPs, S-IGP Shortcut, U-Up/Down Bit Set, LP-Local Prefix-Sid Protect Type: L-Link Protect, N-Node Protect
- Configure an IPv6 L3VPN instance on each PE and bind the IPv6 L3VPN instance to an access-side interface.
# Configure PE1.
[~PE1] ip vpn-instance vpna [*PE1-vpn-instance-vpna] ipv6-family [*PE1-vpn-instance-vpna-af-ipv6] route-distinguisher 100:1 [*PE1-vpn-instance-vpna-af-ipv6] vpn-target 111:1 evpn [*PE1-vpn-instance-vpna-af-ipv6] quit [*PE1-vpn-instance-vpna] quit [*PE1] interface gigabitethernet0/1/16 [*PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/16] ip binding vpn-instance vpna [*PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/16] ipv6 enable [*PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/16] ipv6 address 2001:DB8:11::1 64 [*PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/16] quit [*PE1] bgp 100 [*PE1-bgp] ipv6-family vpn-instance vpna [*PE1-bgp-6-vpna] import-route direct [*PE1-bgp-6-vpna] advertise l2vpn evpn [*PE1-bgp-6-vpna] quit [*PE1-bgp] quit [*PE1] commit
# Configure PE2.
[~PE2] ip vpn-instance vpna [*PE2-vpn-instance-vpna] ipv6-family [*PE2-vpn-instance-vpna-af-ipv6] route-distinguisher 200:1 [*PE2-vpn-instance-vpna-af-ipv6] vpn-target 111:1 evpn [*PE2-vpn-instance-vpna-af-ipv6] quit [*PE2-vpn-instance-vpna] quit [*PE2] interface gigabitethernet0/1/8 [*PE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] ip binding vpn-instance vpna [*PE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] ipv6 enable [*PE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] ipv6 address 2001:DB8:22::1 64 [*PE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] quit [*PE2] bgp 100 [*PE2-bgp] ipv6-family vpn-instance vpna [*PE2-bgp-6-vpna] import-route direct [*PE2-bgp-6-vpna] advertise l2vpn evpn [*PE2-bgp-6-vpna] quit [*PE2-bgp] quit [*PE2] commit
# Configure PE3.
[~PE3] ip vpn-instance vpna [*PE3-vpn-instance-vpna] ipv6-family [*PE3-vpn-instance-vpna-af-ipv6] route-distinguisher 300:1 [*PE3-vpn-instance-vpna-af-ipv6] vpn-target 111:1 evpn [*PE3-vpn-instance-vpna-af-ipv6] quit [*PE3-vpn-instance-vpna] quit [*PE3] interface gigabitethernet0/1/8 [*PE3-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] ip binding vpn-instance vpna [*PE3-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] ipv6 enable [*PE3-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] ipv6 address 2001:DB8:33::1 64 [*PE3-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] quit [*PE3] bgp 100 [*PE3-bgp] ipv6-family vpn-instance vpna [*PE3-bgp-6-vpna] import-route direct [*PE3-bgp-6-vpna] advertise l2vpn evpn [*PE3-bgp-6-vpna] quit [*PE3-bgp] quit [*PE3] commit
- Establish an EBGP peer relationship between each PE and its connected CE.
# Configure CE1.
[~CE1] interface LoopBack1 [*CE1-LoopBack1] ipv6 enable [*CE1-LoopBack1] ipv6 address 11::11 128 [*CE1-LoopBack1] quit [*CE1] bgp 65410 [*CE1-bgp] router-id 10.11.1.1 [*CE1-bgp] peer 2001:DB8:11::1 as-number 100 [*CE1-bgp] ipv6-family unicast [*CE1-bgp-af-ipv6] import-route direct [*CE1-bgp-af-ipv6] peer 2001:DB8:11::1 enable [*CE1-bgp-af-ipv6] commit [~CE1-bgp-af-ipv6] quit [~CE1-bgp] quit
# Configure PE1.
[~PE1] bgp 100 [~PE1-bgp] router-id 1.1.1.1 [*PE1-bgp] ipv6-family vpn-instance vpna [*PE1-bgp-6-vpna] peer 2001:DB8:11::2 as-number 65410 [*PE1-bgp-6-vpna] import-route direct [*PE1-bgp-6-vpna] commit [~PE1-bgp-6-vpna] quit [~PE1-bgp] quit
