mVRRP
Principles
A switch is dual-homed to two routers at the aggregation layer on a metropolitan area network (MAN). Multiple VRRP groups can be configured on the two routers to transmit various types of services. Because each VRRP group must maintain its own state machine, a large number of VRRP Advertisement packets are transmitted between the routers.
To help reduce bandwidth and CPU resource consumption during VRRP packet transmission, a VRRP group can be configured as a management Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol (mVRRP) group. Other VRRP groups are bound to the mVRRP group and become service VRRP groups. Only the mVRRP group sends VRRP packets to negotiate the master/backup status. The mVRRP group determines the master/backup status of service VRRP groups.
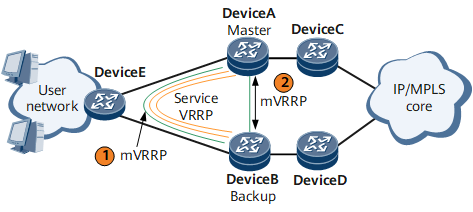
As shown in Figure 1, an mVRRP group can be deployed on the same side as service VRRP groups or on the interfaces that directly connect Device A and Device B.
Related Concepts
mVRRP group: has all functions of a common VRRP group. Different from a common VRRP group, an mVRRP group can be tracked by service VRRP groups and determine their statuses. An mVRRP group provides the following functions:
- When the mVRRP group functions as a gateway, it determines the master/backup status of devices and transmits services. In this situation, a common VRRP group with the same ID as the mVRRP group must be created and assigned a virtual IP address. The mVRRP group's virtual IP address is a gateway IP address set by users.
- When the mVRRP group does not function as a gateway, it determines the master/backup status of devices but does not transmit services. In this situation, the mVRRP group does not require a virtual IP address. You can create an mVRRP group directly on interfaces to simplify maintenance.
Service VRRP group: After common VRRP groups are bound to an mVRRP group, they become service VRRP groups. Service VRRP groups do not need to send VRRP packets to determine their states. The mVRRP group sends VRRP packets to determine its state and the states of all its bound service VRRP groups. A service VRRP group can be bound to an mVRRP group in either of the following modes:
- Flowdown: The flowdown mode applies to networks on which both upstream and downstream packets are transmitted over the same path. If the master device in an mVRRP group enters the Backup or Initialize state, the VRRP module instructs all service VRRP groups that are bound to the mVRRP group in flowdown mode to enter the Initialize state.
- Unflowdown: The unflowdown mode applies to networks on which upstream and downstream packets can be transmitted over different paths. If the mVRRP group enters the Backup or Initialize state, the VRRP module instructs all service VRRP groups that are bound to the mVRRP group in unflowdown mode to enter the same state.

Multiple service VRRP groups can be bound to an mVRRP group. However, the mVRRP group cannot function as a service group and is bound to another mVRRP group.
If a physical interface on which a service VRRP group is configured goes Down, the status of the service VRRP group becomes Initialize, irrespective of the status of the mVRRP group.
Benefits
VRRP offers the following benefits:
- Simplified management. An mVRRP group determines the master/backup status of service VRRP groups.
- Reduced CPU and bandwidth resource consumption. Service VRRP groups do not need to send VRRP packets.