Example for Configuring a Tunnel Selector in an Inter-AS VPN Option B Scenario with MPLS TE Tunnels
After a tunnel selector is used in an inter-AS VPN Option B scenario, VPN data can be carried by MPLS TE tunnels, guaranteeing bandwidth for traffic transmission.
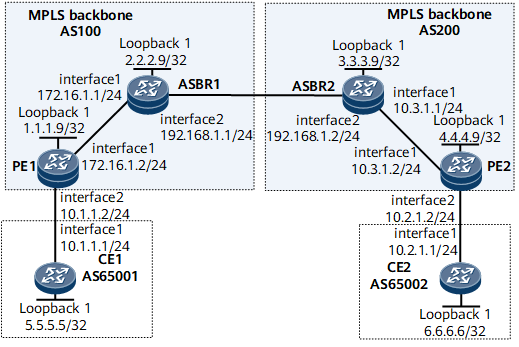
Networking Requirements
On the network shown in Figure 1, CE1 and CE2 belong to the same VPN. PE1 and PE2 belong to different ASs. Therefore, the carrier uses the inter-AS VPN Option B mode to enable different ASs to communicate. By default, the system selects only LDP LSPs for VPN data transmission. A lot of real-time services such as voice and online video services are transmitted between VPNs. To guarantee bandwidth and security for these services, the carrier wants to have all the services transmitted over MPLS TE tunnels. A tunnel selector must be applied on the ASBRs so that the ASBRs can recurse VPNv4 routes to MPLS TE tunnels.
Configuration Roadmap
The configuration roadmap is as follows:
Configure an IGP on the MPLS backbone network for the ASBR and PE in the same AS to communicate.
Enable MPLS and MPLS TE on the ASBRs and PEs and establish an MPLS TE tunnel between the ASBR and PE in the same AS.
Establish an MP-IBGP peer relationship between the ASBR and PE in the same AS.
Configure a VPN instance on each PE and establish an EBGP peer relationship between each PE and its directly connected CE.
Establish an MP-EBGP peer relationship between the ASBRs.
Configure a tunnel policy and a tunnel selector. Apply the tunnel policy to the VPN instance of each PE and the tunnel selector to the BGP-VPNv4 address family of each ASBR.
Data Preparation
To complete the configuration, you need the following data:
MPLS LSR IDs of PE1 (1.1.1.9), ASBR1 (2.2.2.9), ASBR2 (3.3.3.9), and PE2 (4.4.4.9)
Name (vpn1), RD (100:1), and export and import VPN targets (1:1) of the VPN instance on each PE
Tunnel policy name (bindTE) and tunnel selector name (bindTE)
Procedure
- Configure the inter-AS VPN Option B mode and establish MPLS TE tunnels on the BGP/MPLS backbone network.
- Configure an IP address for each interface on each CE, PE, and ASBR, as shown in Figure 1.
- Configure an IGP (OSPF in this example) on the MPLS backbone network. When configuring OSPF, advertise the 32-bit addresses of loopback interfaces on the PEs as LSR IDs.
- Establish an MPLS TE tunnel between the ASBR and PE in the same AS.
- Establish an MP-IBGP peer relationship between the ASBR and PE in the same AS and an MP-EBGP peer relationship between the ASBRs.
- Configure a VPN instance on each PE and establish an EBGP peer relationship between each PE and its directly connected CE.
For configuration details, see Example for Configuring Inter-AS VPN Option B with Basic Networking or "Configuration Files" in this section.
- Configure a tunnel policy and a tunnel selector. Apply the tunnel policy to the VPN instance of each PE and the tunnel selector to the BGP-VPNv4 address family of each ASBR.