# Configure CE2.
[~CE2] interface LoopBack1 [*CE2-LoopBack1] ipv6 enable [*CE2-LoopBack1] ipv6 address 22::22 128 [*CE2-LoopBack1] quit [*CE2] bgp 65420 [*CE2-bgp] router-id 10.12.1.1 [*CE2-bgp] peer 2001:DB8:22::1 as-number 100 [*CE2-bgp] peer 2001:DB8:33::1 as-number 100 [*CE2-bgp] ipv6-family unicast [*CE2-bgp-af-ipv6] import-route direct [*CE2-bgp-af-ipv6] peer 2001:DB8:22::1 enable [*CE2-bgp-af-ipv6] peer 2001:DB8:33::1 enable [*CE2-bgp-af-ipv6] commit [~CE2-bgp-af-ipv6] quit [~CE2-bgp] quit
# Configure PE2.
[~PE2] bgp 100 [~PE2-bgp] router-id 2.2.2.2 [*PE2-bgp] ipv6-family vpn-instance vpna [*PE2-bgp-6-vpna] peer 2001:DB8:22::2 as-number 65420 [*PE2-bgp-6-vpna] import-route direct [*PE2-bgp-6-vpna] commit [~PE2-bgp-6-vpna] quit [~PE2-bgp] quit
# Configure PE3.
[~PE3] bgp 100 [~PE3-bgp] router-id 3.3.3.3 [*PE3-bgp] ipv6-family vpn-instance vpna [*PE3-bgp-6-vpna] peer 2001:DB8:33::2 as-number 65420 [*PE3-bgp-6-vpna] import-route direct [*PE3-bgp-6-vpna] commit [~PE3-bgp-6-vpna] quit [~PE3-bgp] quit
After the configuration is complete, run the display bgp vpnv6 vpn-instance peer command on the PEs and check whether BGP peer relationships have been established between the PEs and CEs. If the Established state is displayed in the command output, the BGP peer relationships have been established successfully.
The following example uses the command output on PE1 to show that a BGP peer relationship has been established between PE1 and CE1.
[~PE1] display bgp vpnv6 vpn-instance vpna peer BGP local router ID : 1.1.1.1 Local AS number : 100 Total number of peers : 1 Peers in established state : 1 VPN-Instance vpna, Router ID 1.1.1.1: Peer V AS MsgRcvd MsgSent OutQ Up/Down State PrefRcv 2001:DB8:11::2 4 65410 98 103 0 01:22:02 Established 2 - Establish a BGP EVPN peer relationship between PEs.
# Configure PE1.
[~PE1] bgp 100 [~PE1-bgp] peer 2::2 as-number 100 [*PE1-bgp] peer 2::2 connect-interface loopback 1 [*PE1-bgp] peer 3::3 as-number 100 [*PE1-bgp] peer 3::3 connect-interface loopback 1 [*PE1-bgp] l2vpn-family evpn [*PE1-bgp-af-evpn] peer 2::2 enable [*PE1-bgp-af-evpn] peer 3::3 enable [*PE1-bgp-af-evpn] quit [*PE1-bgp] quit [*PE1] commit
# Configure PE2.
[~PE2] bgp 100 [~PE2-bgp] peer 1::1 as-number 100 [*PE2-bgp] peer 1::1 connect-interface loopback 1 [*PE2-bgp] l2vpn-family evpn [*PE2-bgp-af-evpn] peer 1::1 enable [*PE2-bgp-af-evpn] quit [*PE2-bgp] quit [*PE2] commit
# Configure PE3.
[~PE3] bgp 100 [~PE3-bgp] peer 1::1 as-number 100 [*PE3-bgp] peer 1::1 connect-interface loopback 1 [*PE3-bgp] l2vpn-family evpn [*PE3-bgp-af-evpn] peer 1::1 enable [*PE3-bgp-af-evpn] quit [*PE3-bgp] quit [*PE3] commit
After the configuration is complete, run the display bgp evpn peer command on the PEs and check whether BGP EVPN peer relationships have been established between the PEs. If the Established state is displayed in the command output, the BGP EVPN peer relationships have been established successfully. The following example uses the command output on PE1.
