Basic VRRP Functions and Concepts
Basic VRRP Functions
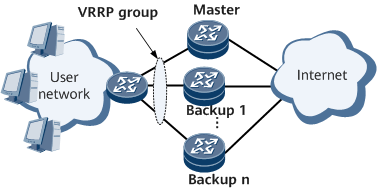
- A single VRRP group is configured and consists of a master device and several backup devices.
- The router with the highest priority functions as the master device and forwards service traffic.
- Other routers function as backup devices and monitor the master device's status. If the master device fails, a backup device with the highest priority preempts the master role and takes over service traffic forwarding.Figure 2 Networking diagram of VRRP in load balancing mode
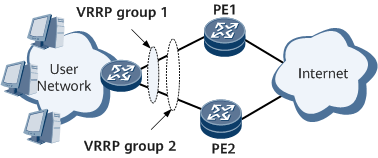
- PE1 functions as the master device in VRRP group 1 and the backup device in VRRP group 2.
- PE2 functions as the master device in VRRP group 2 and the backup device in VRRP group 1.
- In normal circumstances, different routers process different user groups' traffic to implement load balancing.

VRRP load balancing can be implemented in two modes. For details, see VRRP Fundamentals in HUAWEI NetEngine 8000 F Series Router Feature Description - Network Reliability.
Basic VRRP Concepts
- Virtual router: also referred to as a VRRP group, consists of a master device and one or more backup devices. A virtual router is a default gateway used by hosts within a shared LAN, and is identified by a virtual router ID and one or more virtual IP addresses.
VRID: virtual router ID. A group of devices with the same VRID form a virtual router.
Virtual IP address: IP address of a virtual router. A virtual router can have one or more virtual IP addresses, which are manually assigned.
Virtual MAC address: MAC address that is generated by the virtual router based on the VRID. A virtual router has one virtual MAC address, in the format of 00-00-5E-00-01-{VRID} (VRRP for IPv4) or 00-00-5E-00-02-{VRID} (VRRP for IPv6). A virtual router uses the virtual MAC address instead of the actual interface MAC address to respond to ARP (VRRP for IPv4) or NS (VRRP for IPv6) requests.
IP address owner: A VRRP device is considered an IP address owner if it uses the virtual IP address as a real interface address. If an IP address owner is available, it usually functions as the master in a VRRP group.
Primary IP address: an IP address (usually the first configured one) selected from the set of real interface IP addresses. The primary IP address is used as the source IP address in a VRRP Advertisement packet.
- VRRP router: a device running VRRP. It can belong to one or more virtual routers.
Virtual router master: a VRRP device that forwards packets.
Virtual router backup: a group of VRRP devices that do not forward packets. Instead, they can be elected as the new master if the current master fails.
Priority: priority of a router in a VRRP group. A VRRP group elects the master and backup devices based on priorities.
- VRRP preemption mode:
Preemption mode: In this mode, a backup device preempts the master role if it has a higher priority than that of the current master.
Non-preemption mode: In this mode, a backup device does not preempt the master role even if it has a higher priority than that of the current master, provided that the current master is working properly.
- VRRP timers:
- Adver_Interval timer: The master sends a VRRP Advertisement packet each time the Adver_Interval timer expires. The default timer value is 1 second.
- Master_Down timer: A backup device preempts the master role after the Master_Down timer expires. The Master_Down timer value is calculated using the following formula: Master_Down timer value = (3 x Adver_Interval timer value) + Skew_Time, where Skew_Time = (256 - Priority)/256