Priority-based Route Convergence
Definition
Priority-based route convergence is an important technology that improves network reliability. It provides faster route convergence for key services. For example, to minimize the interruption of key services in case of network faults, real-time multicast services require that the routes to the multicast source quickly converge, and the Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) VPN bearer network requires that routes between PEs also quickly converge.
Convergence priorities provide references for the system to converge routes for service forwarding. Different routes can be set with different convergence priorities, which can be identified as critical, high, medium, and low listed in descending order.
Purpose
With the integration of network services, requirements on service differentiation increase. Carriers require that the routes for key services, such as Voice over IP (VoIP) and video conferencing services converge faster than those for common services. Therefore, routes need to converge based on their convergence priorities to improve network reliability.
Route Convergence Priority
Table 1 lists the default convergence priorities of public network routes. You can set convergence priorities for routes based on the requirements of a live network.
Routing Protocol or Route Type |
Convergence Priority |
|---|---|
Direct |
Critical |
Static |
Medium |
32-bit host routes of OSPF and IS-IS |
Medium |
OSPF route (except 32-bit host routes) |
Low |
IS-IS route (except 32-bit host routes) |
Low |
RIP |
Low |
BGP |
Low |

For VPN route priorities, only 32-bit host routes of OSPF and IS-IS are identified as medium, and the other routes are identified as low.
Applications
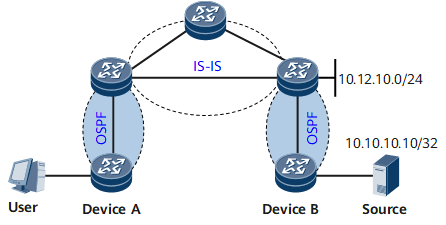
Figure 1 shows networking for multicast services. An IGP runs on the network; Device A is the receiver, and Device B is the multicast source server with IP address 10.10.10.10/32. The route to the multicast source server is required to converge faster than other routes, such as 10.12.10.0/24. In this case, you can set a higher convergence priority for 10.10.10.10/32 than that of 10.12.10.0/24. Then, when routes converge on the network, the route to the multicast source server 10.10.10.10/32 converges first, ensuring the transmission of multicast services.