Example for Configuring Association between LDP and Static Routes
On an MPLS network with primary and secondary LSPs established by LSRs using static routes, association between LDP and static routes prevents traffic from being interrupted during traffic switchover or switchback.
Networking Requirements
On an MPLS network with primary and secondary LSPs established by LSRs using static routes, if association between LDP and static routes is not enabled, traffic is interrupted for a short period of time during traffic switchover from the primary LSP to the secondary LSP when the LDP session on the primary link fails (not because of a link fault) or during traffic switchback when the primary link recovers from a fault.
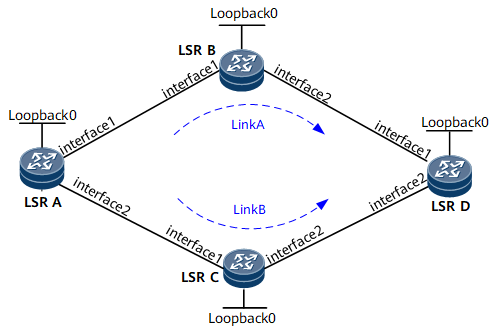
In Figure 1, LSRA has two static routes to LSRD. One of the static routes passes through LSRB, whereas the other static route passes through LSRC. LDP LSPs are established based on the static routes. Link A is the primary link, whereas Link B is the backup link. It is required that association between LDP and static routes be configured to prevent MPLS traffic from being interrupted if the LDP session on Link A or Link A recovers from a fault.

Interfaces 1 and 2 in this example represent GE 0/1/0 and GE 0/1/8, respectively.
Device Name |
Interface Name |
Interface IP Address |
Device Name |
Interface Name |
Interface IP Address |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
LSRA |
GE 0/1/0 |
10.1.1.1/30 |
LSRC |
GE 0/1/0 |
10.2.1.2/30 |
GE 0/1/8 |
10.2.1.1/30 |
GE 0/1/8 |
10.4.1.2/30 |
||
Loopback 0 |
1.1.1.1/32 |
Loopback 0 |
3.3.3.3/32 |
||
LSRB |
GE 0/1/0 |
10.1.1.2/30 |
LSRD |
GE 0/1/0 |
10.3.1.2/30 |
GE 0/1/8 |
10.3.1.1/30 |
GE 0/1/8 |
10.4.1.2/30 |
||
Loopback 0 |
2.2.2.2/32 |
Loopback 0 |
4.4.4.4/32 |
Configuration Roadmap
The configuration roadmap is as follows:
Configure static routes for each LSP to reach other LSRs.
Enable MPLS and MPLS LDP globally and on interfaces of LSRs.
Configure association between LDP and static routes and check configurations.
Data Preparation
To complete the configuration, you need the following data:
IP addresses of interfaces on LSRs
MPLS LSR IDs of LSRs
Hold-down timer value
Procedure
- Assign an IP address and mask to each interface.
Configure an IP address for each interface based on Figure 1. For configuration details, see "Configuration Files" in this section.
- Configure static routes for LSRs to ensure network reachability.
# Configure two static routes with different priorities from LSRA to LSRD, and two static routes with different priorities from LSRD to LSRA.
# Configure LSRA.
[~LSRA] ip route-static 2.2.2.2 32 GigabitEthernet0/1/0 10.1.1.2 [*LSRA] ip route-static 3.3.3.3 32 GigabitEthernet0/1/8 10.2.1.2 [*LSRA] ip route-static 10.3.1.1 30 GigabitEthernet0/1/0 [*LSRA] ip route-static 10.4.1.1 30 GigabitEthernet0/1/8 [*LSRA] ip route-static 4.4.4.4 32 GigabitEthernet0/1/0 10.1.1.2 preference 40 [*LSRA] ip route-static 4.4.4.4 32 GigabitEthernet0/1/8 10.2.1.2 preference 60 [*LSRA] commit
# Configure LSRB.
[~LSRB] ip route-static 1.1.1.1 32 GigabitEthernet0/1/0 10.1.1.1 [*LSRB] ip route-static 4.4.4.4 32 GigabitEthernet0/1/8 10.3.1.2 [*LSRB] commit
