Example for Configuring VXLAN in Centralized Gateway Mode Using BGP EVPN
This section provides an example for configuring VXLAN in centralized gateway mode for dynamic tunnel establishment so that users on the same network segment or different network segments can communicate.
Networking Requirements
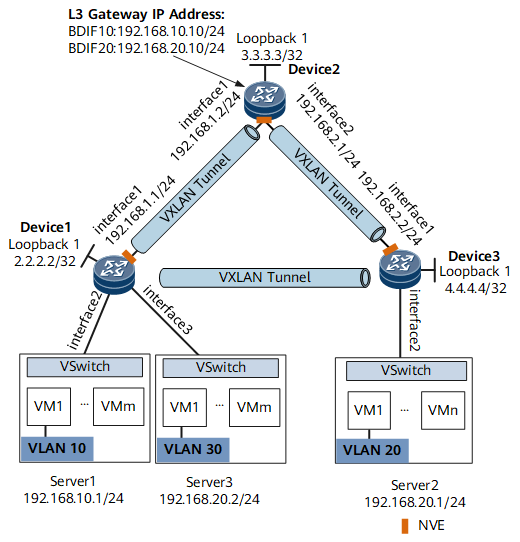
On the network shown in Figure 1, an enterprise has VMs deployed in different areas of a data center. VM 1 on Server 1 belongs to VLAN 10, VM 1 on Server 2 belongs to VLAN 20, and VM 1 on Server 3 belongs to VLAN 30. Server 1 and Server 2 reside on different network segments, whereas Server 2 and Server 3 reside on the same network segment. To allow VM 1s on different servers to communicate with each other, configure IPv6 VXLAN in centralized gateway mode.

In this example, most configurations are performed on Device 1, Device 2, and Device 3. NetEngine 8000 Fs can be deployed as these devices.
Interfaces 1 through 3 represent GE 0/1/1, GE 0/1/2, and GE 0/1/3, respectively.
Configuration Roadmap
Configure a routing protocol on Device 1, Device 2, and Device 3 to allow them to communicate at Layer 3.
Configure a service access point on Device 1 and Device 3 to differentiate service traffic.
Configure a BGP EVPN peer relationship.
Configure EVPN instances.
Configure an ingress replication list.
Configure Device 2 as a Layer 3 VXLAN gateway.
Data Preparation
To complete the configuration, you need the following data.
VMs' VLAN IDs (10, 20, and 30)
IP addresses of interfaces connecting devices
Interior Gateway Protocol (IGP) running between devices (OSPF in this example)
- BD IDs (10 and 20)
- VNI IDs (5010 and 5020)
- EVPN instances' RDs (11:1, 12:1, 21:1, 23:1 and 31:2) and RTs (1:1 and 2:2)
Procedure
- Configure a routing protocol.
Assign an IP address to each interface on Device 1, Device 2, and Device 3 according to Figure 1.
# Configure Device 1.<HUAWEI> system-view [~HUAWEI] sysname Device1 [*HUAWEI] commit [~Device1] interface loopback 1 [*Device1-LoopBack1] ip address 2.2.2.2 32 [*Device1-LoopBack1] quit [*Device1] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/1 [*Device1-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] ip address 192.168.1.1 24 [*Device1-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] quit [*Device1] ospf [*Device1-ospf-1] area 0 [*Device1-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 2.2.2.2 0.0.0.0 [*Device1-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 192.168.1.0 0.0.0.255 [*Device1-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] quit [*Device1-ospf-1] quit [*Device1] commit
The configuration of Device 2 and Device 3 is similar to the configuration of Device 1. For configuration details, see Configuration Files in this section.