# Configure PE1.
[PE1] interface Tunnel 10 [PE1-Tunnel10] mpls te reserved-for-binding [PE1-Tunnel10] quit [PE1] tunnel-policy bindTE [PE1-tunnel-policy-bindTE] tunnel binding destination 2.2.2.9 te Tunnel10 down-switch [PE1-tunnel-policy-bindTE] quit [PE1] ip vpn-instance vpn1 [PE1-vpn-instance-vpn1] tnl-policy bindTE [PE1-vpn-instance-vpn1] quit [PE1] commit
Repeat this step for PE2. For configuration details, see Configuration Files in this section.
# Configure a tunnel policy on ASBR1.
[ASBR1] tunnel-policy bindTE [ASBR1-tunnel-policy-bindTE] tunnel binding destination 1.1.1.9 te Tunnel10 down-switch [ASBR1-tunnel-policy-bindTE] quit [ASBR1] commit
# Configure a tunnel selector and apply it to the BGP-VPNv4 address family of ASBR1 so that VPNv4 routes can recurse to MPLS TE tunnels based on the tunnel policy.
[ASBR1] tunnel-selector bindTE permit node 10 [ASBR1-tunnel-selector] apply tunnel-policy bindTE [ASBR1-tunnel-selector] quit [ASBR1] bgp 100 [ASBR1-bgp] ipv4-family vpnv4 [ASBR1-bgp-af-vpnv4] tunnel-selector bindTE [ASBR1-bgp-af-vpnv4] quit [ASBR1-bgp] quit [ASBR1] commit
The configuration of ASBR2 is similar to the configuration of ASBR1. For configuration details, see Configuration Files in this section.
After completing the configurations, run the display tunnel-policy and display tunnel-selector commands to check the configured tunnel policy or tunnel selector. The following example uses the command output on ASBR1.
<ASBR1> display tunnel-policy Total tunnel policy num: 1 Sel-Seq tunnel policy num: 0 Binding tunnel policy num: 1 Invalid tunnel policy num: 0 Tunnel Policy Name Destination Tunnel Intf Ignore-dest-check Down switch ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- bindTE 1.1.1.9 Tunnel10 Disable Enable <ASBR1> display tunnel-selector Tunnel-selector : bindTE permit : 10 Apply clauses: apply tunnel-policy bindTE - Verify the configuration.
CE1 and CE2 can ping each other successfully. The following example uses the command output on CE1.
[CE1] ping 10.2.1.1 PING 6.6.6.6: 56 data bytes, press CTRL_C to break Reply from 6.6.6.6: bytes=56 Sequence=1 ttl=251 time=3 ms Reply from 6.6.6.6: bytes=56 Sequence=2 ttl=251 time=2 ms Reply from 6.6.6.6: bytes=56 Sequence=3 ttl=251 time=2 ms Reply from 6.6.6.6: bytes=56 Sequence=4 ttl=251 time=2 ms Reply from 6.6.6.6: bytes=56 Sequence=5 ttl=251 time=2 ms --- 6.6.6.6 ping statistics --- 5 packet(s) transmitted 5 packet(s) received 0.00% packet loss round-trip min/avg/max = 2/2/3 msRun the display bgp vpnv4 all routing-table ip-address command on each ASBR. The command output shows information about the VPNv4 route to the address specified by ip-address, including information about the tunnel to which the route recurses. The following example uses network segment 5.5.5.5/32.
<ASBR1> display bgp vpnv4 all routing-table 5.5.5.5 BGP local router ID : 172.16.1.1 Local AS number : 100 Total routes of Route Distinguisher(100:1): 1 BGP routing table entry information of 5.5.5.5/32: Label information (Received/Applied): 16/16 From: 1.1.1.9 (10.1.1.2) Route Duration: 0d01h10m10s Relay IP Nexthop: 172.16.1.2 Relay IP Out-interface: GigabitEthernet0/1/0 Relay Tunnel Out-Interface: GigabitEthernet0/1/0 Original nexthop: 1.1.1.9 Qos information : 0x0 Ext-Community: RT <1 : 1> AS-path 65001, origin igp, MED 0, localpref 100, pref-val 0, valid, internal, b est, select, pre 255 Advertised to such 1 peers: 192.168.1.2
The command output shows that the route to 5.5.5.5/32 recurses to the tunnel with the outbound interface of Tunnel 10. To check detailed information about the tunnel, run the display tunnel-info command.
