TWAMP Implementation Process
A Two-Way Active Measurement Protocol (TWAMP) test covers the establishment of a control session, establishment and start of a test session, and stop of the entire TWAMP session.
Establishment of a Control Session
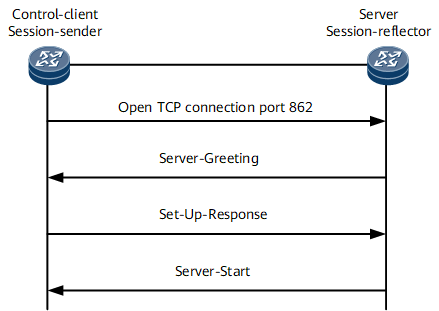
A control session provides a basis for the establishment of a test session. Figure 1 shows how a control session is established.
- The server specifies a TCP port number (the default port number is 862), and the control-client initiates a TCP connection.
- The server replies with a Server-Greeting message to notify the control-client of the server configurations.
- After receiving the Server-Greeting message, the control-client sends a Set-Up-Response message to the server to establish a control session.
- The server verifies the Set-Up-Response message and replies with a Server-Start message.
A control session is established between the control-client and the server.
Establishment of a Test Session
After a control session is established, users can specify an IP address and a UDP port number on the control-client to establish a test session. Figure 2 shows how a test session is established.
- The control-client sends a Request-TW-Session message carrying an IP address and a UDP port number to the server through the TCP connection.
- After receiving the Request-TW-Session message, the server establishes a test session based on the IP address and UDP port number in the Request-TW-Session message and replies to the control-client with an Accept-Session message.
A test session is established between the control-client and the server.
Start of a Test Session
A test session is started based on a control session. After a test session is established, the control-client can send a Start-Session message to the server. After receiving the Start-Session message, the server instructs the control session to start all test sessions that are established based on the control session. Figure 3 shows how a test session is started.
- The control-client sends a Start-Session message to the server.
- After receiving the Start-Session message, the server notifies the session-reflector of the test session information to enable the session-reflector to respond to probes.
- The session-reflector replies to the control-client with a Start-ACK message to start the test sessions.
- After receiving the Start-ACK message, the control-client notifies the session-sender of the test session information to enable the session-sender to send probes.
Test sessions are started, and the session-reflector starts to respond to probes.
Stop of a TWAMP Session
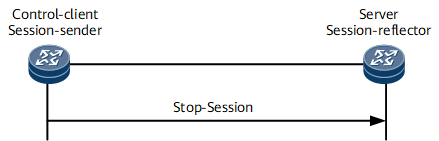
After statistics are collected, users can stop a TWAMP session. Figure 4 shows how a TWAMP session is stopped.
- The control-client sends a Stop-Session message to instruct the server to stop collecting statistics.
- After receiving the Stop-Session message, the server disables the session-reflector from responding to probes in a TWAMP session.
The TWAMP session is stopped.