VRRP Association with NQA
Background
Interface
EFM session
BFD session
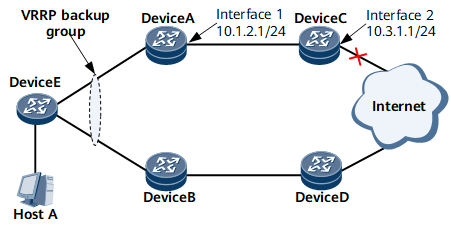
In Figure 1, however, if Interface 2 on Device C goes Down and its IP address (10.3.1.1) becomes unreachable, VRRP is unable to detect the fault. As a result, user traffic is dropped.
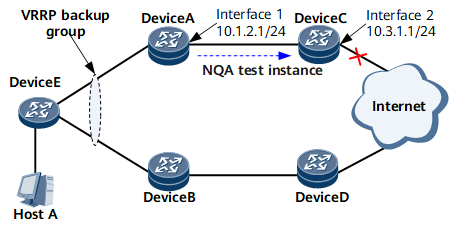
To resolve the preceding issue, you can associate VRRP with network quality analysis (NQA). Using test instances, NQA sends probe packets to check the reachability of destination IP addresses. After VRRP is associated with an NQA test instance, VRRP tracks the NQA test instance to implement rapid master/backup VRRP switchovers. For the example shown in the preceding figure, you can configure an NQA test instance on Device A to check whether the IP address 10.3.1.1 of Interface 2 on Device C is reachable.

VRRP association with an NQA test instance is required on only the local device (Device A).
Implementation
You can configure VRRP association with an NQA test instance to track a gateway router's uplink, which is a cross-device link. If the uplink fails, NQA instructs VRRP to reduce the gateway router's priority by a specified value. Reducing the priority enables another gateway router in the VRRP group to take over services and become the master, thereby ensuring communication continuity between hosts on the LAN served by the gateway and the external network. After the uplink recovers, NQA instructs VRRP to restore the gateway router's priority.
- Device A and Device B run VRRP.
- An NQA test instance is created on Device A to detect the reachability of the destination IP address 10.3.1.1.
- VRRP is configured on Device A to track the NQA test instance. If the status of the NQA test instance is Failed, Device A reduces its priority to trigger a master/backup VRRP switchover. A VRRP group can track a maximum of eight NQA test instances.
Device A tracks the NQA test instance periodically and sends VRRP Advertisement packets to notify its status to Device B.
- When the uplink fails, the status of the NQA test instance changes to Failed. NQA notifies VRRP of the link detection failure, and Device A reduces its priority by a specified value. Because Device B has a higher priority than Device A, Device B preempts the Master state and takes over services.
- When the uplink recovers, the status of the NQA test instance changes to Success. NQA notifies VRRP of the link detection success, and Device A restores the original priority. If preemption is enabled on Device A, Device A preempts the Master state and takes over services after VRRP negotiation.
Benefits
VRRP association with NQA implements a rapid master/backup VRRP switchover if a cross-device uplink fails.