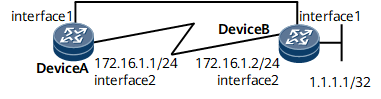
Example for Associating EFM with IPv4 Static Routes
After EFM is associated with IPv4 static routes, the system responds to the interface Up or Down event that is triggered by the change of the EFM OAM extension status and determines whether to activate static routes. This mechanism controls route advertisement and ensures that the traffic from the remote end can be correctly forwarded.
Networking Requirements
In Figure 1, Device A and Device B are connected. EFM OAM is enabled on Device A and Device B. A static route destined for 1.1.1.1/32 is configured on Device A, and this static route is associated with EFM.
Configuration Roadmap
The configuration roadmap is as follows:
Enable EFM OAM both globally and on the interfaces of Device A and Device B.
Configure a static route destined for 1.1.1.1/32 on Device A and associate EFM with this static route.
Procedure
- Configure an IP address for each interface. For configuration details, see Configuration Files in this section.
- Enable EFM OAM both globally and on the interfaces of Device A and Device B.
# Enable EFM OAM both globally and on the interface of Device A.
<DeviceA> system-view [~DeviceA] efm enable [*DeviceA] interface GigabitEthernet 0/1/0 [*DeviceA-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] undo shutdown [*DeviceA-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] efm enable [*DeviceA-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] commit [~DeviceA-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] quit [~DeviceA] quit
# Enable EFM OAM both globally and on the interface of Device B.
<DeviceB> system-view [~DeviceB] efm enable [*DeviceB] interface GigabitEthernet 0/1/0 [*DeviceB-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] undo shutdown [*DeviceB-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] efm enable [*DeviceB-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] commit [~DeviceB-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] quit [~DeviceB] quit
# Display EFM OAM session information on Device A.
<DeviceA> display efm session all Interface EFM State Loopback Timeout ---------------------------------------------------------------------- GigabitEthernet0/1/0 detect --
The preceding command output shows that the EFM OAM status is detect.
- Associating EFM with IPv4 static routes.
# Configure a static route destined for 1.1.1.1/32 on Device A and associate EFM with this static route.
<DeviceA> system-view [~DeviceA] ip route-static 1.1.1.1 255.255.255.255 GigabitEthernet0/1/1 172.16.1.2 track efm-state GigabitEthernet0/1/0 [*DeviceA] commit [~DeviceA] quit
- Verify the configuration.
# Run the display current-configuration | include efm command on Device A. The following command output shows that the static route has been associated with EFM:
<DeviceA> display current-configuration | include efm efm enable ip route-static 1.1.1.1 255.255.255.255 GigabitEthernet0/1/1 172.16.1.2 track efm-state GigabitEthernet0/1/0
# Display the IP routing table on Device A. The following command output shows that the static route destined for 1.1.1.1/32 exists in the IP routing table:
<DeviceA> display ip routing-table Route Flags: R - relay, D - download to fib, T - to vpn-instance, B - black hole route ------------------------------------------------------------------------------ Routing Table : _public_ Destinations : 8 Routes : 8 Destination/Mask Proto Pre Cost Flags NextHop Interface 1.1.1.1/32 Static 60 0 D 172.16.1.2 GigabitEthernet0/1/1 127.0.0.0/8 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 InLoopBack0 127.0.0.1/32 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 InLoopBack0 127.255.255.255/32 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 InLoopBack0 172.16.1.0/24 Direct 0 0 D 172.16.1.1 GigabitEthernet0/1/1 172.16.1.1/32 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 GigabitEthernet0/1/1 172.16.1.255/32 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 GigabitEthernet0/1/1 255.255.255.255/32 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 InLoopBack0
# Run the shutdown command on GE 0/1/0 of Device A to check whether the EFM OAM status changes.
<DeviceA> system-view [~DeviceA] interface GigabitEthernet 0/1/0 [~DeviceA-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] shutdown [*DeviceA-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] commit [~DeviceA-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] quit [~DeviceA] quit
# Run the display efm session all command on Device A. The following command output shows that the EFM OAM status changes to discovery:
<DeviceA> display efm session all Interface EFM State Loopback Timeout ---------------------------------------------------------------------- GigabitEthernet0/1/0 discovery --
# Display the IP routing table on Device A. The command output shows that the static route destined for 1.1.1.1/32 does not exist. The static route is unavailable because it has been associated with EFM and the EFM session has not been established.
<DeviceA> display ip routing-table Route Flags: R - relay, D - download to fib, T - to vpn-instance, B - black hole route ------------------------------------------------------------------------------ Routing Table : _public_ Destinations : 7 Routes : 7 Destination/Mask Proto Pre Cost Flags NextHop Interface 127.0.0.0/8 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 InLoopBack0 127.0.0.1/32 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 InLoopBack0 127.255.255.255/32 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 InLoopBack0 172.16.1.0/24 Direct 0 0 D 172.16.1.1 GigabitEthernet0/1/1 172.16.1.1/32 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 GigabitEthernet0/1/1 172.16.1.255/32 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 GigabitEthernet0/1/1 255.255.255.255/32 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 InLoopBack0
Configuration Files
Router A configuration file
# sysname DeviceA # efm enable # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown efm enable # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/1 undo shutdown ip address 172.16.1.1 255.255.255.0 # ip route-static 1.1.1.1 255.255.255.255 GigabitEthernet0/1/1 172.16.1.2 track efm-state GigabitEthernet0/1/0 # return
Router B configuration file
# sysname DeviceB # efm enable # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown efm enable # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/1 undo shutdown ip address 172.16.1.2 255.255.255.0 # interface LoopBack0 ip address 1.1.1.1 255.255.255.255 # return