Flow-Label-based Load Balancing
Background
Packets of multiple data flows on the same L2VPN carry the same VC labels, which are encapsulated on a PE. When these packets reach a P device, they can be forwarded only over one path.
To load-balance different data flows, configure flow-label-based load balancing on the PE. After you have completed the configuration, the PE encapsulates a data packet and adds a flow label following the PW label. The P device load-balances different data flows based on flow labels.
Implementation
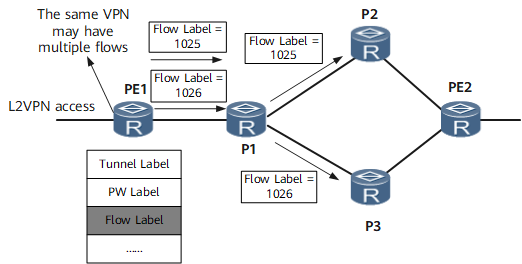
On the L2VPN shown in Figure 1 where two data flows exist:
- PE1 calculates flow labels based on the source and destination IP addresses of the two data flows. In this scenario, the flow labels are calculated as 1025 and 1026.
- PE1 adds the flow labels following the PW labels of the packets in the two data flows.
- When the two data flows reach P1, P1 performs a hash calculation based on the flow labels, and the two data flows are mapped onto different paths. In this example, the next hop of the data flow with the flow label 1025 is P2, and the next hop of the data flow with the flow label 1026 is P3.
- When the two data flows reach PE2, the PW and flow labels are sequentially removed. PE2 then forwards the two data flows to their destination CEs based on their PW labels.
Usage Scenario
Flow-label-based load balancing applies to an L2VPN on which multiple links exist between P devices.
Benefits
Flow-label-based load balancing allows data flows on the same VPN to be load-balanced along different paths based on flow labels, improving resource usage.