[~PE1] display bgp evpn peer BGP local router ID : 1.1.1.1 Local AS number : 100 Total number of peers : 2 Peers in established state : 2 Peer V AS MsgRcvd MsgSent OutQ Up/Down State PrefRcv 2::2 4 100 23 22 0 00:15:33 Established 3 3::3 4 100 23 23 0 00:15:35 Established 3
- Establish an SRv6 BE path between PEs.
# Configure PE1.
[~PE1] segment-routing ipv6 [*PE1-segment-routing-ipv6] encapsulation source-address 1::1 [*PE1-segment-routing-ipv6] locator as1 ipv6-prefix 10:: 64 static 32 [*PE1-segment-routing-ipv6-locator] quit [*PE1-segment-routing-ipv6] quit [*PE1] isis 1 [*PE1-isis-1] segment-routing ipv6 locator as1 [*PE1-isis-1] quit [*PE1] bgp 100 [*PE1-bgp] l2vpn-family evpn [*PE1-bgp-af-evpn] peer 2::2 advertise encap-type srv6 [*PE1-bgp-af-evpn] peer 3::3 advertise encap-type srv6 [*PE1-bgp-af-evpn] quit [*PE1-bgp] ipv6-family vpn-instance vpna [*PE1-bgp-6-vpna] segment-routing ipv6 locator as1 evpn [*PE1-bgp-6-vpna] segment-routing ipv6 best-effort evpn [*PE1-bgp-6-vpna] quit [*PE1-bgp] quit [*PE1] commit
# Configure PE2.
[~PE2] segment-routing ipv6 [*PE2-segment-routing-ipv6] encapsulation source-address 2::2 [*PE2-segment-routing-ipv6] locator as1 ipv6-prefix 20:: 64 static 32 [*PE2-segment-routing-ipv6-locator] quit [*PE2-segment-routing-ipv6] quit [*PE2] isis 1 [*PE2-isis-1] segment-routing ipv6 locator as1 [*PE2-isis-1] quit [*PE2] bgp 100 [*PE2-bgp] l2vpn-family evpn [*PE2-bgp-af-evpn] peer 1::1 advertise encap-type srv6 [*PE2-bgp-af-evpn] quit [*PE2-bgp] ipv6-family vpn-instance vpna [*PE2-bgp-6-vpna] segment-routing ipv6 locator as1 evpn [*PE2-bgp-6-vpna] segment-routing ipv6 best-effort evpn [*PE2-bgp-6-vpna] quit [*PE2-bgp] quit [*PE2] commit
# Configure PE3.
[~PE3] segment-routing ipv6 [*PE3-segment-routing-ipv6] encapsulation source-address 3::3 [*PE3-segment-routing-ipv6] locator as1 ipv6-prefix 30:: 64 static 32 [*PE3-segment-routing-ipv6-locator] quit [*PE3-segment-routing-ipv6] quit [*PE3] isis 1 [*PE3-isis-1] segment-routing ipv6 locator as1 [*PE3-isis-1] quit [*PE3] bgp 100 [*PE3-bgp] l2vpn-family evpn [*PE3-bgp-af-evpn] peer 1::1 advertise encap-type srv6 [*PE3-bgp-af-evpn] quit [*PE3-bgp] ipv6-family vpn-instance vpna [*PE3-bgp-6-vpna] segment-routing ipv6 locator as1 evpn [*PE3-bgp-6-vpna] segment-routing ipv6 best-effort evpn [*PE3-bgp-6-vpna] quit [*PE3-bgp] quit [*PE3] commit
- Configure VPN FRR.
Configure VPN FRR and use BFD to detect locator route reachability. If the locator route is unreachable, VPN FRR is performed, triggering traffic switching.
# Configure PE1.
[~PE1] ip vpn-instance vpna [~PE1-vpn-instance-vpna] ipv6-family [~PE1-vpn-instance-vpna-af-ipv6] vpn frr [*PE1-vpn-instance-vpna-af-ipv6] commit [~PE1-vpn-instance-vpna-af-ipv6] quit [~PE1-vpn-instance-vpna] quit [~PE1] bgp 100 [~PE1-bgp] ipv6-family vpn-instance vpna [~PE1-bgp-6-vpna] route-select delay 300 [*PE1-bgp-6-vpna] commit [~PE1-bgp-6-vpna] quit [~PE1-bgp] quit [~PE1] bfd [*PE1-bfd] quit [*PE1] bfd pe1tope2 bind peer-ipv6 20:: [*PE1-bfd-session-pe1tope2] discriminator local 100 [*PE1-bfd-session-pe1tope2] discriminator remote 200 [*PE1-bfd-session-pe1tope2] commit [~PE1-bfd-session-pe1tope2] quit
