Overview of VSs
Virtual system (VS) partitioning helps manage networks by layer.
Background
As the demand on various types of network services is growing, network management becomes more complex. Requirements for service isolation, system security, and reliability are steadily increasing. The virtual private network (VPN) technique can be used to isolate services on a PS. If a module failure occurs on the PS, all services configured on the PS will be interrupted. To prevent service interruptions, the VS technique is used to partition a PS into several VSs. Each VS functions as an independent network element and uses separate physical resources to isolate services.
Further development of the distributed routing and switching systems allows the VS technique to fully utilize the service processing capability of a single PS. The VS technique helps simplify network deployment and management, and strengthen system security and reliability.
Relationship Between a PS and VSs
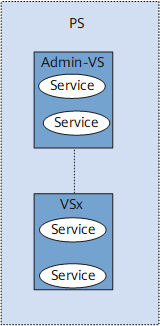
As shown in Figure 1, a physical router, which can be regarded as a PS, is partitioned into several VSs. Each VS functions as an independent router to process services.

The PS administrator has the authority to manage all VSs. The VS administrator has the authority to query VSs but cannot manage them.
Basic Concepts
Figure 2 shows VS concepts.
Concept |
Description |
|---|---|
PS |
Physical system |
VS |
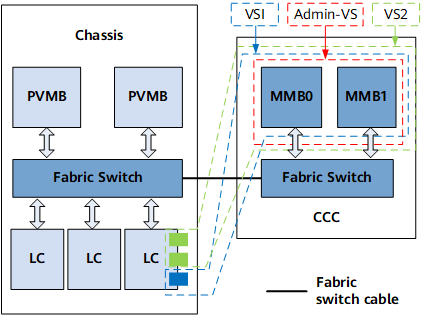
A VS is a virtual system on both software and hardware planes. Each VS performs independent routing tasks. VSs share all resources, such as IPU, except interfaces. That is, VSs can share the IPU resources. Each VS has its own primary VS main board (PVMB) and configuration management instance. Generally, the routing management system and configuration management system work on the PVMB. NOTE:
Each PS has a default VS named Admin-VS. All unassigned interfaces belong to this VS. All VSs in a PS must use the same system software. Each VS is configured with its own configuration management system and routing protocols. |
MB |
Main boards (MBs) are used to carry tasks on the management control plane. In a VS, the IPU refers to a common MB. |
PVMB |
A VS has many MBs, two of which manage the entire VS. The two MBs are PVMBs. |
MMB |
A PS has many MBs, two of which manage the entire system. The two MBs are MMBs. |
LC |
LCs provide physical interfaces connected to other devices. |