After OSPF is configured, the devices can use OSPF to learn the IP addresses of each other's loopback interfaces and successfully ping each other. The following example shows the command output on Device 1 after it pings Device 3:[~Device1] ping 4.4.4.4 PING 4.4.4.4: 56 data bytes, press CTRL_C to break Reply from 4.4.4.4: bytes=56 Sequence=1 ttl=254 time=5 ms Reply from 4.4.4.4: bytes=56 Sequence=2 ttl=254 time=2 ms Reply from 4.4.4.4: bytes=56 Sequence=3 ttl=254 time=2 ms Reply from 4.4.4.4: bytes=56 Sequence=4 ttl=254 time=3 ms Reply from 4.4.4.4: bytes=56 Sequence=5 ttl=254 time=3 ms --- 4.4.4.4 ping statistics --- 5 packet(s) transmitted 5 packet(s) received 0.00% packet loss round-trip min/avg/max = 2/3/5 ms - Configure a service access point on Device 1 and Device 3.# Configure Device 1.
[~Device1] bridge-domain 10 [*Device1-bd10] quit [*Device1] interface gigabitethernet0/1/2.1 mode l2 [*Device1-GigabitEthernet0/1/2.1] encapsulation dot1q vid 10 [*Device1-GigabitEthernet0/1/2.1] rewrite pop single [*Device1-GigabitEthernet0/1/2.1] bridge-domain 10 [*Device1-GigabitEthernet0/1/2.1] quit [*Device1] bridge-domain 20 [*Device1-bd20] quit [*Device1] interface gigabitethernet0/1/3.1 mode l2 [*Device1-GigabitEthernet0/1/3.1] encapsulation dot1q vid 30 [*Device1-GigabitEthernet0/1/3.1] rewrite pop single [*Device1-GigabitEthernet0/1/3.1] bridge-domain 20 [*Device1-GigabitEthernet0/1/3.1] quit [*Device1] commit
The configuration of Device 3 is similar to the configuration of Device 1. For configuration details, see Configuration Files in this section.
- Configure a BGP EVPN peer relationship.
# Configure Device 1.
[~Device1] bgp 100 [*Device1-bgp] peer 3.3.3.3 as-number 100 [*Device1-bgp] peer 3.3.3.3 connect-interface LoopBack1 [*Device1-bgp] peer 4.4.4.4 as-number 100 [*Device1-bgp] peer 4.4.4.4 connect-interface LoopBack1 [*Device1-bgp] l2vpn-family evpn [*Device1-bgp-af-evpn] peer 3.3.3.3 enable [*Device1-bgp-af-evpn] peer 3.3.3.3 advertise encap-type vxlan [*Device1-bgp-af-evpn] peer 4.4.4.4 enable [*Device1-bgp-af-evpn] peer 4.4.4.4 advertise encap-type vxlan [*Device1-bgp-af-evpn] quit [*Device1-bgp] quit [*Device1] commit
The configuration of Device 2 and Device 3 is similar to the configuration of Device 1. For configuration details, see Configuration Files in this section.
- Configure an EVPN instance on Device 1, Device 2, and Device 3.# Configure Device 1.
[~Device1] evpn vpn-instance evrf3 bd-mode [*Device1-evpn-instance-evrf3] route-distinguisher 11:1 [*Device1-evpn-instance-evrf3] vpn-target 1:1 [*Device1-evpn-instance-evrf3] quit [*Device1] bridge-domain 10 [*Device1-bd10] vxlan vni 5010 split-horizon-mode [*Device1-bd10] evpn binding vpn-instance evrf3 [*Device1-bd10] quit [*Device1] evpn vpn-instance evrf4 bd-mode [*Device1-evpn-instance-evrf4] route-distinguisher 12:1 [*Device1-evpn-instance-evrf4] vpn-target 2:2 [*Device1-evpn-instance-evrf4] quit [*Device1] bridge-domain 20 [*Device1-bd20] vxlan vni 5020 split-horizon-mode [*Device1-bd20] evpn binding vpn-instance evrf4 [*Device1-bd20] quit [*Device1] commit
The configuration of Device 2 and Device 3 is similar to the configuration of Device 1. For configuration details, see Configuration Files in this section.
- Configure an ingress replication list.# Configure Device 1.
[~Device1] interface nve 1 [*Device1-Nve1] source 2.2.2.2 [*Device1-Nve1] vni 5010 head-end peer-list protocol bgp [*Device1-Nve1] vni 5020 head-end peer-list protocol bgp [*Device1-Nve1] quit [*Device1] commit
The configuration of Device 3 is similar to the configuration of Device 1. For configuration details, see Configuration Files in this section.