# Configure PE2.
[~PE2] bfd [*PE2-bfd] quit [*PE2] bfd pe2tope1 bind peer-ipv6 10:: [*PE2-bfd-session-pe2tope1] discriminator local 200 [*PE2-bfd-session-pe2tope1] discriminator remote 100 [*PE2-bfd-session-pe2tope1] commit [~PE2-bfd-session-pe2tope1] quit
- Verify the configuration.
Run the display ipv6 routing-table vpn-instance vpna ipv6-address verbose command to check VPN routing information. The following example uses the command output on PE1.
[~PE1] display ipv6 routing-table vpn-instance vpna 22::22 128 verbose Route Flags: R - relay, D - download to fib, T - to vpn-instance, B - black hole route ------------------------------------------------------------------------------ Routing Table : vpna Summary Count : 1 Destination : 22::22 PrefixLength : 128 NextHop : 20::1:0:3C Preference : 255 Neighbour : 2::2 ProcessID : 0 Label : NULL Protocol : IBGP State : Active Adv Relied Cost : 0 Entry ID : 0 EntryFlags : 0x00000000 Reference Cnt: 0 Tag : 0 Priority : low Age : 92sec IndirectID : 0x100016E Instance : RelayNextHop : 20::1:0:3C TunnelID : 0x0 Interface : SRv6 BE Flags : RD BkNextHop : 30::1:0:21 BkInterface : SRv6 BE BkLabel : NULL BkTunnelID : 0x0 BkPETunnelID : 0x0 BkIndirectID : 0x100016A
The preceding command output shows that the VPN route 22::22/128 has a backup outbound interface and a VPN FRR routing entry has been generated.
Check that CEs belonging to the same VPN instance can ping each other. The following example uses the command output on CE1.
[~CE1] ping ipv6 -a 11::11 22::22 PING 22::22 : 56 data bytes, press CTRL_C to break Reply from 22::22 bytes=56 Sequence=1 hop limit=62 time=57 ms Reply from 22::22 bytes=56 Sequence=2 hop limit=62 time=5 ms Reply from 22::22 bytes=56 Sequence=3 hop limit=62 time=5 ms Reply from 22::22 bytes=56 Sequence=4 hop limit=62 time=5 ms Reply from 22::22 bytes=56 Sequence=5 hop limit=62 time=4 ms --- 22::22 ping statistics--- 5 packet(s) transmitted 5 packet(s) received 0.00% packet loss round-trip min/avg/max=4/15/57 ms
Configuration Files
PE1 configuration file
# sysname PE1 # ip vpn-instance vpna ipv6-family route-distinguisher 100:1 vpn frr vpn-target 111:1 export-extcommunity evpn vpn-target 111:1 import-extcommunity evpn # bfd # segment-routing ipv6 encapsulation source-address 1::1 locator as1 ipv6-prefix 10:: 64 static 32 # isis 1 is-level level-2 cost-style wide network-entity 10.0000.0000.0001.00 # ipv6 enable topology ipv6 segment-routing ipv6 locator as1 # # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ipv6 enable ipv6 address 2001:DB8:1::1/96 isis ipv6 enable 1 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/8 undo shutdown ipv6 enable ipv6 address 2001:DB8:3::1/96 isis ipv6 enable 1 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/16 undo shutdown ip binding vpn-instance vpna ipv6 enable ipv6 address 2001:DB8:11::1/64 # interface LoopBack1 ipv6 enable ipv6 address 1::1/128 isis ipv6 enable 1 # bfd pe1tope2 bind peer-ipv6 20:: discriminator local 100 discriminator remote 200 # bgp 100 router-id 1.1.1.1 peer 2::2 as-number 100 peer 2::2 connect-interface LoopBack1 peer 3::3 as-number 100 peer 3::3 connect-interface LoopBack1 # ipv4-family unicast undo synchronization # ipv6-family vpn-instance vpna import-route direct route-select delay 300 advertise l2vpn evpn segment-routing ipv6 locator as1 evpn segment-routing ipv6 best-effort evpn peer 2001:DB8:11::2 as-number 65410 # l2vpn-family evpn policy vpn-target peer 2::2 enable peer 2::2 advertise encap-type srv6 peer 3::3 enable peer 3::3 advertise encap-type srv6 # return
- PE2 configuration file
