Basic Concepts
OAMPDUs
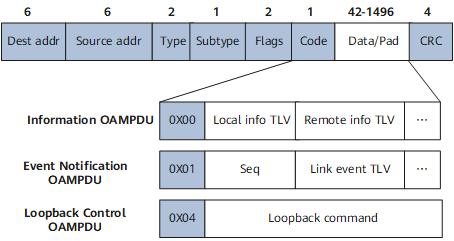
EFM works at the data link layer and uses protocol packets called OAM protocol data units (OAMPDUs). EFM devices periodically exchange OAMPDUs to report link status, helping network administrators effectively manage networks. Figure 1 shows the format and common types of OAMPDUs. Table 1 lists and describes fields in an OAMPDU.
Field |
Description |
|---|---|
Dest addr |
Destination MAC address, which is a slow-protocol multicast address. Network bridges cannot forward slow-protocol packets. EFM OAMPDUs cannot be forwarded over multiple devices, even if OAM is supported or enabled on the devices. |
Source addr |
Source address, which is a unicast MAC address of a port on the transmit end. If no port MAC address is specified on the transmit end, the bridge MAC address of the transmit end is used. |
Type |
Slow protocol type, which has a fixed value of 0x8809. |
Subtype |
Subtype of a slow protocol. The value is 0x03, which means that the slow sub-protocol is EFM. |
Flags |
Status of an EFM entity:
|
Code |
OAMPDU type:
Table 2 describes common types of OAMPDUs. |
OAMPDU Type |
Description |
|---|---|
Information OAMPDU |
|
Event Notification OAMPDU |
Used to monitor links. If an errored frame event, errored symbol period event, or errored frame second summary event occurs on an interface, the interface sends an Event Notification OAMPDU to notify the remote interface of the event. |
Loopback Control OAMPDU |
Used to enable or disable the remote loopback function. |
Connection Modes
EFM supports two connection modes: active and passive. Table 3 describes capabilities of processing OAMPDUs in the two modes.
Capability |
Active Mode |
Passive Mode |
|---|---|---|
Initiate a connection request by sending an Information OAMPDU during the discovery process. |
Supported |
Not supported |
Respond to a connection request during the discovery process. |
Supported |
Supported |
Send Information OAMPDUs. |
Supported |
Supported |
Send Event Notification OAMPDUs. |
Supported |
Supported |
Send Loopback Control OAMPDUs. |
Supported |
Not supported |
Respond to Loopback Control OAMPDUs. |
Supported (The remote EFM entity must work in active mode.) |
Supported |

An EFM connection can be initiated only by an OAM entity working in active mode. An OAM entity working in passive mode waits to receive a connection request from its peer entity. Two OAM entities that both work in passive mode cannot establish an EFM connection between them.
An OAM entity that is to initiate a loopback request must work in active mode.