Anti-ARP Flood Application
Networking Description
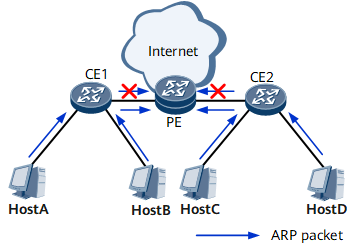
As shown in Figure 1, hosts A and B are connected to CE1, and hosts C and D are connected to CE2. The hosts access the Internet through a gateway provider edge (PE). If a large number of Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) packets are forwarded over the network, the PE becomes busy learning entries and replying to ARP packets. Therefore, the CPU will be overloaded and unable to process other services. If the ARP packets consume a lot of bandwidth, network congestion may easily occur, affecting network communication.
Feature Deployment
Strict ARP learning
After strict ARP entry learning is configured, the PE only learns address information carried in the ARP reply packets that are sent in response to the ARP request packets that the PE sends.
ARP entry limit
After ARP entry limit is configured on the PE, the PE can learn a specified number of ARP packets based on interfaces. Excess ARP packets are discarded.
ARP packet rate limit
After ARP packet rate limit is configured on the PE, the PE counts the ARP packets received. If the number of packets received in a specified period exceeds an upper limit, the PE discards the excess ARP packets.
ARP Miss message rate limit
After ARP Miss message rate limit is configured on the PE, the PE counts the number of ARP Miss messages received. If the number of Miss messages received in a specified period exceeds an upper limit, the PE does not process the excess ARP Miss messages.
Gratuitous ARP packet discarding
After gratuitous ARP packet discarding is configured on the PE, the PE discards all gratuitous ARP packets received.