EVPN VPLS MAC Ping
Overview
VPLS MAC ping can be used to check whether the path across an EVPN VPLS network to a specified destination MAC address is reachable and whether a specified destination MAC address exists.
Similar to MPLS ping, which uses MPLS Echo Request and MPLS Echo Reply packets to detect LSP availability, EVPN VPLS MAC ping uses EVPN Echo Request and EVPN Echo Reply packets to detect EVPN VPLS connectivity. The two types of packets are sent in UDP packets with port number 3503, the receive end identifies the EVPN Echo Request and EVPN Echo Reply packets based on the UDP port number.
An EVPN echo request message carries information about the forwarding equivalence class (FEC) for an EVPN tunnel to be monitored. The EVPN echo request message is forwarded with other service packets of the same FEC along the EVPN tunnel. This procedure enables EVPN connectivity check. In addition, EVPN echo request messages are transmitted to the destination using EVPN tunnels, whereas EVPN echo reply messages are transmitted to the source using IP.

Currently, EVPN VPLS MAC ping can carry traffic over LDP, TE, VXLAN, BGP LSP, SR-MPLS TE, SR-MPLS BE, SRv6 BE, and SRv6 TE Policy tunnels.
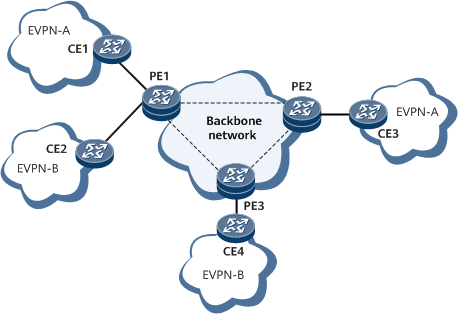
Working process of EVPN VPLS MAC ping in a single-active scenario
As shown in Figure 1, CE1 and CE3 are user-side access devices at both ends of the network and are directly connected to the network. The process of initiating an EVPN MAC ping test from PE1 is as follows:
PE1 accesses an EVPN VPLS network in either of the following modes.
- Common access mode: The EVPN name and destination MAC address must be specified.
- Access through the bridge domain (BD): The BD ID and destination MAC address must be specified.
A destination MAC address can be the bridge MAC address of the remote PE or the MAC address of the remote CE. PE1 queries the MAC address, finds the corresponding EVPN VPLS public network tunnel, and sends an EVPN VPLS MAC ping test packet.
The packet passes along the EVPN VPLS public network tunnel and arrives at PE2.
After receiving the EVPN VPLS MAC ping test packet, PE2 obtains the bridge MAC address of PE1 from the test packet and sends a reply packet.
PE1 receives the reply packet sent from PE2. The EVPN VPLS MAC ping test succeeds, and the EVPN VPLS public network tunnel between PE1 and PE2 is normal.
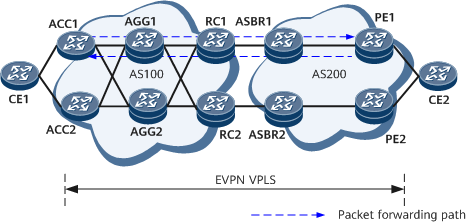
Working process of EVPN VPLS MAC ping in an inter-AS active-active scenario
As shown in Figure 2, CE1 and CE3 are user-side access devices at both ends of the VPLS network and are directly connected to the VPLS network. The process of the EVPN VPLS MAC ping initiated by ACC1 to PE1 is as follows:
- ACC1 initiates an EVPN VPLS MAC ping test. If the destination MAC route fails to be found, ACC1 broadcasts the packet in the BD. The source MAC address of the packet is the system MAC address of ACC1.
- After receiving the ARP Request packet, PE1 finds that the destination MAC address is the MAC address of itself. Then, PE1 replies with an ARP Reply packet, but fails to find the route to the source MAC address. PE1 then broadcasts the ARP Request packet in the BD and delivers the MAC address of itself to the static MAC address table to trigger MAC address learning.
- After receiving the request packet, PE2 finds that the MAC address in the packet is not its own MAC address and discards the packet.
- After receiving the reply packet, ACC1 displays the MAC address, delivers the local MAC address to the static MAC address table to trigger MAC address learning, and sends packets to PE1 in unicast mode.
- After receiving the response packet, ACC2 discards the packet because no detection session is established.
- After receiving the request packet, PE1 checks that the destination MAC address is the MAC address of itself. Then, PE1 responds to PE1 with a unicast response packet after finding the route to the source MAC address.
The process of the EVPN VPLS MAC ping initiated by ACC1 to CE2 is as follows:
- ACC1 initiates an EVPN VPLS MAC ping test. If the destination MAC route fails to be found, ACC1 broadcasts the packet in the BD. The source MAC address of the packet is the system MAC address of ACC1.
- After PE1 or PE2 receives the ARP Request packet, it finds that the destination MAC address is the MAC address of CE2. Then, PE1 or PE2 replies with an ARP Reply packet, but fails to find the route to the source MAC address. As a result, PE1 or PE2 broadcasts the ARP Request packet in the BD.
- After receiving the reply packet, ACC1 displays the MAC address, delivers the local MAC address to the static MAC address table to trigger MAC address learning, and sends packets to PE1 in unicast mode.
- After receiving the response packet, ACC2 discards the packet because no detection session is established.