Association Between ERPS and Ethernet CFM
When a transmission device is connected to an Ethernet Ring Protection Switching (ERPS) ring and fails, ERPS, in absence of an automatic link detection mechanism, cannot quickly detect the device failure. This issue will make convergence slow or even cause service interruption in worse cases. To resolve this problem, ERPS can be associated with Ethernet connectivity fault management (CFM).
After Ethernet CFM is deployed on ERPS nodes connecting to transmission devices and detects a transmission link failure, Ethernet CFM informs the ERPS ring of the failure so that ERPS can perform fast protection switching.

Currently, ERPS can be associated only with outward MEPs.
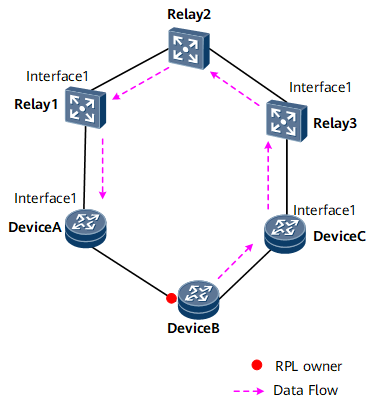
On the network shown in Figure 1, DeviceA, DeviceB, and DeviceC form an ERPS ring. Three relay nodes exist between DeviceA and DeviceC. Ethernet CFM is configured on DeviceA and DeviceC. Interface 1 on DeviceA is associated with Interface 1 on Relay 1, and Interface 1 on DeviceC is associated with Interface 1 on Relay 3.
In normal situations, the RPL owner port sends R-APS (NR) messages to all other nodes on the ring at an interval of 5s, indicating that ERPS links are normal.
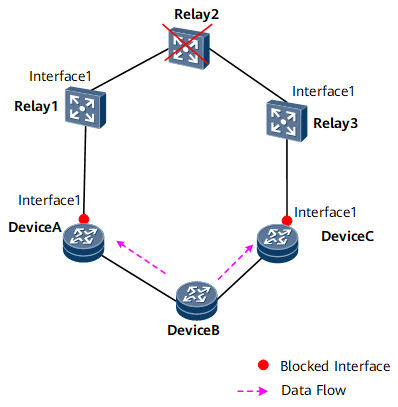
If Relay 2 fails, DeviceA and DeviceC detect the Ethernet CFM failure, block their Interface 1, send R-APS (SF) messages through their respective interfaces connected to DeviceB, and then perform a Filtering Database (FDB) flush.
After receiving an R-APS (SF) message, DeviceB unblocks the RPL owner port and performs an FDB flush. Figure 2 shows the networking after Relay 2 fails.
After Relay 2 recovers, Relay2 in revertive switching mode re-blocks the RPL owner port and sends R-APS (NR, RB) messages.
After DeviceA and DeviceC receive an R-APS (NR, RB) message, DeviceA and DeviceC unblock their blocked Interface 1 and perform an FDB flush so that traffic changes to the normal state, as shown in Figure 1.