TCP6
Transmission Control Protocol version 6 (TCP6) provides a mechanism to establish virtual circuits between processes of two endpoints. A TCP6 virtual circuit is similar to the full-duplex circuit that transmits data between systems. TCP 6 provides reliable data transmission between processes, and is known as a reliable protocol. TCP6 also provides a mechanism to optimize transmission performance according to the network status. When all data can be received and acknowledged, the transmission rate increases gradually. Delay causes the sending host to reduce the sending rate before it receives Acknowledgement packets.
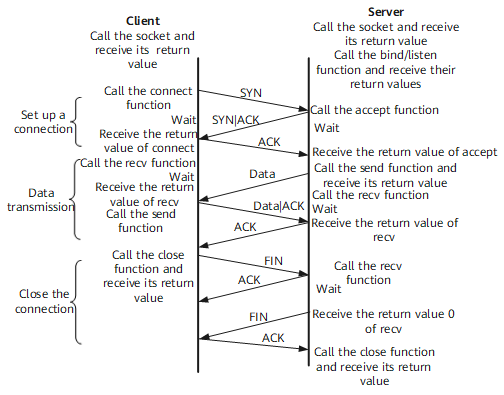
TCP6 is generally used in interactive applications, such as the web application. Certain errors in data receiving affect the normal operation of devices. TCP6 establishes virtual circuits using the three-way handshake mechanism, and all virtual circuits are deleted through the four-way handshake. TCP6 connections provide multiple checksums and reliability functions, but increase cost. As a result, TCP6 has lower efficiency than User Datagram Protocol version 6 (UDP6).
Figure 1 shows the establishment and tearing down of a TCP6 connection.