EFM Enhancements
EFM enhancements are EFM extended functions, including an association between EFM and an EFM interface, an active/standby extension, and single-fiber fault detection.
Association Between EFM and EFM Interfaces
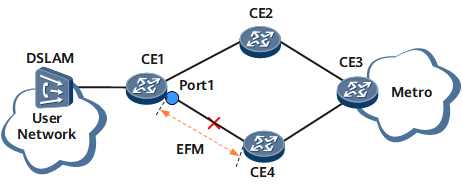
On the network shown in Figure 1, customer edge 1 (CE1) is dual-homed to CE2 and CE4. The dual-homing networking provides device redundancy, making the network more robust and services more reliable. If the active link between CE1 and CE4 fails, traffic switches to the standby link between CE1 and CE2, minimizing the service interruption time.
Association between EFM and EFM interfaces that connect CE2 and CE4 to CE1 allows traffic to switch from the active link to the standby link if EFM detects a link fault or link quality deterioration. On the network shown in Figure 1, when EFM detects a fault in the link between CE1 and CE4, association between EFM and EFM interfaces can be used to trigger an active/standby link switchover, improving transmission quality and reliability.
Single-Fiber Fault Detection
Optical interfaces work in full-duplex mode and therefore consider themselves Up provided that; if they receive packets. This causes the working status of the interfaces to be inconsistent with the physical interface status.
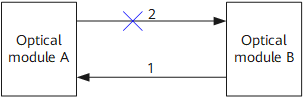
As shown in Figure 2, optical interface A is directly connected to optical interface B. If line 2 fails, interface B cannot receive packets and sets its physical status to Down. Interface A can receive packets from interface B over line 1 and therefore considers its physical status Up. If interface A sends packets to interface B, a service interruption occurs because interface B cannot receive the packets.
EFM single-fiber detection can be used to prevent the preceding issue.
If EFM detects a fault on an interface that is associated with EFM, the association function enables the interface to go Down. The modules for Layer 2 and Layer 3 services can detect the interface status change and trigger a service switchover. The working status and physical status of the interface remain consistent, preventing a service interruption. After the fault is rectified and EFM negotiation succeeds, the interface goes Up and services switch back.
Single-fiber fault detection prevents inconsistency between the working and physical interface statuses and allows the service modules to detect interface status changes.