Bogus DHCP Server Attack
Mechanism
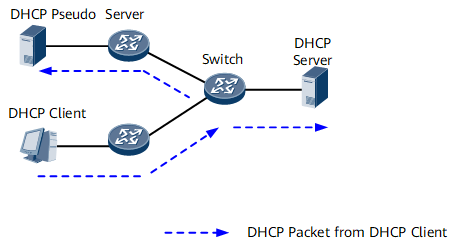
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) clients broadcast DHCP discover packets. Therefore, bogus DHCP servers can also listen to the DHCP discover packets. As shown in Figure 1, the bogus DHCP server monitors the DHCP discover packet sent from the DHCP client and sends the DHCP client a DHCP packet that carries incorrect information, such as and incorrect IP address or incorrect DNS server information. As a result, the client cannot go online.
Solution
To protect against attacks from a bogus DHCP server, configure the trusted and untrusted interfaces.
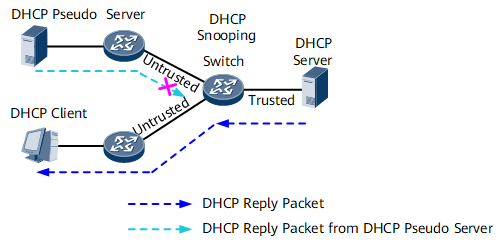
As shown in Figure 3, configure an interface as trusted or untrusted. The DHCP Reply (Offer, ACK, and NAK) packets received from the Untrusted interfaces are simply dropped. Only DHCP request and response packets on the trusted interface are sent to the CPU. This function protects against bogus DHCP server attacks and enables DHCP clients to obtain IP addresses from a legitimate DHCP server.
To prevent bogus DHCP server attacks, you can also configure whitelist rules for DHCP snooping.
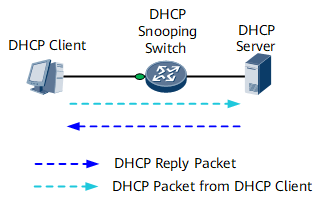
As shown in Figure 4, after a whitelist is configured for DHCP snooping, only DHCP packets listed in the whitelist are sent to the CPU, and the DHCP packets not listed in the whitelist are simply forwarded, without being sent to the CPU. This protects the device against attacks.