Association between VRRP and CFM
Context
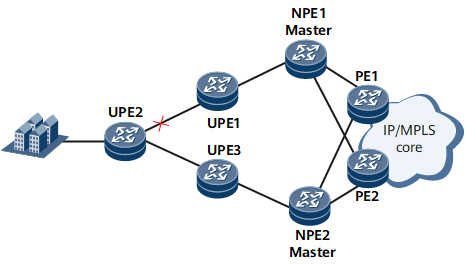
Association between VRRP and Ethernet in the First Mile (EFM) effectively speeds up link fault detection on a network where UPEs do not support BFD. However, EFM can detect faults only on single-hop links. As shown in Figure 1, EFM cannot detect faults on the link between NPE1 and UPE2 or between NPE2 and UPE2 because UPE1 are deployed between NPE1 and NPE2 and UPE3 are deployed between NPE2 and UPE2.
Connectivity fault management (CFM) defined in 802.1ag provides functions, such as E2E connectivity fault detection, fault notification, fault verification, and fault locating. CFM can monitor the connectivity of the entire network and locate connectivity faults. It can also be used together with protection switching techniques to improve network reliability. Association between VRRP and CFM enables a VRRP group to rapidly perform a master/backup VRRP switchover when CFM detects a link fault. This implementation minimizes service interruption time.
Implementation

CFM can detect only local link (NPE1-UPE2 link) failures. If the remote link (NPE2-UPE2 link) fails, NPE2 functioning as the backup cannot detect the failure. NPE2 has to wait for a period three times the interval at which VRRP Advertisement packets are sent before it switches to the Master state. During this period, upstream service traffic is interrupted. To speed up master/backup VRRP switchovers and minimize the service interruption time, configure VRRP also to track the peer BFD session.
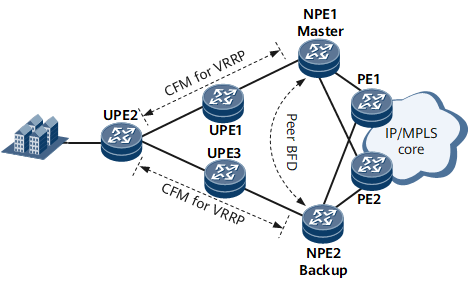
NPE1 and NPE2 run VRRP.
A peer BFD session is established between NPE1 and NPE2 to detect link and device failures between them.
A CFM session is configured between UPE2 and NPE1 and between UPE2 and NPE2 to detect the faults on UPE2 and the NPEs and on links between UPE2 and the NPEs.
- In normal circumstances, NPE1 periodically sends VRRP Advertisement packets to inform NPE2 that it works properly. NPE1 monitors the CFM and peer BFD session status, and NPE2 monitors the master device as well as the CFM and peer BFD session status.
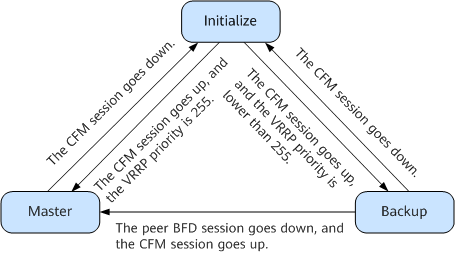
- If NPE1 or the link between NPE1 and UPE2 fails, the CFM session between NPE1 and UPE2 goes down, so does the peer BFD session between NPE1 and NPE2. The CFM session between UPE2 and NPE2 is up. In this case, NPE1's VRRP status directly changes from Master to Initialize, and NPE2's VRRP status directly changes from Backup to Master.
- After NPE1 or the link between UPE2 and NPE1 recovers, the peer BFD session goes up again, and the CFM session between NPE1 and UPE2 also goes up. If NPE1 is configured to work in preemption mode, NPE1 changes back to the Master state after VRRP negotiation, and NPE2 changes back to the Backup state.

In normal circumstances, if the link between NPE2 and UPE2 fails, NPE1 remains in the Master state and continues to forward upstream traffic. However, NPE2's VRRP status switches to Master if both the peer BFD session between NPE1 and PNE2 and the CFM session between NPE2 and UPE2 go down, and NPE2 detects the peer BFD session down event before detecting the CFM session down event. After NPE2 detects the CFM session down event, NPE2's VRRP status switches to Initialize.
Benefits
Association between VRRP and CFM prevents service interruptions caused by dual master devices in a VRRP group and speeds up master/backup VRRP switchovers, thereby improving network reliability.