Configuration Trial Run
Configuration trial run can test new functions and services on live networks without interrupting services.
Usage Scenario
Deploying unverified new services directly on live network devices may affect the current services or even disconnect devices from the network management system (NMS). To address this problem, you can deploy configuration trial run. Configuration trial run will roll back the system to the latest rollback point by discarding the new service configuration if the new services threaten system security or disconnect devices from the NMS. This function improves system security and reliability.
Principles

Configuration trial run takes effect only in two-phase configuration validation mode.
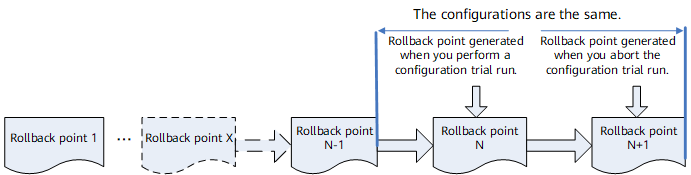
As shown in Figure 1, a user committed configurations N times. Rollback point N indicates the most recent configuration that the user committed. The configuration trial run procedure is as follows:
In two-phase configuration validation mode, you can specify a timer for the configuration trial run to take effect. Committing the configuration trial run is similar to committing an ordinary configuration, but the committed configuration takes effect temporarily for the trial. Each time you commit a configuration, the system generates a rollback point and starts the specified timer for the trial run. You cannot change the configuration during the trial run, but you can check configurations at rollback points or perform maintenance operations.
Before the timer expires, you can confirm or abort the tested configuration. If you commit the tested configuration, the timer stops and the configuration trial run ends. And if you abort the configuration trial run, the system will roll back to the latest rollback point by discarding the tested configuration. Meanwhile, a new rollback point will be generated.
After the timer expires, the system stops the configuration trial run and rolls back to the configuration prior to the configuration trial run. When the rollback is complete, the system generates a new rollback point.
The system configuration at this N+1 rollback point is the same as that at rollback point N-1.
As shown in Figure 1, the system has N-1 rollback points. After you configure the configuration trial run and commit the configuration, the system generates a rollback point N, recording the configuration to be tested. After the timer expires, the system rolls back and then generates a new rollback point N+1. Configurations at rollback points N+1 and N-1 are the same.