- Configure Device 2 as a Layer 3 VXLAN gateway.
[~Device2] interface vbdif 10 [*Device2-Vbdif10] ip address 192.168.10.10 24 [*Device2-Vbdif10] quit [*Device2] interface vbdif 20 [*Device2-Vbdif20] ip address 192.168.20.10 24 [*Device2-Vbdif20] quit [*Device2-Vbdif20] commit
- Verify the configuration.
After completing the configurations, run the display vxlan tunnel and display vxlan vni commands on Device 1, Device 2, and Device 3 to check the VXLAN tunnel and VNI information, respectively. The VNIs are Up. The following example shows the command output on Device 1.
[~Device1] display vxlan tunnel Number of vxlan tunnel : 2 Tunnel ID Source Destination State Type Uptime ------------------------------------------------------------------- 4026531843 2.2.2.2 4.4.4.4 up dynamic 0035h21m 4026531844 2.2.2.2 3.3.3.3 up dynamic 0036h10m [~Device1] display vxlan vni Number of vxlan vni : 2 VNI BD-ID State --------------------------------------- 5010 10 up 5020 20 up
Run the display bgp evpn all routing-table command to check EVPN route information.
[~Device1] display bgp evpn all routing-table Local AS number : 100 BGP Local router ID is 192.168.1.1 Status codes: * - valid, > - best, d - damped, x - best external, a - add path, h - history, i - internal, s - suppressed, S - Stale Origin : i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete EVN address family: Number of Inclusive Multicast Routes: 5 Route Distinguisher: 11:1 Network(EthTagId/IpAddrLen/OriginalIp) NextHop *> 0:32:2.2.2.2 0.0.0.0 Route Distinguisher: 12:1 Network(EthTagId/IpAddrLen/OriginalIp) NextHop *> 0:32:2.2.2.2 0.0.0.0 Route Distinguisher: 21:1 Network(EthTagId/IpAddrLen/OriginalIp) NextHop *>i 0:32:3.3.3.3 3.3.3.3 Route Distinguisher: 23:1 Network(EthTagId/IpAddrLen/OriginalIp) NextHop *>i 0:32:3.3.3.3 3.3.3.3 Route Distinguisher: 31:2 Network(EthTagId/IpAddrLen/OriginalIp) NextHop *>i 0:32:4.4.4.4 4.4.4.4VM1s on different servers can communicate. For example, you can ping VM1 of Server 1 on the Layer 3 gateway Device 2.
[~Device2] ping 192.168.10.1 PING 192.168.10.1: 56 data bytes, press CTRL_C to break Reply from 192.168.10.1: bytes=56 Sequence=1 ttl=254 time=15 ms Reply from 192.168.10.1: bytes=56 Sequence=2 ttl=254 time=5 ms Reply from 192.168.10.1: bytes=56 Sequence=3 ttl=254 time=5 ms Reply from 192.168.10.1: bytes=56 Sequence=4 ttl=254 time=10 ms Reply from 192.168.10.1: bytes=56 Sequence=5 ttl=254 time=10 ms --- 192.168.10.1 ping statistics --- 5 packet(s) transmitted 5 packet(s) received 0.00% packet loss round-trip min/avg/max = 5/10/15 ms
Configuration Files
Device 1 configuration file
# sysname Device1 # evpn vpn-instance evrf3 bd-mode route-distinguisher 11:1 vpn-target 1:1 export-extcommunity vpn-target 1:1 import-extcommunity # bridge-domain 10 vxlan vni 5010 split-horizon-mode evpn binding vpn-instance evrf3 # evpn vpn-instance evrf4 bd-mode route-distinguisher 12:1 vpn-target 2:2 export-extcommunity vpn-target 2:2 import-extcommunity # bridge-domain 20 vxlan vni 5020 split-horizon-mode evpn binding vpn-instance evrf4 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/1 undo shutdown ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/2.1 mode l2 encapsulation dot1q vid 10 rewrite pop single bridge-domain 10 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/3.1 mode