Association Between VRRP and a VRRP-disabled Interface
Background
Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol (VRRP) can monitor the status change only in the VRRP-enabled interface on the master device. If a VRRP-disabled interface on the master device or the uplink connecting the interface to a network fails, VRRP cannot detect the fault, which causes traffic interruptions.
To resolve this issue, configure VRRP to monitor the VRRP-disabled interface status. If a VRRP-disabled interface on the master device or the uplink connecting the interface to a network fails, VRRP instructs the master device to reduce its priority to trigger a master/backup VRRP switchover.
Related Concepts
- Increased mode: The VRRP device increases its VRRP priority by a specified value.
- Reduced mode: The VRRP device reduces its VRRP priority by a specified value.
Implementation
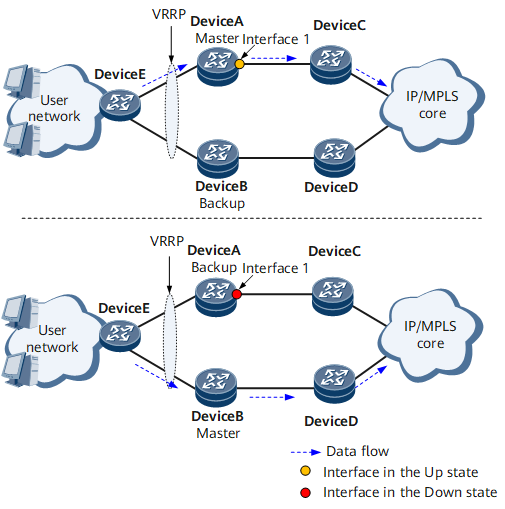
As shown in Figure 1, a VRRP group is configured on Device A and Device B. Device A is the master device, and Device B is the backup device.
Device A is configured to monitor interface 1. If interface 1 fails, Device A reduces its VRRP priority and sends a VRRP Advertisement packet carrying a reduced priority. After Device B receives the packet, it checks that its VRRP priority is higher than the received priority and preempts the Master state.
After interface 1 goes Up, Device A restores the VRRP priority. After Device A receives a VRRP Advertisement packet carrying Device B's priority in preemption mode, Device A checks that its VRRP priority is higher than the received priority and preempts the Master state.
Benefits
The association between VRRP and a VRRP-disabled interface helps trigger a master/backup VRRP switchover if the VRRP-disabled interface fails or the uplink connecting the interface to a network fails.