<ASBR1> display tunnel-info all Tunnel ID Type Destination Status ----------------------------------------------------------------------------- 0x000000000300000002 te 1.1.1.9 UP 0x000000000c00000001 mpls local ifnet 192.168.1.2 UP
In summary, after the tunnel policy and tunnel selector are used in the inter-AS VPN Option B scenario, VPN data can be transmitted over the MPLS TE tunnels between the PEs and ASBRs.
Configuration Files
Configuration file of CE1
# sysname CE1 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ip address 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.0 # interface LoopBack1 ip address 5.5.5.5 255.255.255.255 # bgp 65001 peer 10.1.1.2 as-number 100 # ipv4-family unicast undo synchronization network 5.5.5.5 255.255.255.255 peer 10.1.1.2 enable # returnConfiguration file of PE1
# sysname PE1 # ip vpn-instance vpn1 ipv4-family route-distinguisher 100:1 apply-label per-instance tnl-policy bindTE vpn-target 1:1 import-extcommunity vpn-target 1:1 export-extcommunity # mpls lsr-id 1.1.1.9 # mpls mpls te mpls rsvp-te mpls te cspf # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ip address 172.16.1.2 255.255.255.0 mpls mpls te mpls te bandwidth max-reservable-bandwidth 20000 mpls te bandwidth bc0 15000 mpls rsvp-te # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/8 undo shutdown ip binding vpn-instance vpn1 ip address 10.1.1.2 255.255.255.0 # interface LoopBack1 ip address 1.1.1.9 255.255.255.0 # interface Tunnel10 ip address unnumbered interface LoopBack1 tunnel-protocol mpls te destination 2.2.2.9 mpls te tunnel-id 100 mpls te bandwidth ct0 5000 mpls te reserved-for-binding # bgp 100 peer 2.2.2.9 as-number 100 peer 2.2.2.9 connect-interface LoopBack1 # ipv4-family unicast undo synchronization peer 2.2.2.9 enable # ipv4-family vpnv4 policy vpn-target peer 2.2.2.9 enable # ipv4-family vpn-instance vpn1 import-route direct peer 10.1.1.1 as-number 65001 # ospf 1 opaque-capability enable area 0.0.0.0 mpls-te enable network 1.1.1.9 0.0.0.0 network 172.16.1.0 0.0.0.255 # tunnel-policy bindTE tunnel binding destination 2.2.2.9 te Tunnel10 down-switch # return
Configuration file of ASBR1
# sysname ASBR1 # tunnel-selector bindTE permit node 10 apply tunnel-policy bindTE # mpls lsr-id 2.2.2.9 # mpls mpls te mpls rsvp-te mpls te cspf # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ip address 172.16.1.1 255.255.255.0 mpls mpls te mpls te bandwidth max-reservable-bandwidth 20000 mpls te bandwidth bc0 15000 mpls rsvp-te # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/8 undo shutdown ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 # interface LoopBack1 ip address 2.2.2.9 255.255.255.255 # interface Tunnel10 ip address unnumbered interface LoopBack1 tunnel-protocol mpls te destination 1.1.1.9 mpls te tunnel-id 200 mpls te bandwidth ct0 5000 mpls te reserved-for-binding # bgp 100 peer 1.1.1.9 as-number 100 peer 1.1.1.9 connect-interface LoopBack1 peer 192.168.1.2 as-number 200 # ipv4-family unicast undo synchronization peer 1.1.1.9 enable peer 192.168.1.2 enable # ipv4-family vpnv4 undo policy vpn-target tunnel-selector bindTE peer 1.1.1.9 enable peer 192.168.1.2 enable # ospf 1 opaque-capability enable area 0.0.0.0 mpls-te enable network 2.2.2.9 0.0.0.0 network 172.16.1.0 0.0.0.255 # tunnel-policy bindTE tunnel binding destination 1.1.1.9 te Tunnel10 down-switch # return
Configuration file of ASBR2