l2 encapsulation dot1q vid 30 rewrite pop single bridge-domain 20 # interface LoopBack1 ip address 2.2.2.2 255.255.255.255 # interface Nve1 source 2.2.2.2 vni 5010 head-end peer-list protocol bgp vni 5020 head-end peer-list protocol bgp # bgp 100 peer 3.3.3.3 as-number 100 peer 3.3.3.3 connect-interface LoopBack1 peer 4.4.4.4 as-number 100 peer 4.4.4.4 connect-interface LoopBack1 # ipv4-family unicast peer 3.3.3.3 enable peer 4.4.4.4 enable # l2vpn-family evpn undo policy vpn-target peer 3.3.3.3 enable peer 3.3.3.3 advertise encap-type vxlan peer 4.4.4.4 enable peer 4.4.4.4 advertise encap-type vxlan # ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0 network 2.2.2.2 0.0.0.0 network 192.168.1.0 0.0.0.255 # return
Device 2 configuration file
# sysname Device2 # evpn vpn-instance evrf3 bd-mode route-distinguisher 21:1 vpn-target 1:1 export-extcommunity vpn-target 1:1 import-extcommunity # bridge-domain 10 vxlan vni 5010 split-horizon-mode evpn binding vpn-instance evrf3 # evpn vpn-instance evrf4 bd-mode route-distinguisher 23:1 vpn-target 2:2 export-extcommunity vpn-target 2:2 import-extcommunity # bridge-domain 20 vxlan vni 5020 split-horizon-mode evpn binding vpn-instance evrf4 # interface Vbdif10 ip address 192.168.10.10 255.255.255.0 # interface Vbdif20 ip address 192.168.20.10 255.255.255.0 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/1 undo shutdown ip address 192.168.1.2 255.255.255.0 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/2 undo shutdown ip address 192.168.2.1 255.255.255.0 # interface LoopBack1 ip address 3.3.3.3 255.255.255.255 # interface Nve1 source 3.3.3.3 vni 5010 head-end peer-list protocol bgp vni 5020 head-end peer-list protocol bgp # bgp 100 peer 2.2.2.2 as-number 100 peer 2.2.2.2 connect-interface LoopBack1 peer 4.4.4.4 as-number 100 peer 4.4.4.4 connect-interface LoopBack1 # ipv4-family unicast peer 2.2.2.2 enable peer 4.4.4.4 enable # l2vpn-family evpn peer 2.2.2.2 enable peer 2.2.2.2 advertise encap-type vxlan peer 4.4.4.4 enable peer 4.4.4.4 advertise encap-type vxlan # ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0 network 3.3.3.3 0.0.0.0 network 192.168.1.0 0.0.0.255 network 192.168.2.0 0.0.0.255 # return
Device 3 configuration file
# sysname Device3 # evpn vpn-instance evrf4 bd-mode route-distinguisher 31:2 vpn-target 2:2 export-extcommunity vpn-target 2:2 import-extcommunity # bridge-domain 20 vxlan vni 5020 split-horizon-mode evpn binding vpn-instance evrf4 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/1 undo shutdown ip address 192.168.2.2 255.255.255.0 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/2.1 mode l2 encapsulation dot1q vid 20 rewrite pop single bridge-domain 20 # interface LoopBack1 ip address 4.4.4.4 255.255.255.255 # interface Nve1 source 4.4.4.4 vni 5020 head-end peer-list protocol bgp # bgp 100 peer 2.2.2.2 as-number 100 peer 2.2.2.2 connect-interface LoopBack1 peer 3.3.3.3 as-number 100 peer 3.3.3.3 connect-interface LoopBack1 # ipv4-family unicast peer 2.2.2.2 enable peer 3.3.3.3 enable # l2vpn-family evpn undo policy vpn-target peer 2.2.2.2 enable peer 2.2.2.2 advertise encap-type vxlan peer 3.3.3.3 enable peer 3.3.3.3 advertise encap-type vxlan # ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0 network 4.4.4.4 0.0.0.0 network 192.168.2.0 0.0.0.255 # return