VRRP Advertisement Packets
VRRP Advertisement packets are multicast packets that can be forwarded only within a single broadcast domain, such as a VLAN or VSI. They are used to notify all backup devices in a VRRP group of the master's priority and status.
On an IPv4 network, VRRP packets are encapsulated into IPv4 packets and sent to an IPv4 multicast address assigned to a VRRP group. In the IPv4 packet header, the source address is the primary IPv4 address of the interface that sends the packets (not the virtual IPv4 address), the destination address is 224.0.0.18, the TTL is 255, and the protocol number is 112.
On an IPv6 network, VRRP packets are encapsulated into IPv6 packets and sent to an IPv6 multicast address assigned to a VRRP6 group. In the IPv6 packet header, the source address is the link-local address of the interface that sends the packets (not the virtual IPv6 address), the destination address is FF02::12, the TTL is 255, and the protocol number is 112.

You can manually switch VRRP versions on a NetEngine 8000 F. Unless otherwise specified, VRRP packets in this document refer to VRRPv2 packets.
VRRP Packet Structure
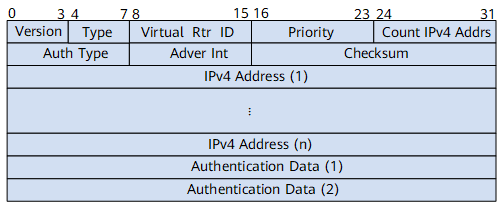
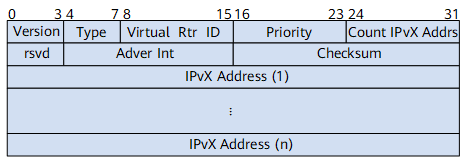
Figure 1 and Figure 2 show VRRPv2 and VRRPv3 packet structures, respectively.
Field |
Description |
|---|---|
Version |
VRRP version number. The value is 2. |
Type |
Type of a VRRP packet. The value is 1, indicating an Advertisement packet. |
Virtual Rtr ID |
Virtual router ID. |
Priority |
Priority of the master device in a VRRP group. |
Count IPv4 Addrs |
Number of virtual IPv4 addresses in a VRRP group. |
Auth Type |
Authentication type of a VRRP packet. Three authentication types are defined:
|
Adver Int |
Interval (in seconds) at which VRRP packets are sent. |
Checksum |
16-bit checksum, used to check the data integrity of a VRRP packet. |
IPv4 Address |
Virtual IPv4 address configured for a VRRP group. The number of virtual IPv4 addresses configured is carried in the Count IPv4 Addrs field. |
Authentication Data |
Authentication key of a VRRP packet. This field applies only when simple or MD5 authentication is used. For other authentication types, this field is fixed at 0. |
Field |
Description |
|---|---|
Version |
VRRP protocol version. The value is 3. |
Type |
Type of a VRRP packet. The value is 1, indicating an Advertisement packet. |
Virtual Rtr ID |
Virtual router ID. |
Priority |
Priority of the master device in a VRRP group. |
Count IPvX Addrs |
Number of virtual IPvX addresses configured for a VRRP group. |
rsvd |
Field reserved in a VRRPv3 packet. The value is fixed at 0. |
Adver Int |
Interval (in centiseconds) at which VRRP packets are sent. |
Checksum |
16-bit checksum, used to check the data integrity of a VRRP packet. |
IPvX Address |
Virtual IPvX address configured for a VRRP group. The number of configured virtual IPvX addresses is carried in the Count IPvX Addrs field. |
Authentication: VRRPv3 does not support authentication, whereas VRRPv2 does.
Time unit of the interval for sending VRRP Advertisement packets: VRRPv3 uses centiseconds, whereas VRRPv2 uses seconds.