# sysname ASBR2 # tunnel-selector bindTE permit node 10 apply tunnel-policy bindTE # mpls lsr-id 3.3.3.9 # mpls mpls te mpls rsvp-te mpls te cspf # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ip address 10.3.1.1 255.255.255.0 mpls mpls te mpls te bandwidth max-reservable-bandwidth 20000 mpls te bandwidth bc0 15000 mpls rsvp-te # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/8 undo shutdown ip address 192.168.1.2 255.255.255.0 # interface LoopBack1 ip address 3.3.3.9 255.255.255.255 # interface Tunnel10 ip address unnumbered interface LoopBack1 tunnel-protocol mpls te destination 4.4.4.9 mpls te tunnel-id 300 mpls te bandwidth ct0 5000 mpls te reserved-for-binding # bgp 200 peer 4.4.4.9 as-number 200 peer 4.4.4.9 connect-interface LoopBack1 peer 192.168.1.1 as-number 100 # ipv4-family unicast undo synchronization peer 4.4.4.9 enable peer 192.168.1.1 enable # ipv4-family vpnv4 undo policy vpn-target tunnel-selector bindTE peer 4.4.4.9 enable peer 192.168.1.1 enable # ospf 1 opaque-capability enable area 0.0.0.0 mpls-te enable network 3.3.3.9 0.0.0.0 network 10.3.1.0 0.0.0.255 # tunnel-policy bindTE tunnel binding destination 4.4.4.9 te Tunnel10 down-switch # return
Configuration file of PE2
# sysname PE2 # ip vpn-instance vpn1 ipv4-family route-distinguisher 100:1 apply-label per-instance tnl-policy bindTE vpn-target 1:1 import-extcommunity vpn-target 1:1 export-extcommunity # mpls lsr-id 4.4.4.9 # mpls mpls te mpls rsvp-te mpls te cspf # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ip address 10.3.1.2 255.255.255.0 mpls mpls te mpls te bandwidth max-reservable-bandwidth 20000 mpls te bandwidth bc0 15000 mpls rsvp-te # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/8 undo shutdown ip binding vpn-instance vpn1 ip address 10.2.1.2 255.255.255.0 # interface LoopBack1 ip address 4.4.4.9 255.255.255.255 # interface Tunnel10 ip address unnumbered interface LoopBack1 tunnel-protocol mpls te destination 3.3.3.9 mpls te tunnel-id 400 mpls te bandwidth ct0 5000 mpls te reserved-for-binding # bgp 200 peer 3.3.3.9 as-number 200 peer 3.3.3.9 connect-interface LoopBack1 # ipv4-family unicast undo synchronization peer 3.3.3.9 enable # ipv4-family vpnv4 policy vpn-target peer 3.3.3.9 enable # ipv4-family vpn-instance vpn1 import-route direct peer 10.2.1.1 as-number 65002 # ospf 1 opaque-capability enable area 0.0.0.0 mpls-te enable network 4.4.4.9 0.0.0.0 network 10.3.1.0 0.0.0.255 # tunnel-policy bindTE tunnel binding destination 3.3.3.9 te Tunnel10 down-switch # return
Configuration file of CE2
# sysname CE2 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ip address 10.2.1.1 255.255.255.0 # interface LoopBack1 ip address 6.6.6.6 255.255.255.255 # bgp 65002 peer 10.2.1.2 as-number 200 # ipv4-family unicast undo synchronization network 6.6.6.6 255.255.255.255 peer 10.2.1.2 enable # return