DHCP DoS Attack by Changing CHADDR
Mechanism
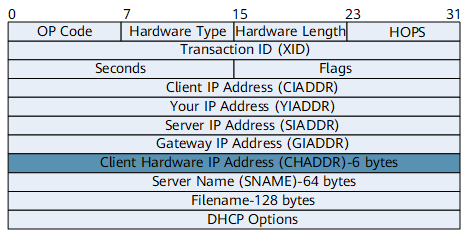
Attackers apply to a Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) server for IP addresses by sending a large number of DHCP request packets with varied media access control (MAC) addresses in the client hardware address (CHADDR) fields. As a result, IP addresses in the address pool are exhausted, and authorized clients cannot obtain IP addresses. Figure 1 shows the format of a DHCP request packet.
Solution
To protect against DHCP DoS attacks, you can configure DHCP snooping on the device to check the CHADDR field in DHCP request packets. After DHCP snooping is enabled, the device checks whether the MAC address in the CHADDR field matches that in the frame header. If they match, the device considers the packet valid and forwards it. If they do not match, the device considers the packet an attack packet and discards it. Therefore, authorized clients can obtain IP addresses.