Basic Multicast Framework
This section describes the basic multicast framework and key multicast techniques that transmit multicast data from a source to multiple receivers. Table 1 shows the key multicast techniques.
Multicast Technique |
Description |
|---|---|
Host registration |
Determines whether a receiver exists. |
Multicast source discovery technology |
Determines the multicast source. |
Multicast addressing mechanism |
Determines the multicast data destination. |
Multicast routing |
Forwards multicast data. |
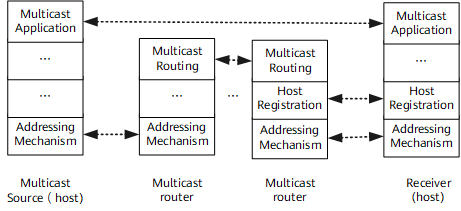
IP multicast is an end-to-end service. Figure 1 shows the four IP multicast functions from the lower protocol layer to the upper protocol layer.
The four functions operate as follows:
Addressing mechanism: transmits data to multicast groups based on multicast destination addresses.
Host registration: allows a host to dynamically join or leave a group, implementing group member management.
Multicast routing: sets up a distribution tree to transmit packets from a source to receivers.
Multicast application: To work together, multicast sources and receivers must support the same multicast application software, such as a video conferencing application. The TCP/IP protocol suite must support multicast data transmission and receipt.