Label Advertisement and Management
After an LDP session is established, LDP starts to exchange messages, such as Label Mapping messages, to establish LSPs. Related standards define how LSRs advertise and manage labels, including label advertisement, distribution control, and retention modes.
The device currently supports the following combinations of modes:
- Downstream unsolicited (DU) label advertisement+ordered label control+liberal label retention
- Downstream on demand (DoD) label advertisement+ordered label control+conservative label retention
The default label advertisement and management modes are DU label advertisement+ordered label control+liberal label retention.
Label Advertisement Mode
An LSR on an MPLS network binds a label to a specific FEC and notifies its upstream LSRs of the binding. That is, labels are specified by downstream LSRs and distributed from downstream to upstream.
The label advertisement modes on upstream and downstream LSRs must be the same. Two label advertisement modes are available:
- DU mode: An LSR binds a label to a specific FEC and notifies its upstream LSR of the binding, without having to first receive a Label Request message sent by the upstream LSR.
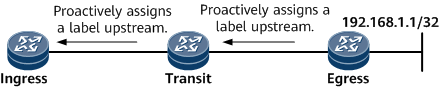
In Figure 1, the downstream egress triggers the establishment of an LSP destined for FEC 192.168.1.1/32 in host mode by sending a Label Mapping message to the upstream transit LSR to advertise the label of its host route 192.168.1.1/32.
- DoD mode: An LSR binds a label to a specific FEC and notifies its upstream LSR of the binding only after it receives a Label Request message from the upstream LSR.
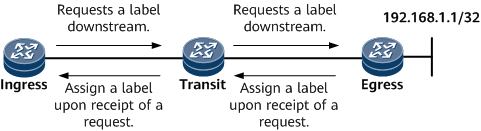
In Figure 2, the downstream egress triggers the establishment of an LSP destined for FEC 192.168.1.1/32 in host mode. The upstream ingress sends a Label Request message to the downstream egress. The downstream egress sends a Label Mapping message to the upstream LSR only after receiving the Label Request message.
Label Distribution Control Mode
The label distribution control mode defines how an LSR distributes labels during the establishment of an LSP. Two label distribution control modes are available:
- Independent mode: A local LSR binds a label to an FEC and distributes this label to an upstream LSR without waiting for a label assigned by a downstream LSR.
- In Figure 1, if the label distribution mode is DU and the label distribution control mode is Independent, the transit LSR distributes labels to the upstream ingress without waiting for labels assigned by the downstream egress.
- In Figure 2, if the label distribution mode is DoD and the label distribution control mode is Independent, the downstream transit LSR directly connected to the ingress LSR that sends a Label Request message replies with labels without waiting for labels assigned by the downstream egress.
- Ordered mode: An LSR advertises the mapping between a label and an FEC to its upstream LSR only when this LSR has received a Label Mapping message from the next hop of the FEC or the LSR is the egress of the FEC.
- In Figure 1, if the label distribution mode is DU and the label distribution control mode is ordered, the transit LSR distributes a label to the upstream ingress only after receiving a Label Mapping message from the downstream egress.
- In Figure 2, if the label distribution mode is DoD and the label distribution control mode is ordered, the transit LSR directly connected to the ingress LSR that sends a Label Request message distributes a label upstream to the ingress only after receiving a Label Mapping message from the downstream egress.
Label Retention Mode
The label retention mode defines how an LSR processes label mappings from non-preferred next hops. The label mappings that an LSR receives may or may not originate from the next hop. Two label retention modes are available:
- Liberal mode: An LSR retains the label mappings received from a neighbor LSR regardless of whether the neighbor LSR is its next hop.
- Conservative mode: An LSR retains the label mappings received from a neighbor LSR only when the neighbor LSR is its next hop.
When the next hop of an LSR changes due to a network topology change:
- In liberal mode, the LSR can use the labels advertised by a non-next hop LSR to quickly reestablish an LSP. This mode, however requires more memory and label space than the conservative mode. An LSP that has been assigned a label but fails to be established is called a liberal LSP.
- In conservative mode, the LSR retains the labels advertised by the next hop only. This mode saves memory and label space but takes more time to reestablish an LSP. Conservative label retention mode is usually used together with DoD on the LSRs that have limited label space.