BGP AD VPLS
Definition
BGP AD VPLS, short for Border Gateway Protocol Auto-Discovery virtual private LAN service, is a new technology for automatically deploying VPLS services.
BGP AD VPLS-enabled devices exchange extended BGP Update packets to automatically discover BGP peers in a VPLS domain. After BGP peer relationships are established, these devices use LDP FEC 129 to negotiate and establish VPLS PWs. In addition, BGP AD HVPLS is deployed with split horizon disabled. This allows all BGP peers in an AS to function as UPEs on an HVPLS network.
Purpose
The wide use of VPLS technologies leads to the growing scale of VPLS networks and configurations. BGP AD VPLS is introduced to simplify configurations, enable automatic service deployment, and reduce operating expense (OPEX).
BGP AD VPLS has the advantages of both BGP and LDP VPLS. BGP AD VPLS-enabled devices exchange extended BGP Update packets to automatically discover BGP peers in a VPLS domain. After BGP peer relationships are established, these devices use LDP FEC 129 to negotiate and establish VPLS PWs. VPLS services are automatically deployed after PWs are established.
Automatic VPLS member discovery and PW establishment simplify the configurations required by VPLS networks, enable automatic service deployment, and reduce OPEX for carriers.
Concepts
Acronym and Abbreviation |
Full Name |
Description |
|---|---|---|
VPLS ID |
virtual private LAN service ID |
Identifier of a VPLS domain |
VSI ID |
virtual switching instance ID |
Identifier of a VSI in a VPLS domain |
RD |
route distinguisher |
Route distinguisher in a BGP packet which carries VSI information |
RT |
route target |
Route attribute carried in a BGP packet used to advertise VSI information |
AGI |
attachment group identifier |
Domain identifier used during PW negotiation between PEs in a VPLS domain |
AII |
attachment individual identifier |
VSI identifier used during PW negotiation between PEs in a VPLS domain |
SAII |
source attachment individual identifier |
Local IP address used by BGP AD VPLS to negotiate PW establishment |
TAII |
target attachment individual identifier |
Remote IP address used by BGP AD VPLS to negotiate PW establishment |
FEC 129 |
forwarding equivalence class 129 |
New type of FEC used by LDP signaling |
Principles
BGP AD VPLS has the advantages of both BGP and LDP VPLS. BGP AD VPLS automatically discovers VPLS BGP peers, simplifying the configurations and saving labels.
BGP AD VPLS-enabled devices exchange extended BGP Update packets carrying VSI member information to automatically discover BGP peers in a VPLS domain. After BGP peer relationships are established, these devices use LDP Mapping (FEC 129) messages to negotiate and establish VPLS PWs. VPLS services are automatically deployed after PWs are established.
Automatically Discovering PEs in a VPLS Domain
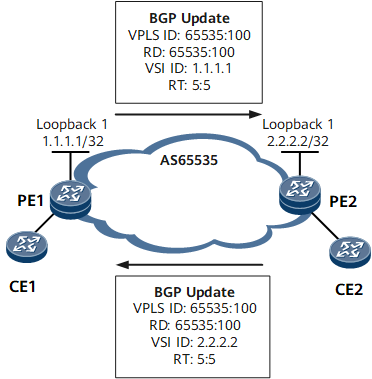
Automatically discovering PEs in a VPLS domain is the first phase of VPLS service deployment. BGP is used to automatically discover PEs in a VPLS domain. Figure 1 shows the process and information used for automatically discovering PEs in a VPLS domain.
The process of automatically discovering PEs in a VPLS domain is as follows:
- After the information, such as the VPLS ID, RD, RT, and VSI ID, is set on PE1 and PE2, the two PEs encapsulate the information into BGP Update messages and send these messages as BGP AD packets to all peer PEs in the BGP domain.
- After receiving a BGP AD packet, a PE checks whether the BGP AD packet matches its RT policy. If they match, the PE obtains the information carried in the packet and compares the obtained information with local configurations:
- If the VPLS IDs of VSIs on the two PEs are the same, the two VSIs are in the same VPLS domain and a PW can be established between them.
- If the VPLS IDs of VSIs on the two PEs are different, the two VSIs are in different VPLS domains and no PW can be established between them.
Automatically Establishing a PW
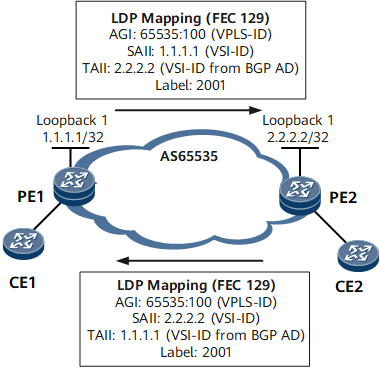
After a PE discovers a remote PE in the same VPLS domain, the two PEs use LDP Mapping (FEC 129) messages to negotiate PW establishment. Figure 2 shows the process of automatically establishing a PW.
The process of automatically establishing a PW is as follows:
- Two PEs connected by an LDP session in a VPLS domain exchange LDP Mapping (FEC 129) messages that carry VSI information, including the AGI, SAII, TAII, and label information. If no LDP session has been established between two PEs in a VPLS domain, the two PEs initiate negotiation upon the creation of an LDP session.

After BGP AD VPLS members are discovered, BGP AD VPLS proactively triggers LDP to establish LDP sessions, facilitating the establishment of PWs for VPLS services. When a VPLS service is deleted, BGP AD VPLS proactively triggers LDP to delete the corresponding LDP sessions. This implementation simplifies LDP session maintenance, improves system resource usage, and optimizes network performance.
- After a PE receives an LDP Mapping message, the PE obtains VSI information, such as the VPLS ID, PW type, MTU, and TAII, carried in the message and compares the obtained VSI information with local VSI information. If the information matches, the PE establishes a PW to the remote PE.
Application of BGP AD VPLS on a Full-Mesh Network
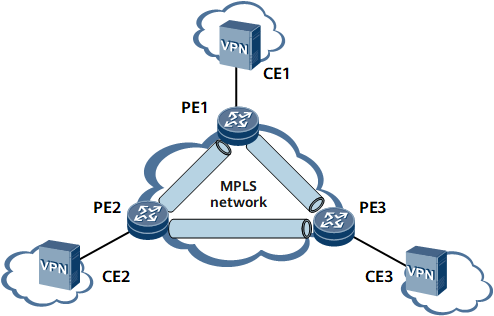
On the network shown in Figure 3:
BGP peer relationships are established between PE1, PE2, and PE3.
BGP AD VPLS is configured on PE1 and PE2 in a VPLS domain.
PE3 is assigned the same VPLS ID as that on PE1 and PE2, which allows PE3 to join the VPLS domain. (PE3 is to be added to the VPLS domain as the network expands.)
BGP AD VPLS is enabled on PE3, allowing PWs to be automatically established between PE3 and PE1 and between PE3 and PE2.