Configuring the ETH-Test Function for a VLL
The ETH-test function is short for Ethernet test signal. ETH-test instances are performed for a unidirectional on-demand service or during an on-demand-service interruption to calculate parameters, including the maximum bandwidth, frame loss ratio, and bit error rate.
Context
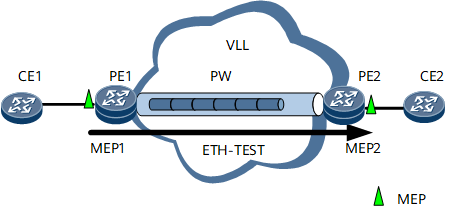
In Figure 1, a VLL is established between PE1 and PE2. MEP1 is configured on an AC interface of PE1, and MEP2 is configured on an AC interface of PE2. MEP1 initiates an ETH-test and sends test packets with a specified size and code type at a specified rate and interval. Then check the number of packets MEP1 sends and the number of packets MEP2 receives. If MEP1 sends more packets than MEP2 receives, some packets have been dropped. Then MEP1 is configured to use the bisection method to continue the test and send test packets at a lower rate. The bisection method is used to send test packets at different rates between the upper and lower rate thresholds. The test process repeats until a maximum bandwidth is found when no packets are dropped in a test. In addition, check for bit errors on MEP2 that receives test packets.
Procedure
- Run system-view
The system view is displayed.
- Run cfm enable
CFM is enabled globally.
- Run cfm md md-name
The MD view is displayed.
- Run ma ma-name
The MA view is displayed.
- Associate the MA with a service.
-
Run map mpls l2vc[ peer-address ] l2vc-id { raw | tagged }
The MA is bound to a specified L2VC.
-
Run mapmpls l2vpnl2vpn-namecece-idce-offsetce-offset-id
The MA is bound to a specified PW.
-
- Run mep mep-id
A MEP is configured.
- Run remote mep mep-id mep-id
A RMEP is configured.
- Run eth-test enable mep mep-id
The ETH-test function is enabled.
- Run eth-test start mep mep-id { mac mac-address | remote-mep mep-id } rate rate-value [ [ timeout timeout-value ] | [ pattern { zero-no-crc | zero-crc } ] | [ 8021p 8021p-value ] | [ packet-size packet-size-value ] | out-of-service { lck-level level-value } ]
The MEP is enabled to send test packets.
- (Optional) Run eth-test stop mep mep-id
The MEP is disabled from sending test packets.
- Run commit
The configuration is committed.