Example for Configuring an Associated Bidirectional Static CR-LSP
This section provides an example for configuring an associated bidirectional static CR-LSP.
Networking Requirements
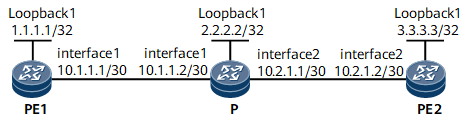
In Figure 1, a forward static CR-LSP is established along the path PE1 -> PE2, and a reverse static CR-LSP is established along the path PE2 -> PE1. To allow a traffic switchover to be performed on both CR-LSPs, bind the two static CR-LSPs to each other to form an associated bidirectional static CR-LSP.
Configuration Roadmap
The configuration roadmap is as follows:
Assign an IP address to every interface and configure a loopback interface address as an LSR ID on every node.
Configure a forward static CR-LSP and a reverse static CR-LSP.
Bind the forward and reverse static CR-LSPs to each other.
Data Preparation

In this example, a forward static CR-LSP is established along the path PE1 -> PE2, and a reverse static CR-LSP is established along the path PE2 -> PE1.
Device Name |
Parameter |
Value |
|---|---|---|
PE1 |
Number of a tunnel interface on the forward CR-LSP |
Tunnel10 |
Tunnel ID of the forward CR-LSP |
100 |
|
Outgoing label of the forward CR-LSP |
20 |
|
Name of the reverse CR-LSP |
Tunnel20 |
|
Incoming label of the reverse CR-LSP |
130 |
|
P |
Name of the forward CR-LSP |
Tunnel10 |
Incoming label of the forward CR-LSP |
20 |
|
Outgoing label of the forward CR-LSP |
30 |
|
Name of the reverse CR-LSP |
Tunnel20 |
|
Incoming label of the reverse CR-LSP |
120 |
|
Outgoing label of the reverse CR-LSP |
130 |
|
PE2 |
Number of a tunnel interface on the reverse CR-LSP |
Tunnel20 |
Tunnel ID of the reverse CR-LSP |
200 |
|
Outgoing label of the reverse CR-LSP |
120 |
|
Name of the forward CR-LSP |
Tunnel10 |
|
Incoming label of the forward CR-LSP |
30 |
Procedure
- Assign an IP address and a mask to each interface.
Assign IP addresses and masks to interfaces. For configuration details, see Configuration Files in this section.
- Configure a forward static CR-LSP and a reverse static CR-LSP.
For configuration details, see Configuration Files in this section.
- Bind the forward and reverse static CR-LSPs to each other.
# Configure PE1.
[~PE1] interface Tunnel 10 [~PE1-Tunnel10] mpls te reverse-lsp protocol static lsp-name Tunnel20 [*PE1-Tunnel10] commit
# Configure PE2.
[~PE2] interface Tunnel 20 [~PE2-Tunnel20] mpls te reverse-lsp protocol static lsp-name Tunnel10 [*PE2-Tunnel20] commit
- Verify the configuration.
After completing the preceding configurations, run the display mpls te reverse-lsp verbose command on PE1 and PE2 to view reserve static CR-LSP information. The following example uses the command output on PE1.
[~PE1] display mpls te reverse-lsp verbose ------------------------------------------------------------------------------- LSP Information: STATIC LSP ------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Obverse Tunnel : Tunnel10 //Tunnel interface on the forward CR-LSP Reverse LSP Name : Tunnel20 //Name of the reverse CR-LSP Reverse LSP State : Up //Status of the reverse CR-LSP Incoming Label : 130 Incoming Interface : GE0/1/0
Configuration Files
PE1 configuration file
# sysname PE1 # mpls lsr-id 1.1.1.1 # mpls mpls te # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ip address 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.252 mpls mpls te # interface LoopBack1 ip address 1.1.1.1 255.255.255.255 # interface Tunnel10 ip address unnumbered interface LoopBack1 tunnel-protocol mpls te destination 3.3.3.3 mpls te signal-protocol cr-static mpls te reverse-lsp protocol static lsp-name Tunnel20 mpls te tunnel-id 100 # static-cr-lsp ingress tunnel-interface Tunnel10 destination 3.3.3.3 nexthop 10.1.1.2 out-label 20 # static-cr-lsp egress Tunnel20 incoming-interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 in-label 130 # return
P configuration file
# sysname P # mpls lsr-id 2.2.2.2 # mpls mpls te # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ip address 10.1.1.2 255.255.255.252 mpls mpls te # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/8 undo shutdown ip address 10.2.1.1 255.255.255.252 mpls mpls te # interface LoopBack1 ip address 2.2.2.2 255.255.255.255 # static-cr-lsp transit Tunnel10 incoming-interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 in-label 20 nexthop 10.2.1.2 out-label 30 # static-cr-lsp transit Tunnel20 incoming-interface GigabitEthernet0/1/8 in-label 120 nexthop 10.1.1.1 out-label 130 # return
PE2 configuration file
# sysname PE2 # mpls lsr-id 3.3.3.3 # mpls mpls te # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/8 undo shutdown ip address 10.2.1.2 255.255.255.252 mpls mpls te # interface LoopBack1 ip address 3.3.3.3 255.255.255.255 # interface Tunnel20 ip address unnumbered interface LoopBack1 tunnel-protocol mpls te destination 1.1.1.1 mpls te signal-protocol cr-static mpls te reverse-lsp protocol static lsp-name Tunnel10 mpls te tunnel-id 200 # static-cr-lsp ingress tunnel-interface Tunnel20 destination 1.1.1.1 nexthop 10.2.1.1 out-label 120 # static-cr-lsp egress Tunnel10 incoming-interface GigabitEthernet0/1/8 in-label 30 # return