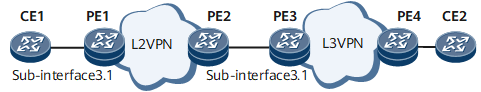
Example for Configuring Two-Way Frame Delay Measurement (When an L2VPN Is Connected to an L3VPN)
This section provides an example for configuring two-way frame delay measurement when an L2VPN is connected to an L3VPN.
Networking Requirements
As networks continue to develop and diversify, various value-added services such as IPTV, video conferencing, and VoIP are becoming increasingly popular. The performance monitoring function can be used to check the performance of links that transmit services.
On the network shown in Figure 1, connectivity fault management (CFM) is deployed on CE1 and PE3. Sending a large number of continuity check messages (CCMs) affects network performance, and therefore CCMs are not used for continuity check. To provide higher-quality voice services, carriers hope to monitor frame loss performance on mobile bearer links in real time so that they can promptly respond to video service quality deterioration.

A VLAN dot1q sub-interface, dot1q termination sub-interface, QinQ termination sub-interface, or L3VE interface on an L2VPN can be connected to an L3VPN. In this example, a VLAN dot1q sub-interface is used.
Configuration Roadmap
The configuration roadmap is as follows:
- Configure on-demand two-way frame delay measurement for links.
- Configure proactive two-way frame delay measurement for links.
Data Preparation
To complete the configuration, you need the following data:
MD name and MA name on CE1 and PE3
Interval at which DMMs are sent and number of intervals
Procedure
- Configure basic Ethernet CFM functions, including outward-facing MEPs.
Configure basic Ethernet CFM functions on CE1 and PE3. Configure Ethernet CFM in compliance with IEEE Std 802.1ag-2007. Create an MD named md3 and an MA named ma3.
# Configure CE1.
<HUAWEI> system-view [~HUAWEI] sysname CE1 [*HUAWEI] commit [*CE1] interface gigabitethernet0/1/17.1 [*CE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/17.1] vlan-type dot1q 200 [*CE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/17.1] commit [*CE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/17.1] quit [~CE1] cfm enable [*CE1] cfm md md3 [*CE1-md-md3] ma ma3 [*CE1-md-md3-ma-ma3] mep mep-id 3 interface gigabitethernet0/1/17.1 vlan 200 outward [*CE1-md-md3-ma-ma3] mep ccm-send mep-id 3 enable [*CE1-md-md3-ma-ma3] remote-mep mep-id 4 [*CE1-md-md3-ma-ma3] remote-mep ccm-receive mep-id 4 enable [*CE1-md-md3-ma-ma3] test-id 1 mep 3 remote-mep 4 [*CE1-md-md3-ma-ma3] commit
# Configure PE3.
<HUAWEI> system-view [~HUAWEI] sysname PE3 [*HUAWEI] commit [*PE3-GigabitEthernet0/1/17.1] vlan-type dot1q 200 [*PE3-GigabitEthernet0/1/17.1] commit [*PE3-GigabitEthernet0/1/17.1] quit [*PE3] commit [*PE3] cfm enable [*PE3] cfm commit [*PE3] cfm md md3 [*PE3-md-md3] ma ma3 [*PE3-md-md3-ma-ma3] mep mep-id 4 interface gigabitethernet0/1/17.1 vlan 200 outward [*PE3-md-md3-ma-ma3] mep ccm-send mep-id 4 enable [*PE3-md-md3-ma-ma3] remote-mep mep-id 3 [*PE3-md-md3-ma-ma3] remote-mep ccm-receive mep-id 3 enable [*PE3-md-md3-ma-ma3] test-id 1 mep 4 [*PE3-md-md3-ma-ma3] commit
- Enable PE3 to receive DMMs.
# Configure PE3.
[~PE3-md-md3-ma-ma3] delay-measure two-way receive test-id 1 [*PE3-md-md3-ma-ma3] quit [*PE3-md-md3] quit [*PE3] commit
- Enable on-demand two-way frame delay measurement.
# Configure CE1.
[~CE1-md-md3-ma-ma3] delay-measure two-way send test-id 1 interval 1000 count 10 [*CE1-md-md3-ma-ma3] quit [*CE1-md-md3] quit
- Verify the configuration.
After completing the configuration, run the display y1731 statistic-type command to view one-way frame delay statistics on CE1.
<CE1> display y1731 statistic-type twoway-delay Latest two-way delay statistics of test-id 1: ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Index Delay(usec) Delay variation(usec) ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 1 108 - 2 119 11 3 115 4 4 116 1 5 159 43 6 113 46 7 160 47 8 110 50 9 122 12 10 109 13 ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Average delay(usec) : 123 Average delay variation(usec) : 25 Maximum delay(usec) : 160 Maximum delay variation(usec) : 50 Minimum delay(usec) : 108 Minimum delay variation(usec) : 1
Configuration Files
CE1 configuration file
# sysname CE1 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/17.1 vlan-type dot1q 200 # cfm version standard cfm enable # cfm md md3 ma ma3 mep mep-id 3 interface GigabitEthernet0/1/17.1 vlan 200 outward mep ccm-send mep-id 3 enable remote-mep mep-id 4 remote-mep ccm-receive mep-id 4 enable test-id 1 mep 3 remote-mep 4 delay-measure two-way send test-id 1 interval 1000 count 10 # return
PE3 configuration file
# sysname PE3 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/17.1 vlan-type dot1q 200 # cfm version standard cfm enable # cfm md md3 ma ma3 mep mep-id 4 interface GigabitEthernet0/1/17.1 vlan 200 outward mep ccm-send mep-id 4 enable remote-mep mep-id 3 remote-mep ccm-receive mep-id 3 enable test-id 1 mep 4 delay-measure two-way receive test-id 1 # return