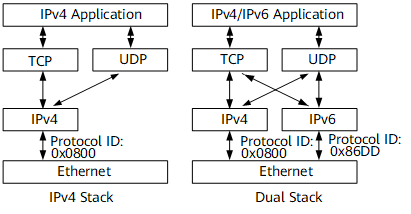
Dual Protocol Stacks
A dual-stack node supports both IPv4 and IPv6 protocol stacks. Figure Structure of a single stack and a dual stack in Ethernet shows the structure of a single stack and a dual stack.
A dual stack has the following advantages:
Multiple link protocols support the dual stack.
Multiple link protocols, such as Ethernet, support the dual stack. In Figure 1, the link protocol is Ethernet. If the value of the Protocol ID field is 0x0800 in an Ethernet frame, the network layer receives IPv4 packets; if the value is 0x86DD, the network layer receives IPv6 packets.
Multiple applications support the dual stack.
Multiple applications, such as DNS, FTP, and Telnet, support the dual stack. The upper layer applications, such as the DNS, use TCP or UDP as the transmission layer protocol and prefer the IPv6 protocol stack rather than the IPv4 protocol stack as the network layer protocol.