Configuring LDP VPWS
Usage Scenario
Carriers have constructed various types of backbone networks using different technologies. For example, they have constructed backbone public switched telephone networks (PSTNs) to carry voice services, FR backbone networks to carry FR data, and ATM backbone networks to transmit ATM data. As IP services develop rapidly, carriers have established IP backbone networks to meet this trend. In addition to backbone networks, diverse access networks are also constructed. As a result, low interoperability exists between different types of networks. It is an urgent task for carriers to find a way to effectively integrate these networks, enhance network utilization, and provide more types of services for users.
By converging previous access modes with the current IP backbone network, VPWS prevents repetitious network construction and saves operation costs. With the VPWS technology, an IP backbone network can be connected to various access networks, upgrading and enhancing the entire network. After an MPLS IP backbone network is constructed, the traditional datacom networks such as ATM and FR networks can be used as access networks. ATM and FR users are unaware of such network changes. With the VPWS technology, access networks of different protocols can interwork with each other. For example, ATM users and FR users can communicate with each other.
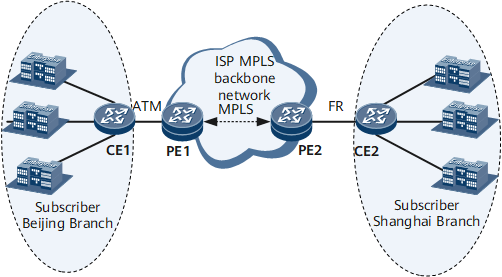
Figure 1 is a typical VPWS networking diagram. The backbone network is an IP network accessed by LANs in different modes.
Assume that a carrier has established a nationwide backbone network to provide VPWS services. A customer has two branches: one in city A and one in city B. The branch in city A accesses the carrier's backbone network over an ATM network, and the branch in city B accesses the carrier's backbone network over an FR network. The carrier can set up a VPWS connection between access sites PE1 in city A and PE2 in city B.
In this manner, the carrier can provide point-to-point private network services over a WAN without taking special measures to address different access modes. In this solution, the customer does not need to modify the original enterprise network plan; the carrier can implement smooth migration to the IP backbone network without modifying existing access modes.
Pre-configuration Tasks
Before configuring LDP VPWS, complete the following tasks:
Configure static routes or an IGP protocol on PEs and Ps on the MPLS backbone network to ensure IP connectivity.
Configure basic MPLS functions on PEs and Ps of the MPLS backbone network.
Set up LDP sessions among PEs (if the PEs are indirectly connected, set up remote LDP sessions between them).
Establish tunnels between PEs based on the tunnel policy (if no tunnel policy is configured, the default tunnel policy LDP is used).
Configuration Procedures
Configuring LDP VPWS (Same Type of AC Link) |
Configuring LDP VPWS (Different Types of AC Links) |
|---|---|
(Optional) Configuring Flow Label-based Load Balancing |
|
(Optional) Configuring a PW Template |
|
Configuring a VPWS PW |
Configuring VPWS IP Interworking |
(Optional) Configuring a Secondary PW |
|
(Optional) Configuring the Revertive Switchover |
|
- (Optional) Configuring Flow Label-based Load Balancing
- Flow label-based load balancing enables L2VPN data flows on a PW to be load-balanced over tunnels between P devices based on flow labels, improving forwarding efficiency.
- (Optional) Configuring a PW Template
- A PW template is a collection of common PW attributes. Configuring PWs using a PW template helps save configuration workload.
- Configuring a VPWS PW
- This section describes how to establish a P2P VPWS PW between two PEs for communication.
- Configuring VPWS IP Interworking
- If AC types at the two ends of a VPWS PW are different, configure VPWS IP interworking for the two CEs to communicate.
- (Optional) Configuring a Secondary VPWS PW
- This section describes how to configure a secondary VPWS PW for VLL FRR, so that L2VPN traffic can be quickly switched to the secondary path if the primary path fails. After the primary path recovers, the L2VPN traffic can be switched back to it according to the corresponding revertive switching policy.
- (Optional) Configuring the Revertive Switchover
- The revertive switching policies can be classified into three modes: immediate revertive mode, delayed revertive mode, and non-revertive mode.