# Configure LSRC.
[~LSRC] ip route-static 1.1.1.1 32 GigabitEthernet0/1/0 10.2.1.1 [*LSRC] ip route-static 4.4.4.4 32 GigabitEthernet0/1/8 10.4.1.2 [*LSRC] commit
# Configure LSRD.
[~LSRD] ip route-static 2.2.2.2 32 GigabitEthernet0/1/0 10.3.1.1 [*LSRD] ip route-static 3.3.3.3 32 GigabitEthernet0/1/8 10.4.1.1 [*LSRD] ip route-static 10.1.1.2 30 GigabitEthernet0/1/0 [*LSRD] ip route-static 10.2.1.2 30 GigabitEthernet0/1/8 [*LSRD] ip route-static 1.1.1.1 32 GigabitEthernet0/1/0 10.3.1.1 preference 40 [*LSRD] ip route-static 1.1.1.1 32 GigabitEthernet0/1/8 10.4.1.1 preference 60 [*LSRD] commit
# After completing the configurations, run the display ip routing-table protocol static command on each LSR to check the static route configurations. The following example uses the command output on LSRA.
[~LSRA] display ip routing-table protocol static Route Flags: R - relay, D - download to fib, T - to vpn-instance, B - black hole route ------------------------------------------------------------------------------ _public_ Routing Table : Static Destinations : 5 Routes : 5 Configured Routes : 5 Static routing table status : Destinations : 5 Routes : 5 Destination/Mask Proto Pre Cost Flags NextHop Interface 2.2.2.2/32 Static 60 0 D 10.1.1.1 GigabitEthernet0/1/0 3.3.3.3/32 Static 60 0 D 10.2.1.1 GigabitEthernet0/1/8 4.4.4.4/32 Static 40 0 D 10.1.1.1 GigabitEthernet0/1/0 10.3.1.0/30 Static 60 0 D 10.1.1.1 GigabitEthernet0/1/0 10.4.1.0/30 Static 60 0 D 10.2.1.1 GigabitEthernet0/1/8 Static routing table status : <Inactive> Destinations : 0 Routes : 0
- Enable MPLS LDP on each LSR to set up LDP LSPs.
# Configure LSRA.
[~LSRA] mpls lsr-id 1.1.1.1 [*LSRA] mpls [*LSRA-mpls] quit [*LSRA] mpls ldp [*LSRA-mpls-ldp] commit [~LSRA-mpls-ldp] quit [~LSRA] interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 [~LSRA-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] mpls [*LSRA-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] mpls ldp [*LSRA-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] commit [~LSRA-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] quit [~LSRA] interface GigabitEthernet0/1/8 [~LSRA-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] mpls [*LSRA-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] mpls ldp [*LSRA-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] commit [~LSRA-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] quit
Repeat this step for LSRB, LSRC, and LSRD. For configuration details, see "Configuration Files" in this section.
# Run the display mpls ldp session command on each LSR to view information about established LDP sessions (in Operational state). The following example uses the command output on LSRA.
[~LSRA] display mpls ldp session LDP Session(s) in Public Network Codes: LAM(Label Advertisement Mode), SsnAge Unit(DDDD:HH:MM) An asterisk (*) before a session means the session is being deleted. ------------------------------------------------------------------------------ PeerID Status LAM SsnRole SsnAge KASent/Rcv ------------------------------------------------------------------------------ 2.2.2.2:0 Operational DU Passive 0000:15:34 3738/3738 3.3.3.3:0 Operational DU Passive 0000:00:45 182/182 ------------------------------------------------------------------------------ TOTAL: 2 Session(s) Found. - Configure association between LDP and static routes on LSRA and LSRD.
# Configure LSRA.
[~LSRA] ip route-static 4.4.4.4 32 GigabitEthernet0/1/0 10.1.1.2 preference 40 ldp-sync [*LSRA] interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 [*LSRA-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] static-route timer ldp-sync hold-down 20 [*LSRA-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] commit [~LSRA-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] quit
# Configure LSRD.
[~LSRD] ip route-static 1.1.1.1 32 GigabitEthernet0/1/0 10.3.1.1 preference 40 ldp-sync [*LSRD] interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 [*LSRD-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] static-route timer ldp-sync hold-down 20 [*LSRD-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] commit [~LSRD-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] quit
- Verify the configuration.
