Example for Configuring Static BFD for IPv6 Static Routes
To improve IPv6 network reliability, you can configure static BFD for IPv6 static routes to fast detect link failures and speed up route convergence.
Networking Requirements
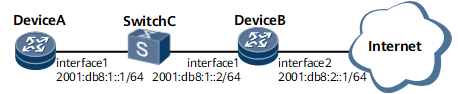
On the network shown in Figure 1, Device A is connected to Device B through Switch C. A static default route is configured on Device A so that Device A can communicate with external devices. In addition, a BFD session is configured between Device A and Device B to rapidly detect link faults if any.
Configuration Roadmap
The configuration roadmap is as follows:
Configure a BFD session on Device A and Device B to detect the link between the two devices.
Configure a default static route from Device A to the external network and bind the default static route to a BFD session.
Data Preparation
To complete the configuration, you need the following data:
Peer IPv6 address to be detected by BFD
Local discriminator and remote discriminator of a BFD session
Default values of the local detection multiplier and of the minimum intervals at which BFD Control packets are sent and received
Procedure
- Configure an IPv6 address for each interface.
For configuration details, see Configuration Files in this section.
- Configure a BFD session between Device A and Device B.
# On Device A, configure a BFD session between Device A and Device B.
<DeviceA> system-view [~DeviceA] bfd [*DeviceA-bfd] quit [*DeviceA] bfd aa bind peer-ipv6 2001:db8:1::2 [*DeviceA-bfd-session-aa] discriminator local 10 [*DeviceA-bfd-session-aa] discriminator remote 20 [*DeviceA-bfd-session-aa] commit [~DeviceA-bfd-session-aa] quit
# On Device B, configure a BFD session between Device A and Device B.
<DeviceB> system-view [~DeviceB] bfd [*DeviceB-bfd] quit [*DeviceB] bfd bb bind peer-ipv6 2001:db8:1::1 [*DeviceB-bfd-session-bb] discriminator local 20 [*DeviceB-bfd-session-bb] discriminator remote 10 [*DeviceB-bfd-session-bb] commit [~DeviceB-bfd-session-bb] quit
- Configure a default static route and bind it to a BFD session.
# On Device A, configure a default static route to the external network and bind it to BFD session named aa.
[~DeviceA] ipv6 route-static 0::0 0 2001:db8:1::2 track bfd-session aa
- Verify the configuration.
# Run the display bfd session all command on Device A and Device B. The command output shows that a BFD session has been established and is Up. Then, run the display current-configuration | include bfd command in the system view. The command output shows that the default static route has been bound to the BFD session.
Use the command output on Device A as an example.
[~DeviceA] display bfd session all (w): State in WTR (*): State is invalid -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Local Remote PeerIpAddr State Type InterfaceName -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 10 20 2001:db8:1::2 Up S_IP_PEER - -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Total UP/DOWN Session Number : 1/0 [~DeviceA] display current-configuration | include bfd bfd bfd aa bind peer-ipv6 2001:db8:1::2 ipv6 route-static :: 0 2001:db8:1::2 track bfd-session aa
# Check the IP routing table of Device A. The command output shows that the static route exists in the routing table.
[~DeviceA] display ipv6 routing-table Routing Table : _public_ Destinations : 5 Routes : 5 Destination : :: PrefixLength : 0 NextHop : 2001:db8:1::2 Preference : 60 Cost : 0 Protocol : Static RelayNextHop : :: TunnelID : 0x0 Interface : GigabitEthernet0/1/0 Flags : RD Destination : ::1 PrefixLength : 128 NextHop : ::1 Preference : 0 Cost : 0 Protocol : Direct RelayNextHop : :: TunnelID : 0x0 Interface : InLoopBack0 Flags : D Destination : 2001:db8:1:: PrefixLength : 64 NextHop : 2001:db8:1::1 Preference : 0 Cost : 0 Protocol : Direct RelayNextHop : :: TunnelID : 0x0 Interface : GigabitEthernet0/1/0 Flags : D Destination : 2001:db8:1::1 PrefixLength : 128 NextHop : ::1 Preference : 0 Cost : 0 Protocol : Direct RelayNextHop : :: TunnelID : 0x0 Interface : GigabitEthernet0/1/0 Flags : D Destination : FE80:: PrefixLength : 10 NextHop : :: Preference : 0 Cost : 0 Protocol : Direct RelayNextHop : :: TunnelID : 0x0 Interface : NULL0 Flags : D
# Run the shutdown command on GE 0/1/0 of Device B to simulate a link fault.
[~DeviceB] interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 [~DeviceB-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] shutdown
# Check the IP routing table of Device A. The command output shows that default route 0::0/0 does not exist. This is because the default static route has been bound to a BFD session. When BFD detects a link fault, BFD rapidly notifies that the bound static route becomes unavailable.
[~DeviceA] display ipv6 routing-table Routing Table : _public_ Destinations : 1 Routes : 1 Destination : ::1 PrefixLength : 128 NextHop : ::1 Preference : 0 Cost : 0 Protocol : Direct RelayNextHop : :: TunnelID : 0x0 Interface : InLoopBack0 Flags : D
Configuration Files
Device A configuration file
# sysname DeviceA # ipv6 # bfd # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ipv6 enable ipv6 address 2001:db8:1::1/64 # ipv6 route-static :: 0 2001:db8:1::2 track bfd-session aa # bfd aa bind peer-ipv6 2001:db8:1::2 discriminator local 10 discriminator remote 20 # return
Device B configuration file
# sysname DeviceB # ipv6 # bfd # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ipv6 enable ipv6 address 2001:db8:1::2/64 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/8 undo shutdown ipv6 enable ipv6 address 2001:db8:2::1/64 # bfd bb bind peer-ipv6 2001:db8:1::1 discriminator local 20 discriminator remote 10 # return