Load Balancing and Route Backup
Load Balancing
The NetEngine 8000 F supports the multi-route model (multiple routes with the same destination and priority). Routes discovered by one routing protocol with the same destination and cost can load-balance traffic. In each routing protocol view, you can run the maximum load-balancing number command to perform load balancing. Load balancing can work per-destination or per-packet.
Per-packet load balancing
With per-packet load balancing, the router forwards packets destined for the same destination through equal-cost routes, and each time the next hop address is different from the last one.
Per-destination load balancing
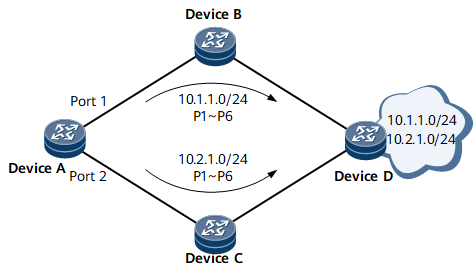
After per-destination load balancing is configured, the router forwards packets based on the quintuple (the source address, destination address, source port, destination port, and protocol in the packets). When the quintuple is the same, the router always chooses the next hop address that is the same as the last one to send packets. Figure 1 per-destination load balancing.
Device A needs to forward packets to 10.1.1.0/24 and 10.2.1.0/24. Based on per-destination load balancing, packets of the same flow are transmitted along the same path. The processes for forwarding packets on Device A are as follows:
The first packet P1 to 10.1.1.0/24 is forwarded through Port 1, and all subsequent packets to 10.1.1.0/24 are forwarded through Port 1.
The first packet P1 to 10.2.1.0/24 is forwarded through Port 2, and all subsequent packets to 10.2.1.0/24 are forwarded through Port 2.
Currently, RIP, OSPF, BGP, and IS-IS support load balancing, and static routes also support load balancing.

The number of equal-cost routes for load balancing varies with products.
Route Backup
The NetEngine 8000 F supports route backup to improve network reliability. You can configure multiple routes to the same destination as required. The route with the highest priority functions as the primary route, and the other routes with lower priorities function as backup routes.
In most cases, the NetEngine 8000 F uses the primary route to forward packets. If the link fails, the primary route becomes inactive. The NetEngine 8000 F then selects a backup route with the highest priority to forward packets, and the primary route is switched to the backup route. When the original primary route recovers, the NetEngine 8000 F restores and reselects the optimal route. Because the original primary route has the highest priority, the NetEngine 8000 F selects this route to send packets. Therefore, the backup route is switched to the primary route.