# Display outbound interface status of the static route that is associated with LDP on LSRA.
[~LSRA] display static-route ldp-sync Total number of routes enable Ldp-Sync: 1 ----------------------------------------------------- Interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 Enable ldp-sync static routes number: 1 Static-route ldp-sync holddown timer: 20s Sync state: Normal Dest = 4.4.4.4, Mask = 32, NextHop = 10.1.1.2. -----------------------------------------------------
The command output shows that association between LDP and static routes has been configured (in Normal state).
If the LDP session on Link A fails, traffic is switched to Link B immediately to ensure association between LDP and static routes and prevent a traffic interruption.
If Link A fails and then recovers, the static route with the next hop of 10.1.1.2 is not preferentially selected until the hold-down timer (20 seconds) expires (by then the LDP session on Link A has been set up). Then traffic is switched back to Link A. In this way, association between LDP and static routes is ensured, and MPLS traffic is not interrupted.
Configuration Files
- LSRA configuration file
# sysname LSRA # mpls lsr-id 1.1.1.1 # mpls # mpls ldp # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ip address 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.252 static-route timer ldp-sync hold-down 20 mpls mpls ldp # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/8 undo shutdown ip address 10.2.1.1 255.255.255.252 mpls mpls ldp # interface LoopBack0 ip address 1.1.1.1 255.255.255.255 # ip route-static 2.2.2.2 255.255.255.255 GigabitEthernet0/1/0 10.1.1.2 ip route-static 3.3.3.3 255.255.255.255 GigabitEthernet0/1/8 10.2.1.2 ip route-static 4.4.4.4 255.255.255.255 GigabitEthernet0/1/0 10.1.1.2 preference 40 ldp-sync ip route-static 4.4.4.4 255.255.255.255 GigabitEthernet0/1/8 10.2.1.2 ip route-static 10.3.1.0 255.255.255.252 GigabitEthernet0/1/0 ip route-static 10.4.1.0 255.255.255.252 GigabitEthernet0/1/8 # return
- LSRB configuration file
# sysname LSRB # mpls lsr-id 2.2.2.2 # mpls # mpls ldp # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ip address 10.1.1.2 255.255.255.252 mpls mpls ldp # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/8 undo shutdown ip address 10.3.1.1 255.255.255.252 mpls mpls ldp # interface LoopBack0 ip address 2.2.2.2 255.255.255.255 # ip route-static 1.1.1.1 255.255.255.255 GigabitEthernet0/1/0 10.1.1.1 ip route-static 4.4.4.4 255.255.255.255 GigabitEthernet0/1/8 10.3.1.2 # return
- LSRC configuration file
# sysname LSRC # mpls lsr-id 3.3.3.3 # mpls # mpls ldp # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ip address 10.2.1.2 255.255.255.252 mpls mpls ldp # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/8 undo shutdown ip address 10.4.1.1 255.255.255.252 mpls mpls ldp # interface LoopBack0 ip address 3.3.3.3 255.255.255.255 # ip route-static 1.1.1.1 255.255.255.255 GigabitEthernet0/1/0 10.2.1.1 ip route-static 4.4.4.4 255.255.255.255 GigabitEthernet0/1/8 10.4.1.2 # return
- LSRD configuration file
# sysname LSRD # mpls lsr-id 4.4.4.4 # mpls # mpls ldp # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ip address 10.3.1.2 255.255.255.252 static-route timer ldp-sync hold-down 20 mpls mpls ldp # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/8 undo shutdown ip address 10.4.1.2 255.255.255.252 mpls mpls ldp # interface LoopBack0 ip address 4.4.4.4 255.255.255.255 # ip route-static 1.1.1.1 255.255.255.255 GigabitEthernet0/1/0 10.3.1.1 preference 40 ldp-sync ip route-static 1.1.1.1 255.255.255.255 GigabitEthernet0/1/8 10.4.1.1 ip route-static 2.2.2.2 255.255.255.255 GigabitEthernet0/1/0 10.3.1.1 ip route-static 3.3.3.3 255.255.255.255 GigabitEthernet0/1/8 10.4.1.1 ip route-static 10.1.1.0 255.255.255.252 GigabitEthernet0/1/0 ip route-static 10.2.1.0 255.255.255.252 GigabitEthernet0/1/8 # return