Background
As telecommunication technologies develop quickly and the demand for service diversity is increasing, various user-oriented tele services are being provided over digital and intelligent media through broadband paths. Backbone network technologies, such as synchronous digital hierarchy (SDH), passive optical network (PON), and dense wavelength division multiplexing (DWDM), grow mature and popular. The technologies allow the voice, data, and video services to be transmitted over a single path to every home. Telecommunication experts and carriers focus on using existing network resources to support new types of services and improve the service quality. The key point is to provide a solution to the last-mile link to a user network.
A "last mile" reliability solution also needs to be provided. High-end clients, such as banks and financial companies, demand high reliability. They expect carriers to monitor both carrier networks and last-mile links that connect users to those carrier networks. EFM can be used to satisfy these demands.
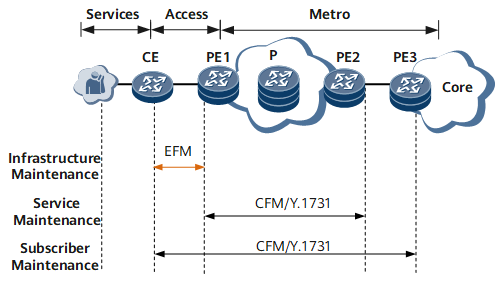
On the network shown in Figure 1, EFM is an OAM mechanism that applies to the last-mile Ethernet access links to users. Carriers use EFM to monitor link status in real time, rapidly locate failed links, and identify fault types if faults occur. OAM entities exchange various OAMPDUs to monitor link connectivity and locate link faults.