BMP
Background
The BGP Monitoring Protocol (BMP) can monitor the BGP running status and trace data of BGP routes on network devices in real time. The BGP running status includes the establishment and termination of peer relationships and update of routing information. The trace data of BGP routes indicates how BGP routes on a device are processed; for example, processing of the routes that match an import or export route-policy.
Before BMP is implemented, only manual query can be used to obtain the BGP running status of devices, resulting in low monitoring efficiency.
After BMP is implemented, a device can be connected to a BMP server and configured to report its BGP running status to the server, significantly improving monitoring efficiency.
BMP Message Types
BMP sessions can be used to exchange the following types of messages, which are sent in packets. The information reported in these messages mainly includes BGP routing information, BGP peer information, and device vendor and version information.
Initiation message: sent by a monitored device to the monitoring server to report information such as the device vendor and software version.
Peer Up Notification (PU) message: sent by a monitored device to notify the monitoring server that a BGP peer relationship has been established.
Route Monitoring (RM) message: used to provide the monitoring server with a collection of all routes received from a BGP peer and notify the server of route addition or withdrawal in real time.
Peer Down Notification (PD) message: sent to notify the monitoring server that a BGP peer relationship has been disconnected.
Stats Reports (SR) message: sent to report statistics about the device running status to the monitoring server.
Termination message: sent to report the cause for closing a BMP session to the monitoring server.
- Route Policy and Attribute Trace (ROFT) message: used to report the trace data of routes to the monitoring server in real time.

BMP sessions are unidirectional. Devices send messages to the monitoring server but ignore messages sent by the server.
Implementation
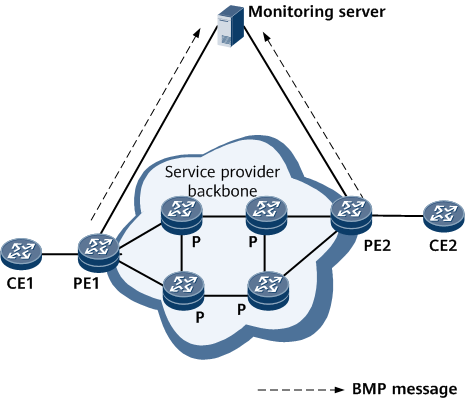
On the network shown in Figure 1, TCP connections are established between the monitoring server and monitored devices (PE1 and PE2 shown in the figure). The monitored devices send unsolicited BMP messages to the monitoring server to report information about the BGP running status. Upon receiving these BMP messages, the monitoring server parses them and displays the BGP running status in the monitoring view. By analyzing the headers in the received BMP messages, the monitoring server can determine which BGP peers have advertised the routes carried in these messages.
When establishing a connection between a BGP device and monitoring server, note the following guidelines:
- BMP operates over TCP, and you can specify a port number for the TCP connection between the BGP device and monitoring server.
- One device can connect to multiple monitoring servers, and one monitoring server can also connect to multiple devices.
- Each BMP instance can connect to multiple monitoring servers. The advantages are as follows:
- Multiple monitoring servers back up each other, improving reliability.
- The load of a single server in monitoring BGP peers is reduced.
- Different servers can be used to monitor routes from the same BGP peer in different address families, allowing each BGP service to be monitored by a different server.
- A monitoring server can monitor all BGP peers or a specified one.
Benefits
BMP facilitates the monitoring of the BGP running status and reports security risks on networks in real time so that preventive measures can be taken promptly to improve network stability.