Basic Concepts
Background
Layer 2 protocols running between user networks, such as Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) and Link Aggregation Control Protocol (LACP), must traverse a backbone network to perform Layer 2 protocol calculation.
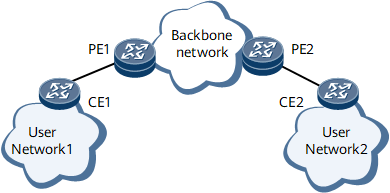
On the network shown in Figure 1, User Network 1 and User Network 2 both run a Layer 2 protocol, Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol (MSTP). Layer 2 protocol data units (PDUs) on User Network 1 must traverse a backbone network to reach User Network 2 to build a spanning tree. Generally, the destination MAC addresses in Layer 2 PDUs of the same Layer 2 protocol are the same. For example, the MSTP PDUs are BPDUs with the destination MAC address 0180-C200-0000. Therefore, when a Layer 2 PDU reaches an edge device on a backbone network, the edge device cannot identify whether the PDU comes from a user network or the backbone network and sends the PDU to the CPU to calculate a spanning tree.
In Figure 1, CE1 on User Network 1 builds a spanning tree together with PE1 but not with CE2 on User Network 2. As a result, the Layer 2 PDUs on User Network 1 cannot traverse the backbone network to reach User Network 2.
To resolve the preceding problem, use Layer 2 protocol tunneling. The NetEngine 8000 F supports tunneling for the following Layer 2 protocols:
- Cisco Discovery Protocol (CDP)
- Ethernet Local Management Interface (E-LMI)
- Ethernet in the First Mile OAM (EOAM3AH)
- Device link detection protocol (DLDP)
- Dynamic Trunking Protocol (DTP)
- Ethernet in the First Mile (EFM)
- GARP Multicast Registration Protocol (GMRP)
- GARP VLAN Registration Protocol (GVRP)
- Huawei Group Management Protocol (HGMP)
- Link Aggregation Control Protocol (LACP)
- Link Layer Discovery Protocol (LLDP)
- Multiple MAC Registration Protocol (MMRP)
- Multiple VLAN Registration Protocol (MVRP)
- Port Aggregation Protocol (PAgP)
- Secure Socket Tunneling Protocol (SSTP)
- Spanning Tree Protocol (STP)
- Unidirectional Link Detection (UDLD)
- VLAN Trunking Protocol (VTP)
Layer 2 PDUs can be tunneled across a backbone network if all of the following conditions are met:
All sites of a user network can receive Layer 2 PDUs from one another.
Layer 2 PDUs of a user network are not processed by the CPUs of backbone network devices.
Layer 2 PDUs of different user networks must be isolated and not affect each other.
Layer 2 protocol tunneling prevents Layer 2 PDUs of different user networks from affecting each other, which cannot be achieved by other technologies.
BPDU
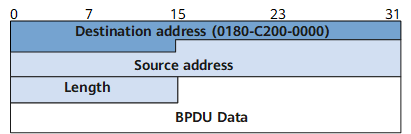
Bridge protocol data units (BPDUs) are most commonly used by Layer 2 protocols, such as STP and MSTP. BPDUs are protocol packets multicast between Layer 2 switches. BPDUs of different protocols have different destination MAC addresses and are encapsulated in compliance with IEEE 802.3. Figure 2 shows the BPDU format.
A BPDU consists of four fields:
Destination Address: destination MAC address, 6 bytes
Source Address: source MAC address, 6 bytes
Length: length of the BPDU, 2 bytes
BPDU Data: BPDU content
Layer 2 protocol tunneling provides a BPDU tunnel for BPDUs. The BPDU tunnel can be considered a Layer 2 tunneling technology that allows user networks at different regions to transparently transmit BPDUs across a backbone network, isolating user networks from the backbone network.