BFD for IP
A BFD session can be established to quickly detect faults of an IP link.
BFD for IP detects single- and multi-hop IPv4 and IPv6 links:
Single-hop BFD checks the IP continuity between directly connected systems. The single hop refers to a hop on an IP link. Single-hop BFD allows only one BFD session to be established for a specified data protocol on a specified interface.
Multi-hop BFD detects all paths between two systems. Each path may contain multiple hops, and these paths may partially overlap.
IPv4 Usage Scenario
Typical application 1:
As shown in Figure 1, BFD monitors the single-hop IPv4 path between Device A and Device B, and BFD sessions are bound to outbound interfaces.
Typical application 2:
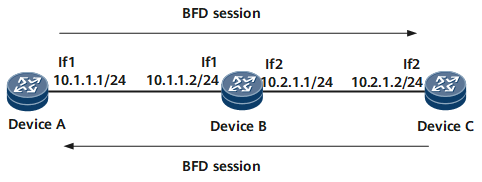
As shown in Figure 2, BFD monitors the multi-hop IPv4 path between Device A and Device C, and BFD sessions are bound only to peer IP addresses.
IPv6 Usage Scenario
Typical application 3:
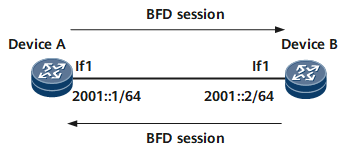
As shown in Figure 3, BFD monitors the single-hop IPv6 path between Device A and Device B, and BFD sessions are bound to outbound interfaces.
Typical application 4:
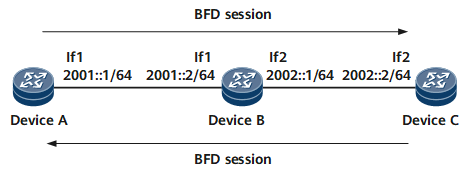
As shown in Figure 4, BFD monitors the multi-hop IPv6 path between Device A and Device C, and BFD sessions are bound only to peer IP addresses.
In BFD for IP scenarios, BFD for PST is configured on a device. If a link fault occurs, BFD detects the fault and triggers the PST to go Down. If the device restarts and the link fault persists, BFD is in the AdminDown state and does not notify the PST of BFD Down. As a result, the PST is not triggered to go Down and the interface bound to BFD is still Up.