PW Redundancy
PW Redundancy Signaling
In conventional Pseudowire Emulation Edge-to-Edge (PWE3), one-to-one mapping is implemented between ACs and PWs. To ensure the same forwarding capability, the PW redundancy mechanism to be used must allow only a single PW in a PW group to forward traffic.
Relevant standards specify the PW Status TLV to transmit the PW forwarding status. The PW Status TLV is transported to the remote PW end using a Label Mapping or LDP Notification message. The PW Status TLV is 32 bits long. Each bit can be set individually to indicate a PW forwarding state. PW redundancy introduces a new PW status code of 0x00000020 indicating "PW forwarding standby."

PW redundancy is supported only in PWE3 VPWS.
Primary/Secondary and Active/Inactive PWs
PW redundancy involves the following terms:
Primary/Secondary: indicates the forwarding priority of a PW and can be specified.
The primary PW is preferentially used to forward traffic, and the secondary PW is used to protect the primary PW. The primary PW forwards traffic when the primary and secondary PWs work in the active state. Currently, only a single secondary PW can be configured for a primary PW. Note that a bypass PW can be considered as a secondary PW.
Active/Inactive: indicates the PW forwarding status, as known as the PW running status. The forwarding status cannot be configured.
Traffic can only be forwarded along active PWs. The signaling status and configured forwarding priority (primary/secondary) determine the PW forwarding status (active/inactive). Only the PW with the optimal signalling status and the higher priority is selected as an active PW to forward traffic. Other PWs are in the inactive state. Inactive PWs cannot forward traffic. If VLL PWs are used, inactive VLL PWs can be configured to receive traffic.
PW Redundancy Modes
PW redundancy modes are specified on PEs where primary and secondary PWs are configured. If no working mode is specified, PWE3 FRR is used.

In PWE3 FRR, a PE locally determines the primary/secondary PW status and does not notify a remote PE of such status. Therefore, the remote PE is unaware of the primary and secondary PWs. PWE3 FRR is implemented on Huawei devices only and is not recommended.
Master/Slave mode:
In this mode, the local PE determines the primary/secondary PW status and uses a signaling protocol to notify the remote PE of such status. The remote PE then can obtain the primary/secondary PW status. The PW-side and AC-side primary/secondary status do not affect each other, and therefore, PW- and AC-side faults are isolated.
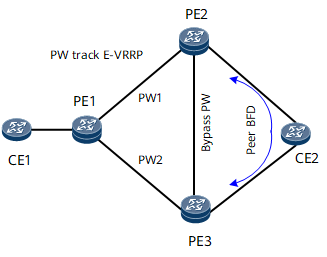
As shown in Figure 1, in a 3PE PW redundancy scenario, the master/slave mode is used, which means that the local end determines the primary/secondary PW status. If the master/slave mode is deployed on PE1, PE1 selects a PW based on the configured priority and the PW up/down status. If the primary PW is up, PE1 always selects the configured primary PW to forward traffic. In master/slave PW redundancy mode, PE1 notifies the remote PEs (PE2 and PE3) of the selection result. PE2 and PE3 determine whether to forward traffic over this PW based on the PW status notified by PE1.
Independent mode:
In this mode, the primary/secondary status of the local PWs is determined by the negotiation result on the remote end (PE2 and PE3), and the remote end notifies the local end of the primary/secondary status. If a fault occurs on the AC side, it affects both the AC and PW sides and triggers protection switching on both sides, indicating a fault isolation failure.
As shown in Figure 1, in a 3PE PW redundancy scenario, the independent mode is used, which means that the remote end determines the primary/secondary PW status. If the independent mode is deployed on PE1, PE1 does not concern the locally configured primary/secondary priority, but uses the status notified by the remote PEs (PE2 and PE3). If PE2 notifies its active PW state to PE1, PE1 selects PW1 connected to PE2 to forward traffic. If PE3 notifies its active PW state to PE1, PE1 selects PW2 connected to PE3. If both remote PEs notify PE1 of their active PW states, PE2 selects the PW whose status is notified later.

In PWE3 scenarios, the independent mode is usually used to improve switching performance.
PW Redundancy Usage Scenarios
3PE PW redundancy
E-Trunk 1:1 protection is used.
The master/slave mode is supported, and in this mode, bypass PWs can be configured.
The independent mode is supported, and in this mode, bypass PWs can be configured.
4PE PW redundancy
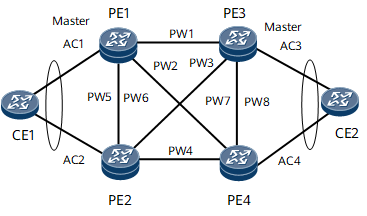
VRRP or E-Trunk 1:1 protection is supported.
The master/slave mode is not supported.
The independent mode is supported.
- Dual bypass PWs can be configured only for Ethernet services.
Dual bypass PWs do not support heterogeneous interworking.
Bypass PWs do not support VPN QoS.
The bypass PW must be fault-free.