BGP Best External
Background
If multiple routes to the same destination are available, a BGP device selects one optimal route based on BGP route selection policies and advertises the route to its BGP peers.

For details about BGP route selection rules, see BGP Fundamentals.
However, in scenarios with master and backup provider edges (PEs), if routes are selected based on the preceding policies and the primary link fails, the BGP route convergence takes a long time because no backup route is available. To address this problem, the BGP Best External feature was introduced.
Related Concepts
BGP Best External: A mechanism that enables a backup device to select a sub-optimal route and send the route to its BGP peers if the route preferentially selected based on BGP route selection policies is an Internal Border Gateway Protocol (IBGP) route advertised by the master device. Therefore, BGP Best External speeds up BGP route convergence if the primary link fails.
Best External route: The sub-optimal route selected after BGP Best External is enabled.
Networking with Master and Backup PEs
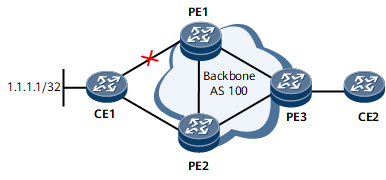
In the networking shown in Figure 1, CE1 is dual-homed to PE1 and PE2. PE1 has a greater Local_Pref value than PE2. EBGP peer relationships are established between CE1 and PE1, and between CE1 and PE1. In addition, IBGP peer relationships are established among PE1, PE2, and PE3. PE1 and PE2 receive the same route to 1.1.1.1/32 from CE1, and PE2 receives the route from PE1. Of the two routes, PE2 preferentially selects the route from PE1 because PE1 has a larger Local_Pref value than CE1. PE2 does not advertise the route received from PE1 to PE3. Therefore, PE3 has only one route, which is advertised by PE1. If the primary link fails, traffic can be switched to the backup link only after routes are re-converged.
BGP Best External can be enabled on PE2 to address this problem. With BGP Best External, PE2 selects the EBGP route from CE1 and advertises it to PE3. In this case, a backup link is available. Table 1 lists the differences with and without BGP Best External.
Feature Enabling Status |
Route Advertisement |
Optimal Route |
Route Convergence in Case of a Link Fault |
|---|---|---|---|
Before the BGP Best External feature is enabled |
PE3 can receive only one route: CE1→PE1→PE3 |
CE1 -> PE1 -> PE3 |
The backup link can be selected only after PE1 and PE2 re-select a route. |
After BGP Best External is enabled |
PE3 receives two routes: CE1→PE1→PE3 CE1→PE2→PE3 |
CE1 -> PE1 -> PE3 |
Traffic can be directly switched to the backup link. |
Usage Scenario
The BGP Best External feature applies to scenarios in which master and backup PEs are deployed and the backup PE needs to advertise the sub-optimal route (Best External route) to its BGP peers to speed up BGP route convergence.
Benefits
As networks develop, services, such as Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP), online video, and financial services, pose higher requirements for real-time transmission. After BGP Best External is deployed, if the optimal route selected by a device is an IBGP route, the device selects the suboptimal route and advertises it to BGP peers. This implements fast route convergence in the case of a link fault and reduces the impact of traffic interruption on services.