Example for Configuring Inter-VLAN Communication by Using Sub-interfaces
Configuring sub-interfaces enables users in different VLANs and network segments to communicate with each other.
Networking Requirements
Users in different residential compounds in different network segments require various services such as Internet, IPTV, and VoIP services. The network administrator of each residential compound configures a VLAN for each service to simplify management. After the configuration, users in different residential compounds belong to different VLANs, but they need to communicate with each other for the same type of service.
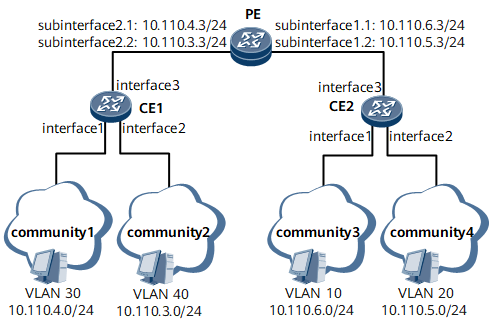
On the network shown in Figure 1, users in residential compounds 1 to 4 belong to different VLANs in different network segments but all require the Internet service. Therefore, communication between these users is required.

Interfaces 1 through 3, sub-interface 1.1, sub-interface 1.2, sub-interface 2.1, and sub-interface 2.2 in this example represent GE 0/1/1, GE 0/1/2, GE 0/1/3, GE 0/1/1.1, GE 0/1/1.2, GE 0/1/2.1, and GE 0/1/2.2, respectively.
Configuration Roadmap
The configuration roadmap is as follows:
- Create VLANs on CEs and determine mappings between users and VLANs.
- Configure trunk ports on CEs to allow frames with certain VLAN IDs to pass through.
- Create sub-interfaces on PE and associate the sub-interfaces with VLANs.
- Assign an IP address to each sub-interface for communication at the network layer.

The default gateway address of each PC in a VLAN must be the IP address of the corresponding sub-interface. Otherwise, inter-VLAN communication fails.
Data Preparation
- User VLAN ID
- User IP address
- Number of each port connecting a CE to a PC
- Number of each port connecting a CE to the PE
- Number and IP address of each sub-interface on PE
Procedure
- Create VLANs on CE 1 and CE 2.
# Configure CE 1.
<HUAWEI> system-view [~HUAWEI] sysname CE1 [*HUAWEI] commit [~CE1] vlan batch 30 40 [*CE1] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/1 [*CE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] portswitch [*CE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] undo shutdown [*CE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] port link-type access [*CE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] port default vlan 30 [*CE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] quit [*CE1] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/2 [*CE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/2] portswitch [*CE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/2] undo shutdown [*CE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/2] port link-type access [*CE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/2] port default vlan 40 [*CE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/2] quit
# Configure CE 2.
<HUAWEI> system-view [~HUAWEI] sysname CE2 [*HUAWEI] commit [~CE2] vlan batch 10 20 [*CE2] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/1 [*CE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] portswitch [*CE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] undo shutdown [*CE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] port link-type access [*CE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] port default vlan 10 [*CE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] quit [*CE2] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/2 [*CE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/2] portswitch [*CE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/2] undo shutdown [*CE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/2] port link-type access [*CE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/2] port default vlan 20 [*CE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/2] quit
- Configure trunk ports on CE 1 and CE 2 to allow frames with certain VLAN IDs to pass through.
# Configure CE 1.
[*CE1] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/3 [*CE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/3] portswitch [*CE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/3] undo shutdown [*CE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/3] port link-type trunk [*CE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/3] port trunk allow-pass vlan 30 40 [*CE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/3] quit [*CE1] commit
# Configure CE 2.
[*CE2] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/3 [*CE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/3] portswitch [*CE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/3] undo shutdown [*CE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/3] port link-type trunk [*CE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/3] port trunk allow-pass vlan 10 20 [*CE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/3] quit [*CE2] commit
- Create sub-interfaces on PE and associate the sub-interfaces with VLANs.
<HUAWEI> system-view [~HUAWEI] sysname PE [*HUAWEI] commit [~PE] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/1 [*PE-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] undo shutdown [*PE-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] quit [*PE] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/1.1 [*PE-GigabitEthernet0/1/1.1] vlan-type dot1q 10 [*PE-GigabitEthernet0/1/1.1] quit [*PE] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/1.2 [*PE-GigabitEthernet0/1/1.2] vlan-type dot1q 20 [*PE-GigabitEthernet0/1/1.2] quit [*PE] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/2 [*PE-GigabitEthernet0/1/2] undo shutdown [*PE-GigabitEthernet0/1/2] quit [*PE] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/2.1 [*PE-GigabitEthernet0/1/2.1] vlan-type dot1q 30 [*PE-GigabitEthernet0/1/2.1] quit [*PE] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/2.2 [*PE-GigabitEthernet0/1/2.2] vlan-type dot1q 40 [*PE-GigabitEthernet0/1/2.2] quit
- Configure IP addresses.
[*PE] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/1.1 [*PE-GigabitEthernet0/1/1.1] ip address 10.110.6.3 24 [*PE-GigabitEthernet0/1/1.1] quit [*PE] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/1.2 [*PE-GigabitEthernet0/1/1.2] ip address 10.110.5.3 24 [*PE-GigabitEthernet0/1/1.2] quit [*PE] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/2.1 [*PE-GigabitEthernet0/1/2.1] ip address 10.110.4.3 24 [*PE-GigabitEthernet0/1/2.1] quit [*PE] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/2.2 [*PE-GigabitEthernet0/1/2.2] ip address 10.110.3.3 24 [*PE-GigabitEthernet0/1/2.2] quit [*PE] commit
- Verify the configuration.
On PCs in VLAN 10, configure the IP address 10.110.6.3/24 of GE 0/1/1.1 as the default gateway address.
On PCs in VLAN 20, configure the IP address 10.110.5.3/24 of GE 0/1/1.2 as the default gateway address.
On PCs in VLAN 30, configure the IP address 10.110.4.3/24 of GE 0/1/2.1 as the default gateway address.
On PCs in VLAN 40, configure the IP address 10.110.3.3/24 of GE 0/1/2.2 as the default gateway address.
After the configurations, PCs in VLANs 10, 20, 30, and 40 can ping each other successfully.
Configuration Files
-
# sysname CE1 # vlan batch 30 40 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/1 portswitch undo shutdown port link-type access port default vlan 30 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/2 portswitch undo shutdown port link-type access port default vlan 40 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/3 portswitch undo shutdown port link-type trunk port trunk allow-pass vlan 30 40 # return
-
# sysname CE2 # vlan batch 10 20 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/1 portswitch undo shutdown port link-type access port default vlan 10 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/2 portswitch undo shutdown port link-type access port default vlan 20 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/3 portswitch undo shutdown port link-type trunk port trunk allow-pass vlan 10 20 # return
Configuration file of PE
# sysname PE # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/1 undo shutdown # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/1.1 vlan-type dot1q 10 ip address 10.110.6.3 255.255.255.0 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/1.2 vlan-type dot1q 20 ip address 10.110.5.3 255.255.255.0 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/2 undo shutdown # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/2.1 vlan-type dot1q 30 ip address 10.110.4.3 255.255.255.0 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/2.2 vlan-type dot1q 40 ip address 10.110.3.3 255.255.255.0 # return