ERPS Multi-instance
On a common ERPS network, a physical ring can be configured with a single ERPS ring, and a single blocked port can be specified on the ring. If the ERPS ring is complete, the blocked port prevents all user packets from passing through. As a result, all user packets travel through a single path over the ERPS ring, and the other link on the blocked port becomes idle, causing bandwidth wastes.
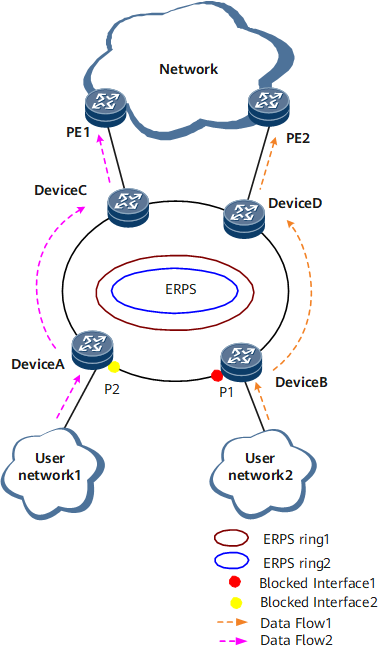
ERPS multi-instance allows two logical ERPS rings on a physical ring. On the network shown in Figure 1, Device A through Device D constitute a physical ring that has two single ERPS rings. Each ERPS ring has its devices, port roles, and control VLANs independently configured. Therefore, the physical ring has two blocked ports. Each blocked port verifies the completeness of the physical ring and blocks or forwards data without affecting each other.
ERPS multi-instance allows a physical ring to have two ERPS rings. Each ERPS ring is configured with one or more ERP instances. Each ERP instance represents a VLAN range. The topology calculated for an ERPS ring does not apply to or affect the other ERPS ring. With a specific ERP instance for each ERPS ring, a blocked port takes effect only for VLANs of that specific ERPS ring. Different VLANs can use separate paths, implementing traffic load balancing and link backup.