# sysname PE2 # ip vpn-instance vpna ipv6-family route-distinguisher 200:1 vpn-target 111:1 export-extcommunity evpn vpn-target 111:1 import-extcommunity evpn # bfd # segment-routing ipv6 encapsulation source-address 2::2 locator as1 ipv6-prefix 20:: 64 static 32 # isis 1 is-level level-2 cost-style wide network-entity 10.0000.0000.0002.00 # ipv6 enable topology ipv6 segment-routing ipv6 locator as1 # # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ipv6 enable ipv6 address 2001:DB8:1::2/96 isis ipv6 enable 1 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/8 undo shutdown ip binding vpn-instance vpna ipv6 enable ipv6 address 2001:DB8:22::1/64 # interface LoopBack1 ipv6 enable ipv6 address 2::2/128 isis ipv6 enable 1 # bfd pe2tope1 bind peer-ipv6 10:: discriminator local 200 discriminator remote 100 # bgp 100 router-id 2.2.2.2 peer 1::1 as-number 100 peer 1::1 connect-interface LoopBack1 # ipv4-family unicast undo synchronization # ipv6-family unicast undo synchronization # ipv6-family vpn-instance vpna import-route direct advertise l2vpn evpn segment-routing ipv6 locator as1 evpn segment-routing ipv6 best-effort evpn peer 2001:DB8:22::2 as-number 65420 # l2vpn-family evpn policy vpn-target peer 1::1 enable peer 1::1 advertise encap-type srv6 # return
PE3 configuration file
# sysname PE3 # ip vpn-instance vpna ipv6-family route-distinguisher 300:1 vpn-target 111:1 export-extcommunity evpn vpn-target 111:1 import-extcommunity evpn # segment-routing ipv6 encapsulation source-address 3::3 locator as1 ipv6-prefix 30:: 64 static 32 # isis 1 is-level level-2 cost-style wide network-entity 10.0000.0000.0004.00 # ipv6 enable topology ipv6 segment-routing ipv6 locator as1 # # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ipv6 enable ipv6 address 2001:DB8:3::2/96 isis ipv6 enable 1 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/8 undo shutdown ip binding vpn-instance vpna ipv6 enable ipv6 address 2001:DB8:33::1/64 # interface LoopBack1 ipv6 enable ipv6 address 3::3/128 isis ipv6 enable 1 # bgp 100 router-id 3.3.3.3 peer 1::1 as-number 100 peer 1::1 connect-interface LoopBack1 # ipv4-family unicast undo synchronization # ipv6-family unicast undo synchronization # ipv6-family vpn-instance vpna import-route direct advertise l2vpn evpn segment-routing ipv6 locator as1 evpn segment-routing ipv6 best-effort evpn peer 2001:DB8:33::2 as-number 65420 # l2vpn-family evpn policy vpn-target peer 1::1 enable peer 1::1 advertise encap-type srv6 # return
CE1 configuration file
# sysname CE1 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ipv6 enable ipv6 address 2001:DB8:11::2/64 # interface LoopBack1 ipv6 enable ipv6 address 11::11/128 # bgp 65410 router-id 10.11.1.1 peer 2001:DB8:11::1 as-number 100 # ipv4-family unicast undo synchronization # ipv6-family unicast undo synchronization import-route direct peer 2001:DB8:11::1 enable # returnCE2 configuration file
# sysname CE2 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ipv6 enable ipv6 address 2001:DB8:22::2/64 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/8 undo shutdown ipv6 enable ipv6 address 2001:DB8:33::2/64 # interface LoopBack1 ipv6 enable ipv6 address 22::22/128 # bgp 65420 router-id 10.12.1.1 peer 2001:DB8:22::1 as-number 100 peer 2001:DB8:33::1 as-number 100 # ipv4-family unicast undo synchronization # ipv6-family unicast undo synchronization import-route direct peer 2001:DB8:22::1 enable peer 2001:DB8:33::1 enable # return