Example for Configuring IPv6 Floating Static Routes
IPv6 Floating static routes can be used for the static route backup.
Networking Requirements
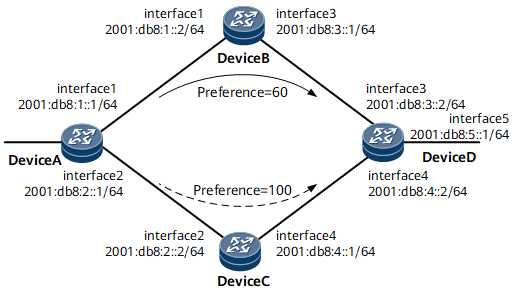
Figure Networking for configuring IPv6 floating static routes shows the IPv6 addresses and masks of each router interface and a host. Two IPv6 static routes to 2001:db8:5::/64 are configured on Device A. The primary static route passes through Device B, and the floating static route passes through Device C.
Precautions
When configuring an IPv6 floating static route, a next-hop address of this route must be specified if the outbound interface is of the broadcast type.
Configuration Roadmap
The configuration roadmap is as follows:
Configure an IPv6 address for each interface of each router.
On Devices B and C, configure IPv6 static routes to 2001:db8:5::/64.
On Device A, configure IPv6 static routes to 2001:db8:3::/64 and 2001:db8:4::/64.
On Device A, configure two IPv6 static routes to 2001:db8:5::/64 with different priorities.
On Device D, configure IPv6 static routes to 2001:db8:1::/64 and 2001:db8:2::/64 so that routers can communicate.
Data Preparation
To complete the configuration, you need the following data:
On Device A, priority values of two static routes (60 for the one with 2001:db8:1::2 as the next hop address and 100 for the one with 2001:db8:2::2 as the next-hop address)
Procedure
- Configure an IPv6 address for each interface. For configuration details, see Configuration Files in this section.
- Configure IPv6 static routes.
# Configure IPv6 static routes on Device B.
[~DeviceB] ipv6 route-static 2001:db8:5:: 64 2001:db8:3::2 [*DeviceB] commit
# Configure IPv6 static routes on Device C.
[~DeviceC] ipv6 route-static 2001:db8:5:: 64 2001:db8:4::2 [*DeviceC] commit
# Configure IPv6 static routes on Device A.
[~DeviceA] ipv6 route-static 2001:db8:3:: 64 2001:db8:1::2 [*DeviceA] ipv6 route-static 2001:db8:4:: 64 2001:db8:2::2 [*DeviceA] ipv6 route-static 2001:db8:5:: 64 2001:db8:1::2 [*DeviceA] ipv6 route-static 2001:db8:5:: 64 2001:db8:2::2 preference 100 [*DeviceA] commit
# Configure IPv6 static routes on Device D.
[~DeviceD] ipv6 route-static 2001:db8:1:: 64 2001:db8:3::1 [*DeviceD] ipv6 route-static 2001:db8:2:: 64 2001:db8:4::1 [*DeviceD] commit
- Verify the configuration.
# View information about static routes in the IP routing table of Device A.
[~DeviceA] display ipv6 routing-table protocol static _public_ Routing Table : Static Summary Count : 3 Static routing table status : <Active> Summary Count : 3 Destination : 2001:db8:3:: PrefixLength : 64 NextHop : 2001:db8:1::2 Preference : 60 Cost : 0 Protocol : Static RelayNextHop : 2001:db8:1::2 TunnelID : 0x0 Interface : GigabitEthernet0/1/1 Flags : RD Destination : 2001:db8:4:: PrefixLength : 64 NextHop : 2001:db8:2::2 Preference : 60 Cost : 0 Protocol : Static RelayNextHop : 2001:db8:2::2 TunnelID : 0x0 Interface : GigabitEthernet0/1/2 Flags : RD Destination : 2001:db8:5:: PrefixLength : 64 NextHop : 2001:db8:1::2 Preference : 60 Cost : 0 Protocol : Static RelayNextHop : 2001:db8:1::2 TunnelID : 0x0 Interface : GigabitEthernet0/1/1 Flags : RD Static routing table status : <Inactive> Summary Count : 0
# Use the tracert ipv6 command to check the connectivity on Device A.
<DeviceA> tracert ipv6 2001:db8:5::1 traceroute to 2001:db8:5::1 30 hops max,60 bytes packet 1 2001:db8:1::2 195 ms 5 ms 2 ms 2 * 2001:db8:3::2 45 ms !N 5 ms !N# Run the shutdown command on GE 0/1/1 of Device A to simulate a link fault.
[~DeviceA] interface GigabitEthernet 0/1/1 [~DeviceA-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] shutdown [*DeviceA-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] commit [~DeviceA-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] quit [~DeviceA] quit
# View information about static routes in the IP routing table of Device A. The route to 2001:db8:5::/64 switches to the floating static route with next hop 2001:db8:2::2.
<DeviceA> display ipv6 routing-table protocol static _public_ Routing Table : Static Summary Count : 2 Static routing table status : <Active> Summary Count : 2 Destination : 2001:db8:4:: PrefixLength : 64 NextHop : 2001:db8:2::2 Preference : 60 Cost : 0 Protocol : Static RelayNextHop : 2001:db8:2::2 TunnelID : 0x0 Interface : GigabitEthernet0/1/2 Flags : RD Destination : 2001:db8:5:: PrefixLength : 64 NextHop : 2001:db8:2::2 Preference : 100 Cost : 0 Protocol : Static RelayNextHop : 2001:db8:2::2 TunnelID : 0x0 Interface : GigabitEthernet0/1/2 Flags : RD Static routing table status : <Inactive> Summary Count : 0
# Use the tracert ipv6 command to check the connectivity on Device A.
<DeviceA> tracert ipv6 2001:db8:5::1 traceroute to 2001:db8:5::1 30 hops max,60 bytes packet 1 2001:db8:2::2 87 ms 2 ms 4 ms 2 * 2001:db8:4::2 6 ms !N 2 ms !N
Configuration Files
Device A configuration file
# sysname DeviceA # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/1 undo shutdown ipv6 enable ipv6 address 2001:db8:1::1/64 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/2 undo shutdown ipv6 enable ipv6 address 2001:db8:2::1/64 # ipv6 route-static 2001:db8:3:: 64 2001:db8:1::2 ipv6 route-static 2001:db8:4:: 64 2001:db8:2::2 ipv6 route-static 2001:db8:5:: 64 2001:db8:1::2 ipv6 route-static 2001:db8:5:: 64 2001:db8:2::2 preference 100 # return
Device B configuration file
# sysname DeviceB # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/1 undo shutdown ipv6 enable ipv6 address 2001:db8:1::2/64 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/3 undo shutdown ipv6 enable ipv6 address 2001:db8:3::1/64 # ipv6 route-static 2001:db8:5:: 64 2001:db8:3::2 # return
Device C configuration file
# sysname DeviceC # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/2 undo shutdown ipv6 enable ipv6 address 2001:db8:2::2/64 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/11 undo shutdown ipv6 enable ipv6 address 2001:db8:4::1/64 # ipv6 route-static 2001:db8:5:: 64 2001:db8:4::2 # return
Device D configuration file
# sysname DeviceD # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/3 undo shutdown ipv6 enable ipv6 address 2001:db8:3::2/64 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/11 undo shutdown ipv6 enable ipv6 address 2001:db8:4::2/64 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/19 undo shutdown ipv6 enable ipv6 address 2001:db8:5::1/64 # ipv6 route-static 2001:db8:1:: 64 2001:db8:3::1 ipv6 route-static 2001:db8:2:: 64 2001:db8:4::1 # return